Market rate salary reflects the average compensation for a specific role across various regions, ensuring competitiveness within the industry. Location-based pay adjusts salaries according to the cost of living and local economic conditions, providing fair wages tailored to employees' geographic areas. Balancing market rate and location-based pay strategies helps companies attract talent while managing labor costs effectively.
Table of Comparison
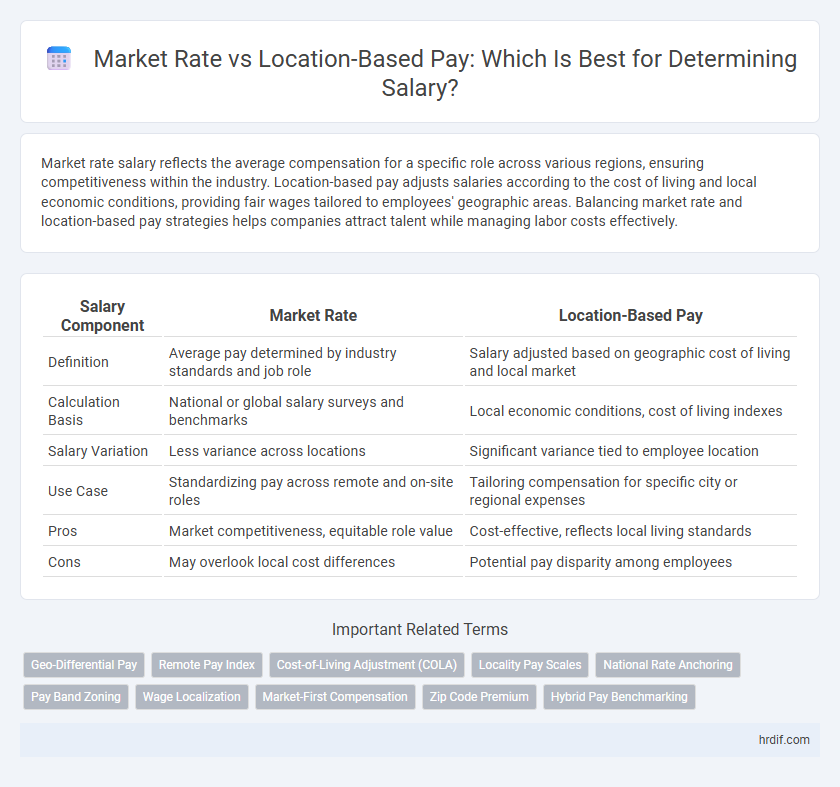
| Salary Component | Market Rate | Location-Based Pay |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Average pay determined by industry standards and job role | Salary adjusted based on geographic cost of living and local market |
| Calculation Basis | National or global salary surveys and benchmarks | Local economic conditions, cost of living indexes |
| Salary Variation | Less variance across locations | Significant variance tied to employee location |
| Use Case | Standardizing pay across remote and on-site roles | Tailoring compensation for specific city or regional expenses |
| Pros | Market competitiveness, equitable role value | Cost-effective, reflects local living standards |
| Cons | May overlook local cost differences | Potential pay disparity among employees |
Understanding Market Rate Compensation
Market rate compensation reflects the typical salary range for a specific role within a particular industry and skill level, providing a benchmark based on supply and demand dynamics. Location-based pay adjusts this baseline by considering regional cost of living differences, ensuring equitable purchasing power across areas. Understanding market rate compensation enables employers to attract qualified talent while maintaining competitive and fair salary structures aligned with industry standards.
The Fundamentals of Location-Based Pay
Location-based pay adjusts salaries according to geographic cost of living and local market demand, ensuring compensation remains competitive within specific regions. This approach accounts for variations in housing, transportation, and daily expenses, aligning employee wages with localized economic conditions. Implementing location-based pay helps attract and retain talent by reflecting true market value rather than relying solely on generalized national salary data.
Key Differences Between Market Rate and Location-Based Pay
Market rate salary is determined by industry standards and competitive pay within a specific job role, reflecting what employers typically offer regardless of geography. Location-based pay adjusts compensation based on the cost of living and economic conditions in a particular area, ensuring employees are paid fairly relative to local expenses. Key differences include market rate focusing on role-specific demand and skills, while location-based pay prioritizes regional economic factors and living costs.
Factors Influencing Market Rate Salary Structures
Market rate salary structures are influenced by industry demand, skill scarcity, and economic conditions, which establish competitive pay standards within a sector. Location-based pay adjusts salaries according to regional cost of living, local labor market competitiveness, and geographic economic disparities. Companies balance these factors to offer salaries that attract talent while aligning with budget constraints and market realities.
How Location Impacts Your Earning Potential
Location significantly influences earning potential as market rates for salaries vary widely based on regional economic conditions, cost of living, and local demand for specific skills. Urban areas with high living costs, such as New York or San Francisco, tend to offer higher salaries to attract talent, whereas rural or less competitive regions generally provide lower pay scales. Understanding this location-based pay disparity helps employees and employers align compensation packages with prevailing market standards to ensure competitiveness and equity.
