Salary structures increasingly factor in a remote premium to address location-based pay disparities. Companies adjust compensation to reflect the cost of living and local market rates, ensuring fairness for remote employees regardless of geographic location. This approach balances competitive salaries with the financial realities of different regions, promoting equity in remote work arrangements.
Table of Comparison
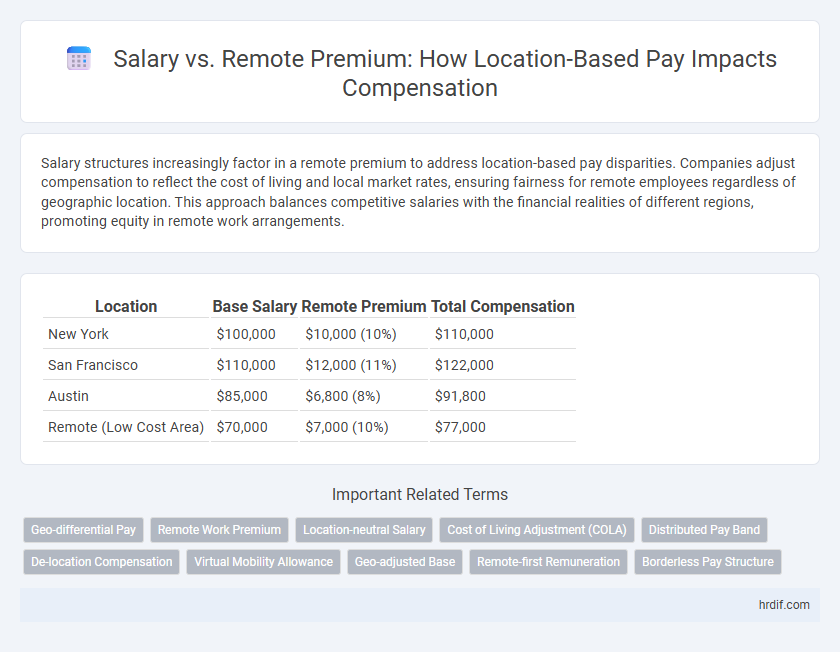
| Location | Base Salary | Remote Premium | Total Compensation |
|---|---|---|---|
| New York | $100,000 | $10,000 (10%) | $110,000 |
| San Francisco | $110,000 | $12,000 (11%) | $122,000 |
| Austin | $85,000 | $6,800 (8%) | $91,800 |
| Remote (Low Cost Area) | $70,000 | $7,000 (10%) | $77,000 |
Understanding Salary Structures: Base Pay vs. Remote Premium
Salary structures differentiate between base pay, which is the fixed compensation tied to an employee's role and experience, and the remote premium, an additional allowance reflecting cost-of-living adjustments based on an employee's geographic location. Companies implement location-based pay to maintain competitive salaries in varying markets, balancing equity with budget constraints. Understanding how base salary and remote premium interact helps employees and employers align compensation strategies with market trends and individual circumstances.
The Rise of Remote Work: Impact on Traditional Salary Models
The rise of remote work has transformed traditional salary models by introducing location-based pay adjustments known as remote premiums, which account for cost-of-living differences across regions. Companies increasingly implement remote premiums to attract talent in high-demand locations while maintaining equitable compensation for remote employees in lower-cost areas. This shift challenges standard salary structures and requires dynamic pay strategies to balance competitiveness and fairness in a geographically dispersed workforce.
Location-Based Pay: How Geography Influences Compensation
Location-based pay structures adjust employee salaries according to geographic cost of living and market demand, ensuring competitive compensation that aligns with regional economic conditions. Remote premiums vary significantly, with higher adjustments in high-cost urban areas like San Francisco and New York, compared to lower or no premiums in lower-cost regions. Companies implement these differential pay strategies to attract talent while managing payroll expenses effectively across diverse locations.
Remote Premium Explained: Incentives for Remote Employees
Remote premium serves as a strategic incentive for companies to compensate employees based on their geographical location while encouraging remote work flexibility. Salaries adjusted with a remote premium often reflect cost-of-living variations, ensuring equitable pay that aligns with local market standards and employee productivity. This location-based pay model enhances talent retention and attraction by recognizing remote workers' unique contributions and living expenses.
Salary Equity: Addressing Disparities in Remote and Onsite Pay
Salary equity demands addressing disparities between remote and onsite pay by implementing location-based pay adjustments that reflect local cost of living and market rates. Companies adopting transparent compensation frameworks ensure fair remuneration regardless of work location, reducing potential bias and enhancing workforce satisfaction. Data-driven salary structures contribute to closing gaps caused by remote premium policies, fostering inclusivity and retention.
