Salary provides a consistent and predictable income stream with fixed monthly payments, offering financial stability and benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Gig pay varies based on projects or hours worked, allowing for flexibility but often leading to income fluctuations and lack of traditional employee benefits. Choosing between salary and gig pay depends on personal preference for stability versus flexibility in earning structure.
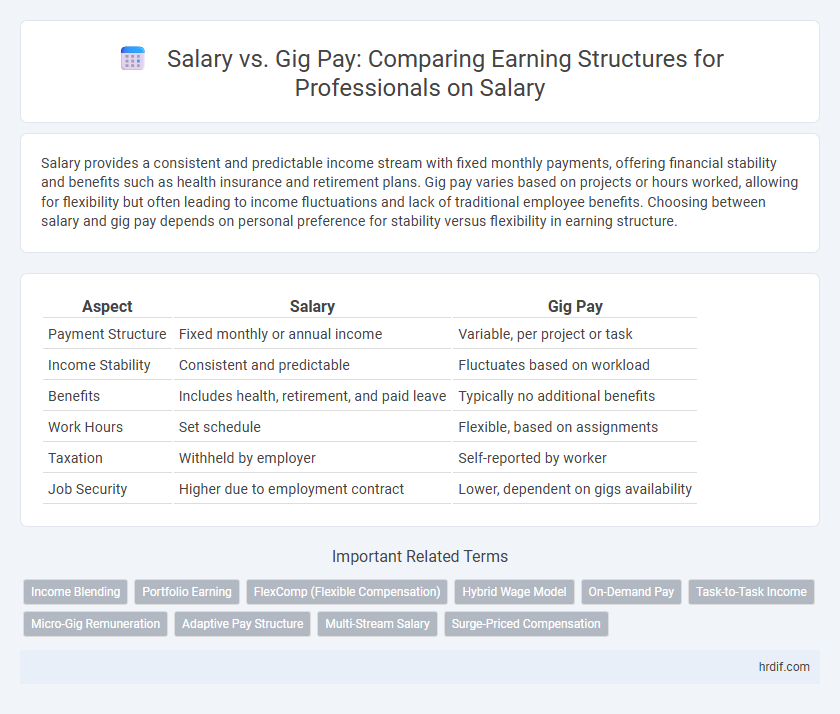
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Salary | Gig Pay |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Structure | Fixed monthly or annual income | Variable, per project or task |
| Income Stability | Consistent and predictable | Fluctuates based on workload |
| Benefits | Includes health, retirement, and paid leave | Typically no additional benefits |
| Work Hours | Set schedule | Flexible, based on assignments |
| Taxation | Withheld by employer | Self-reported by worker |
| Job Security | Higher due to employment contract | Lower, dependent on gigs availability |
Understanding Traditional Salary Structures
Traditional salary structures provide employees with a fixed, predictable income paid regularly, often supplemented by benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. This steady compensation model supports financial stability and long-term planning, contrasting with gig pay's variable earnings based on individual tasks or projects. Understanding these differences highlights the security aspects of salary versus the flexibility offered by gig economy payments.
The Rise of Gig Pay: What It Means
The rise of gig pay reflects a significant shift in the earning structure, with flexible, task-based payments challenging traditional salaried roles. Gig pay offers increased autonomy, allowing workers to monetize skills on a per-project basis, often leading to variable income compared to fixed monthly salaries. This trend highlights the growing demand for adaptable work arrangements in the digital economy and reshapes how financial stability and career growth are perceived.
Stability vs Flexibility: Comparing Financial Predictability
Salary offers consistent monthly income, providing financial stability and predictable budgeting for long-term commitments, such as mortgages and savings plans. Gig pay delivers flexible earnings based on task completion, allowing greater control over work hours but introducing variability that can complicate monthly financial planning. Choosing between salary and gig pay depends on prioritizing steady income security or adaptable earnings tailored to personal lifestyle needs.
Benefits Packages: Salary Jobs vs Gig Work
Salary jobs typically offer comprehensive benefits packages including health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and job security, which contribute to overall financial stability. Gig work, while providing flexibility and diverse income opportunities, often lacks these traditional benefits, requiring workers to independently manage health coverage, retirement savings, and time off. This difference in benefits packages fundamentally impacts the total compensation and long-term financial planning for individuals choosing between salaried employment and gig-based roles.
Income Growth Potential: Career Paths in Both Models
Salary offers a predictable income growth trajectory through promotions and performance-based raises, providing stability in long-term financial planning. Gig pay models deliver fluctuating earnings dependent on project availability and client demand, often requiring continuous effort to secure new gigs for income growth. Career advancement in salaried roles typically follows structured paths, whereas gig workers rely on building diverse portfolios and reputation to enhance earning potential.