Pros and Cons of Market Rate Compensation
Market rate compensation ensures salaries align with industry standards, attracting top talent and promoting fairness across roles; however, it may disregard cost-of-living differences, leading to potential employee dissatisfaction in high-expense areas. This approach facilitates competitive positioning by benchmarking against similar companies but can create budget challenges for employers in lower-cost regions who try to match market rates. Emphasizing market rate pay supports equity among peers without geographic bias but risks overlooking local economic conditions that affect employee purchasing power.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Location-Based Pay
Location-based pay offers the benefit of aligning salaries with local cost of living and market conditions, helping employers manage labor costs effectively and attract talent in specific regions. However, this approach can create disparities in employee compensation, potentially leading to reduced morale and challenges in retaining remote workers who may feel undervalued if their pay does not match their contributions. Balancing fairness and competitiveness requires careful consideration of regional salary benchmarks and employee expectations.
The Impact of Remote Work on Salary Determination
Remote work has significantly shifted salary determination by emphasizing market rates over traditional location-based pay structures, allowing companies to offer competitive salaries irrespective of an employee's physical location. This trend has led to salary adjustments aligned with industry standards and skill demand rather than geographic cost of living, creating a more global and equitable compensation model. Organizations increasingly leverage data-driven compensation platforms to analyze market trends and ensure pay equity across remote and hybrid workforces.
Industry Trends: Moving Toward Market Rate or Location-Based Pay
Industry trends reveal a growing shift toward location-based pay to address cost-of-living variations and attract talent in competitive markets. Companies increasingly analyze local economic factors and living expenses to determine equitable compensation, enhancing employee satisfaction and retention. Despite this, certain sectors maintain market rate salaries aligned with industry standards to ensure competitive positioning and attract specialized skills globally.
Choosing the Right Salary Model for Your Career
Choosing the right salary model depends on evaluating market rate benchmarks and location-based pay scales to maximize compensation alignment with industry standards and cost of living. Market rate pay ensures competitiveness by reflecting national or global salary trends within your profession, while location-based pay adjusts compensation according to regional economic factors and local living expenses. Consider personal career goals and mobility when deciding between these models to optimize earning potential and job satisfaction.
Related Important Terms
Geo-Differential Pay
Geo-differential pay adjusts salaries based on regional cost of living and local market rates, ensuring competitive compensation aligned with specific geographic economic conditions. Companies use this strategy to balance talent acquisition and retention by offering salaries that reflect location-specific financial realities rather than a uniform market rate.
Remote Pay Index
Remote Pay Index provides a nuanced approach to salary determination by comparing market rate salaries with location-based pay adjustments, ensuring equitable compensation for remote workers across different geographic regions. This index helps companies balance competitive pay aligned with industry standards while accounting for cost-of-living variations and regional economic factors.
Cost-of-Living Adjustment (COLA)
Market rate salaries reflect industry standards while location-based pay incorporates Cost-of-Living Adjustment (COLA) factors such as housing, transportation, and healthcare expenses to ensure equitable compensation. Employers use COLA to adjust wages according to regional economic conditions, balancing competitive pay with geographic cost disparities.
Locality Pay Scales
Locality pay scales adjust salaries based on the cost of living and economic conditions in specific geographic areas, ensuring competitive compensation aligned with local market rates. This approach helps attract and retain talent by reflecting regional salary variations rather than relying solely on national averages.
National Rate Anchoring
National rate anchoring sets a consistent salary benchmark across regions by referencing the average market pay at the country level, ensuring internal equity while mitigating regional cost-of-living disparities. This approach aligns compensation standards with broad market data, balancing competitiveness and fairness regardless of geographic location.
Pay Band Zoning
Pay Band Zoning adjusts salary ranges based on the cost of living and market rates specific to geographic locations, ensuring compensation competitiveness while maintaining internal equity. Companies leverage location-based pay structures to align salaries with local economic conditions, optimizing talent acquisition and retention without distorting overall pay fairness.
Wage Localization
Market rate salaries reflect industry standards and demand for specific roles, while location-based pay adjusts wages according to regional cost of living and economic conditions. Wage localization ensures competitive compensation by aligning salaries with local market dynamics and living expenses, attracting talent and reducing turnover in diverse geographic areas.
Market-First Compensation
Market-first compensation prioritizes competitive salaries based on industry standards and skill demand, ensuring talent attraction regardless of geographical location. This approach adjusts pay according to market rate data rather than local cost of living, promoting equity and retaining top performers in a global workforce.
Zip Code Premium
Salary determination often hinges on the market rate adjusted by location-based pay factors, with the Zip Code Premium reflecting wage variations specific to geographic areas. This premium accounts for cost of living, local demand, and economic conditions within a particular zip code, ensuring salaries align with regional compensation standards.
Hybrid Pay Benchmarking
Hybrid pay benchmarking combines market rate data with location-based pay adjustments to create competitive and equitable salary structures for remote and hybrid workforces. This approach ensures companies attract top talent nationwide by aligning compensation with both industry standards and local living costs.
Market Rate vs Location-Based Pay for determining salary. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com