Pros and Cons of Location-Based Salary Adjustments
Location-based salary adjustments offer companies the benefit of aligning compensation with local cost of living and labor market rates, potentially reducing payroll expenses while attracting local talent. However, such location-based pay scales may create disparities among employees with similar roles but different locations, potentially impacting team cohesion and equity perceptions. Balancing competitive salaries with remote premiums remains a crucial challenge for organizations adopting flexible work models to ensure fairness and talent retention.
Attracting Talent: Does Remote Premium Give Employers an Edge?
Offering a remote premium can significantly enhance employers' ability to attract top talent by providing competitive compensation regardless of geographic location. Companies that integrate a location-based salary strategy with remote premiums often see increased candidate interest and improved employee retention. Data shows that remote premiums bridge pay disparities, making roles more appealing to high-quality applicants in diverse markets.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Location-Based Compensation
Employers must navigate complex legal frameworks such as the Fair Labor Standards Act and anti-discrimination laws when implementing location-based pay models, ensuring compliance across jurisdictions. Ethical considerations include maintaining pay equity and transparency to prevent disparities that disproportionately affect remote workers in lower-cost regions. Incorporating consistent, documented policies helps mitigate legal risks while promoting fairness in salary versus remote premium decisions.
Negotiating Salary: Strategies for Remote vs In-Office Roles
Negotiating salary for remote roles often involves evaluating the remote premium, with companies adjusting pay based on geographical cost of living and market rates. Candidates should leverage data on local salary benchmarks and highlight productivity metrics to justify compensation beyond location-based pay scales. Emphasizing skills and remote work efficiency can help secure competitive salaries regardless of geographic constraints.
The Future of Salary Models: Fixed, Flexible, and Remote Premiums
Salary models are evolving to include fixed base pay, flexible compensation structures, and remote premiums tailored to geographic cost-of-living differences. Companies increasingly implement location-based pay adjustments to attract global talent while balancing local market competitiveness. Remote premiums incentivize employees in lower-cost areas without inflating salary expenses in high-cost locations.
Related Important Terms
Geo-differential Pay
Geo-differential pay adjusts salary based on an employee's geographic location, reflecting cost-of-living and market demand variations to ensure competitive compensation. Remote premium locations often receive higher pay rates where local living costs or talent scarcity exceed base salary benchmarks.
Remote Work Premium
Remote work premium often varies significantly based on geographic location, with employees in high-cost urban areas receiving lower premiums compared to those in lower-cost regions where remote roles can command a higher salary adjustment. Salary structures increasingly incorporate remote work premiums to attract top talent in competitive markets, reflecting a strategic balance between location-based pay scales and the flexibility of remote employment.
Location-neutral Salary
Location-neutral salary structures offer consistent compensation regardless of an employee's geographic location, eliminating the need for remote premiums tied to local cost-of-living adjustments. This approach streamlines payroll management and promotes equity by providing uniform pay based on skill and role rather than location-specific factors.
Cost of Living Adjustment (COLA)
Salary adjustments incorporating a Cost of Living Adjustment (COLA) address disparities in living expenses for remote employees across different geographic locations, ensuring equitable compensation. Remote premium pay supplements base salary by factoring in local market demand and lifestyle costs, balancing competitive wages with regional affordability.
Distributed Pay Band
Distributed pay bands allow companies to set salary ranges based on geographic location, balancing competitive compensation with cost-effectiveness by applying a remote premium for high-cost areas. This approach ensures equitable pay while attracting top talent regardless of where they work, optimizing workforce distribution and salary budgets.
De-location Compensation
De-location compensation adjusts salary to reflect cost-of-living differences when employees work remotely from lower-cost regions, ensuring equitable pay without inflating expenses. Employers balance location-based pay with retention strategies by offering remote premiums that account for market competitiveness and talent acquisition challenges.
Virtual Mobility Allowance
Virtual Mobility Allowance enhances salary packages by compensating for cost-of-living differences in remote work locations, aligning pay with local economic conditions. This strategic adjustment ensures equitable remuneration while supporting flexible, location-independent employment models.
Geo-adjusted Base
Geo-adjusted base salary aligns compensation with local cost of living and market demand, ensuring equitable pay across different regions. Remote premium supplements this by rewarding flexibility and access to broader talent pools without disregarding location-specific economic factors.
Remote-first Remuneration
Remote-first remuneration strategies often incorporate a remote premium that adjusts salary based on an employee's geographic location, reflecting cost-of-living variances and market demand. Companies adopting location-based pay leverage data analytics to ensure competitive compensation, balancing equitable pay with regional economic factors.
Borderless Pay Structure
A borderless pay structure eliminates traditional location-based salary disparities by standardizing compensation across global regions, reducing reliance on remote premiums tied to geographic cost-of-living differences. This approach ensures equitable pay by valuing employee skills and market demand rather than physical location, promoting fairness and talent retention in remote work environments.
Salary vs Remote Premium for location-based pay. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com