Tax Implications: Salaried Employees vs Gig Workers
Salaried employees experience consistent tax withholding through payroll, simplifying tax payments and reducing the risk of underpayment penalties. Gig workers face complex tax obligations, including self-employment tax and the responsibility to make quarterly estimated tax payments, increasing the need for diligent record-keeping and tax planning. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing net income and ensuring compliance with IRS regulations.
Job Security Factors: Permanence and Risk
Salary offers job security through fixed, predictable income and long-term employment stability, reducing financial risk for workers. Gig pay provides income variability with higher risk due to inconsistent work availability and lack of guaranteed hours. Permanence in salaried roles supports benefits like healthcare and retirement plans, which gig roles often lack, intensifying economic insecurity.
Work-Life Balance: Scheduled Hours vs On-Demand Gigs
Salary offers predictable income with fixed, scheduled work hours that promote consistent work-life balance and help employees plan personal time effectively. Gig pay provides flexible, on-demand opportunities allowing workers to choose when to work, which can enhance autonomy but may lead to irregular hours and income variability. This earning structure often challenges maintaining steady work-life boundaries due to unpredictable gig availability and fluctuating workloads.
Social Perception: Professionalism and Status
Salary-based earnings are often perceived as a marker of professionalism and higher social status due to their stability and consistent income flow. In contrast, gig pay, despite its flexibility and potential for varied income, is frequently viewed as less prestigious and more precarious, influencing societal judgments about career legitimacy. This perception affects how individuals in each category are valued within professional networks and broader social contexts.
Choosing the Right Earning Structure for Your Career
Salary offers stable, predictable income with benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, ideal for professionals seeking financial security and long-term growth. Gig pay provides flexible, project-based earnings that suit freelancers or those valuing autonomy and varied work experiences. Evaluating personal financial goals, job stability, and lifestyle preferences is essential to choosing the right earning structure for career satisfaction and success.
Related Important Terms
Income Blending
Income blending combines the stability of a fixed salary with the flexibility of gig pay, allowing professionals to maximize earnings by leveraging steady wages alongside variable project-based income. This hybrid approach optimizes financial security while capitalizing on high-paying gigs, creating a balanced and diversified income structure.
Portfolio Earning
Portfolio earning from gig pay offers greater flexibility and diverse income streams compared to traditional salary structures, allowing individuals to maximize earnings through multiple projects. This approach leverages varied skill sets and client engagements, enhancing overall financial growth beyond fixed monthly salaries.
FlexComp (Flexible Compensation)
Flexible Compensation (FlexComp) offers a dynamic earning structure by combining a stable salary with gig pay opportunities, enabling employees to maximize income based on performance and workload flexibility. This approach enhances financial adaptability, appealing to professionals seeking both security and variable rewards in their compensation package.
Hybrid Wage Model
Hybrid wage models combine fixed salary with gig pay, allowing workers to secure a stable base income while earning extra through flexible gig opportunities. This structure optimizes financial stability and income growth by leveraging the predictability of salary and the variable rewards of gig work.
On-Demand Pay
On-demand pay offers immediate access to earnings from gig work, providing flexibility compared to traditional salaried structures that disburse fixed payment on a set schedule. This model supports financial agility for gig workers, enabling real-time income access without waiting for the conventional payroll cycle.
Task-to-Task Income
Task-to-task income in gig pay offers flexibility and immediate earnings per assignment, contrasting with the stable, predictable monthly salary that provides consistent financial security. Gig pay structures emphasize performance-based compensation, where each completed task directly influences total earnings, unlike salary models that separate income from individual task output.
Micro-Gig Remuneration
Micro-gig remuneration offers flexible earning opportunities by compensating per task completed, contrasting with fixed salaries that provide consistent income regardless of output. This pay structure enables workers to maximize earnings through multiple small gigs, optimizing revenue streams in the growing gig economy.
Adaptive Pay Structure
Adaptive pay structures blend salary and gig pay, enabling dynamic compensation that aligns with performance metrics and market demand. This flexible earning model enhances motivation by rewarding both consistent work and project-based achievements, optimizing workforce productivity.
Multi-Stream Salary
Multi-stream salary structures combine fixed salaries with gig pay to diversify income sources, enhancing financial stability and growth potential. This hybrid model leverages steady base pay alongside variable gig earnings, optimizing overall compensation through flexibility and performance-based rewards.
Surge-Priced Compensation
Surge-priced compensation in gig pay offers dynamic earnings based on real-time demand, enabling workers to capitalize on peak hours for higher income, unlike fixed monthly salaries which provide consistent but static pay. This flexible model incentivizes gig workers to maximize productivity during high-demand periods, often resulting in earnings that can surpass traditional salaried positions when surge multipliers are substantial.
Salary vs Gig Pay for earning structure. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com