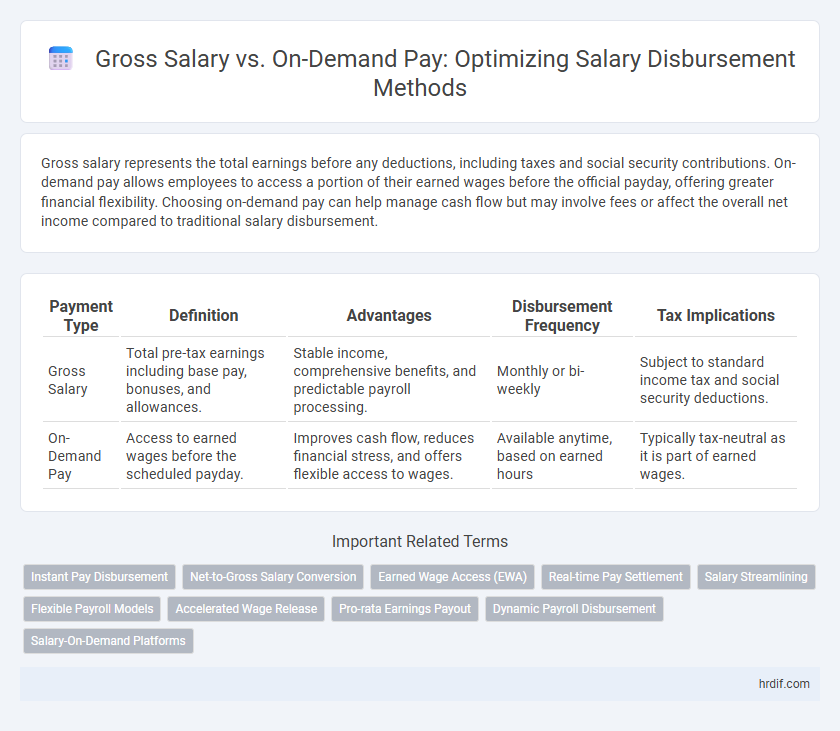
Gross salary represents the total earnings before any deductions, including taxes and social security contributions. On-demand pay allows employees to access a portion of their earned wages before the official payday, offering greater financial flexibility. Choosing on-demand pay can help manage cash flow but may involve fees or affect the overall net income compared to traditional salary disbursement.
Table of Comparison
| Payment Type | Definition | Advantages | Disbursement Frequency | Tax Implications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gross Salary | Total pre-tax earnings including base pay, bonuses, and allowances. | Stable income, comprehensive benefits, and predictable payroll processing. | Monthly or bi-weekly | Subject to standard income tax and social security deductions. |
| On-Demand Pay | Access to earned wages before the scheduled payday. | Improves cash flow, reduces financial stress, and offers flexible access to wages. | Available anytime, based on earned hours | Typically tax-neutral as it is part of earned wages. |
Understanding Gross Salary: Definition and Components
Gross salary represents the total earnings an employee receives before any deductions such as taxes, social security, or retirement contributions are applied. It includes base pay, bonuses, overtime, and any allowances like housing or transportation. Understanding these components is essential for comparing traditional payroll structures with on-demand pay options, which offer employees access to earned wages before the official payday.
What Is On-Demand Pay? Key Features Explained
On-demand pay allows employees to access a portion of their earned wages before the traditional payday, providing financial flexibility and immediate liquidity. Key features include real-time access to earned income, reducing reliance on high-interest payday loans, and improving cash flow management for unexpected expenses. This model contrasts with gross salary, which represents the total earnings before deductions and is disbursed on a fixed schedule.
Gross Salary vs On-Demand Pay: Fundamental Differences
Gross Salary represents the total earnings before any deductions, encompassing base pay, bonuses, and benefits, forming the fixed compensation structure within employment contracts. On-Demand Pay, also known as earned wage access, allows employees to access a portion of their accrued salary before the official payday, offering financial flexibility and reduced reliance on loans or credit. The fundamental difference lies in gross salary being the comprehensive, contractual income figure, while on-demand pay functions as an advance on that income, not altering the total salary but improving liquidity for immediate financial needs.
Pros and Cons of Gross Salary Disbursement
Gross salary disbursement provides employees with a clear, consistent income before taxes and deductions, simplifying budgeting and financial planning. However, it can result in delayed access to actual take-home pay since taxes, social security, and other mandatory contributions are deducted later. This method may reduce flexibility for employees needing immediate funds but offers a straightforward and regulated payroll process for employers.
Advantages and Drawbacks of On-Demand Pay for Employees
On-demand pay offers employees immediate access to earned wages, improving financial flexibility and reducing reliance on high-interest loans. However, frequent withdrawals may lead to budgeting challenges and potential fees that diminish overall earnings. While it enhances liquidity, on-demand pay may also impact long-term savings and financial planning for employees.
Impact on Financial Planning: Gross Salary Compared to On-Demand Pay
Gross salary provides a consistent and predictable income stream essential for long-term financial planning, enabling employees to budget and manage expenses effectively. On-demand pay offers immediate access to earned wages, enhancing liquidity and reducing reliance on credit but may introduce variability that complicates monthly budgeting. Balancing gross salary stability with the flexibility of on-demand pay can optimize cash flow management and improve overall financial resilience.
Employer Perspectives: Adopting Gross Salary or On-Demand Pay
Employers considering gross salary versus on-demand pay must weigh cash flow management and administrative complexities, as gross salary offers predictable budgeting while on-demand pay enhances employee satisfaction through flexibility. Adopting on-demand pay requires integration with payroll systems and compliance with tax regulations, impacting operational efficiency. Initial data shows organizations implementing on-demand pay report reduced turnover rates and improved engagement, influencing long-term talent retention strategies.
Employee Satisfaction: Which Disbursement Method Wins?
Gross salary provides employees with a predictable, fixed income that simplifies budgeting and financial planning, enhancing overall satisfaction. On-demand pay offers flexibility and immediate access to earned wages, reducing financial stress and increasing employee morale. Studies show that employees increasingly prefer on-demand pay for its convenience and ability to alleviate payday anxieties, making it a strong contender in boosting workplace satisfaction.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Gross salary disbursement must comply with labor laws, tax regulations, and social security contributions, ensuring accurate statutory deductions before payment. On-demand pay services require adherence to financial regulations, anti-money laundering laws, and data privacy standards to protect employee rights and employer obligations. Both payment methods necessitate transparent reporting and strict compliance with local and international regulatory frameworks to avoid legal penalties.
Future Trends: Is On-Demand Pay Replacing Gross Salary?
On-demand pay is increasingly preferred for its flexibility, allowing employees instant access to earned wages, contrasting with the traditional fixed schedule of gross salary payments. Studies show a 2024 rise of over 30% in companies adopting on-demand pay platforms to improve employee satisfaction and reduce turnover rates. Despite its growth, gross salary remains the standard for consistent financial planning and benefits calculation across industries.
Related Important Terms
Instant Pay Disbursement
Instant pay disbursement allows employees to access a portion of their earned gross salary immediately, improving cash flow without waiting for the traditional payroll cycle. This on-demand pay feature enhances financial flexibility by providing real-time access to wages, reducing reliance on loans or credit cards.
Net-to-Gross Salary Conversion
Net-to-gross salary conversion is crucial for accurately comparing gross salary and on-demand pay disbursement, ensuring employees understand their total earnings before deductions. This calculation accounts for taxes, social security, and other deductions, providing a clear view of the gross amount required to achieve a specific net income.
Earned Wage Access (EWA)
Gross salary represents the total earnings before deductions, whereas On-Demand Pay through Earned Wage Access (EWA) allows employees to access a portion of their earned wages before the scheduled payday, improving financial flexibility. EWA services facilitate real-time wage disbursement, reducing dependency on traditional payroll cycles and enhancing cash flow management for workers.
Real-time Pay Settlement
Real-time pay settlement enhances employee financial flexibility by enabling on-demand pay disbursement, allowing access to earned wages before the traditional gross salary payout date. This method reduces the waiting period, improves cash flow management, and supports immediate personal expense needs without altering the gross salary structure.
Salary Streamlining
Gross salary represents the total earnings before any deductions, forming the basis for calculating taxes and benefits, while on-demand pay allows employees to access a portion of their earned wages before the official payday, enhancing cash flow flexibility. Implementing on-demand pay streamlines salary disbursement by reducing payroll complexities and improving employee satisfaction with timely access to earned income.
Flexible Payroll Models
Gross salary represents the total earnings before any deductions, while on-demand pay allows employees to access a portion of their earned wages before the regular payroll cycle, enhancing cash flow flexibility. Flexible payroll models integrating on-demand pay options improve financial well-being by reducing reliance on traditional pay schedules and supporting real-time wage access.
Accelerated Wage Release
Accelerated wage release offers employees access to earned wages before the traditional pay cycle, providing greater financial flexibility compared to gross salary disbursement that occurs on fixed dates. This on-demand pay system reduces the waiting period for salary access, improving cash flow and employee satisfaction without affecting the total gross salary earned.
Pro-rata Earnings Payout
Gross salary reflects the total earnings before deductions, while on-demand pay allows employees to access a portion of their pro-rata earnings instantly, enhancing cash flow flexibility. Pro-rata earnings payout calculates salary based on actual days worked or hours logged, ensuring accurate and fair disbursement aligned with real-time labor contributions.
Dynamic Payroll Disbursement
Dynamic payroll disbursement enables employees to access a portion of their gross salary on-demand before the standard payday, improving financial flexibility and reducing payday loan dependency. This approach integrates real-time earnings tracking with automated pay delivery systems, optimizing cash flow management for both employers and employees.
Salary-On-Demand Platforms
Salary-On-Demand platforms enable employees to access a portion of their earned gross salary before the traditional payday, improving financial flexibility and reducing reliance on high-interest loans. These platforms disburse earned wages instantly, contrasting with the lump-sum payment structure of gross salary paid on scheduled payroll dates.
Gross Salary vs On-Demand Pay for disbursement. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com