Salary offers consistent and predictable income with benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, providing financial stability and long-term security. Gig pay, on the other hand, allows flexible earning potential based on completed tasks or projects but lacks guaranteed monthly income and employee benefits. Choosing between salary and gig pay depends on individual priorities for stability versus flexibility and variable earnings.
Table of Comparison
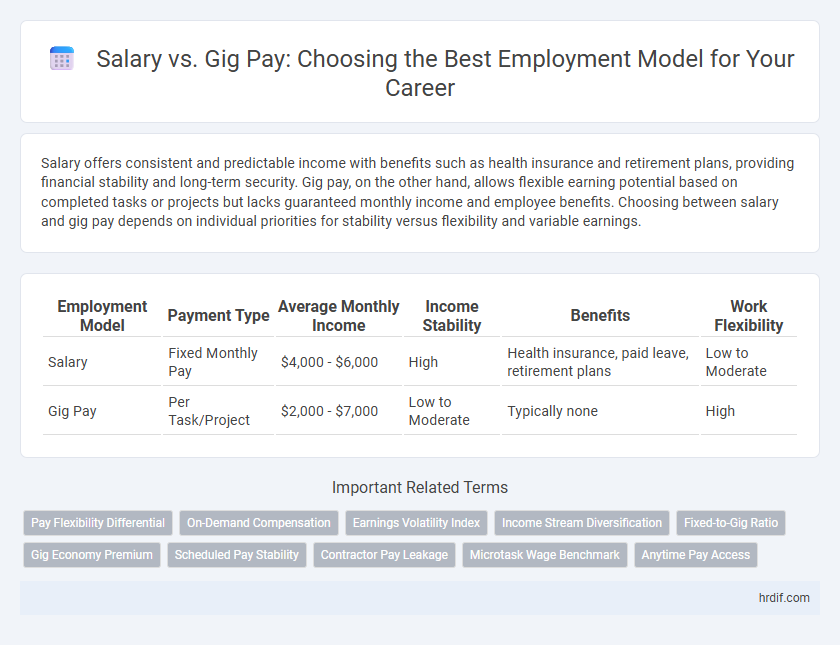
| Employment Model | Payment Type | Average Monthly Income | Income Stability | Benefits | Work Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salary | Fixed Monthly Pay | $4,000 - $6,000 | High | Health insurance, paid leave, retirement plans | Low to Moderate |
| Gig Pay | Per Task/Project | $2,000 - $7,000 | Low to Moderate | Typically none | High |
Understanding Salary and Gig Pay: Key Differences
Salary offers a fixed, predictable income based on an employment contract, providing financial stability and benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Gig pay varies by task or project, often lacking consistent earnings and employee benefits, making it suitable for those seeking flexible schedules or supplemental income. Understanding these differences helps workers choose between steady compensation and the variability of gig economy opportunities.
Stability vs Flexibility: Choosing Your Income Model
Salary offers predictable, stable income with consistent paychecks and benefits, ensuring financial security and long-term planning ease. Gig pay provides flexibility to control work hours and project selection, ideal for those valuing autonomy and diverse income sources. Evaluating personal financial needs and lifestyle preferences helps determine whether stability or adaptability is the optimal income model.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Salary Employment
Traditional salary employment offers consistent monthly income, comprehensive benefits like health insurance and retirement plans, and job security that supports long-term financial planning. However, it often limits flexibility with fixed working hours and can restrict earning potential compared to gig pay models, which reward task-based performance. Employees may face slower income growth due to predetermined raises and less opportunity for diversified income streams.
Advantages and Challenges of Gig Pay Work
Gig pay work offers flexibility, allowing individuals to control their schedules and choose projects that match their skills, leading to potential income diversification. However, gig work often lacks stability, with irregular income and limited access to benefits like health insurance and retirement plans creating financial uncertainty. Navigating tax responsibilities and self-employment expenses can also present significant challenges for gig workers compared to salaried employees.
Financial Security: Which Model Provides More Consistency?
Salary offers consistent, predictable income with regular paychecks, ensuring steady financial security and easier budgeting for employees. Gig pay varies based on completed jobs, making income unpredictable and often leading to fluctuating financial stability. For individuals prioritizing reliable earnings and long-term financial planning, salaried employment generally provides stronger consistency than gig-based pay.
Benefits and Perks: Beyond Your Paycheck
Salaried employment often includes comprehensive benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, which provide financial security beyond base pay. Gig pay, while typically offering higher immediate earnings, usually lacks these traditional perks, placing the burden of securing benefits on the worker. Evaluating overall compensation involves weighing guaranteed benefits against flexible income potential in gig roles.
Work-Life Balance: Comparing Salary and Gig Positions
Salary positions typically offer a consistent income and structured hours, fostering better work-life balance through predictable schedules and benefits like paid time off and health insurance. Gig pay often introduces income variability and irregular hours, which can increase stress and complicate managing personal time but provides flexibility for those prioritizing autonomy. Choosing between salary and gig pay depends on whether stability or freedom is more valued in balancing professional and personal life.
Job Growth and Career Progression: Is One Model Better?
Salary-based employment often provides more stable job growth and clearer career progression due to structured roles and annual reviews, facilitating long-term skill development and promotions. Gig pay offers flexibility but may limit consistent professional advancement and access to employer-sponsored training, often resulting in slower career growth. Employers and workers seeking sustained career development typically benefit more from salaried positions with defined growth pathways.
Tax Implications: Salary vs Gig Income Explained
Salary income typically undergoes automatic tax withholding, simplifying tax compliance for employees, whereas gig pay requires individuals to manage quarterly estimated tax payments due to the absence of withholding. Gig workers often face self-employment tax obligations, which cover both employer and employee Social Security and Medicare contributions, increasing their overall tax liability compared to salaried employees. Understanding these distinctions enables informed decisions on employment models, allowing for effective tax planning and financial management.
Which Model Fits You Best: Factors to Consider
Evaluating whether salary or gig pay fits you best involves considering job stability, income predictability, and flexibility needs. Salaried positions offer consistent monthly earnings and benefits, ideal for those seeking financial security and long-term growth. Gig pay suits individuals valuing autonomy and varied projects but requires managing irregular income and self-employment responsibilities.
Related Important Terms
Pay Flexibility Differential
Salary offers a fixed, predictable income, providing financial stability and consistent budgeting, while gig pay introduces significant pay flexibility, allowing workers to adjust earnings based on workload and availability. This differential in pay models caters to distinct employment preferences, with salaried roles favoring security and gig roles supporting autonomy and variable income potential.
On-Demand Compensation
On-demand compensation offers flexible payment based on completed tasks or gigs, contrasting with the fixed monthly salary that provides consistent income regardless of workload fluctuations. Gig pay models appeal to workers seeking autonomy and immediate earnings, while salaried positions offer financial stability and benefits tied to traditional employment structures.
Earnings Volatility Index
The Earnings Volatility Index highlights significant fluctuations in gig pay compared to the stability of fixed salaries, with gig workers experiencing up to 50% higher income variability monthly. Salaried employees benefit from predictable earnings and consistent cash flow, reducing financial risk and improving long-term planning capabilities.
Income Stream Diversification
Salary provides steady, predictable income with fixed monthly payments, whereas gig pay offers variable earnings dependent on task completion, enabling greater income stream diversification. Combining salary with gig work allows individuals to balance financial stability and flexible revenue sources, optimizing overall income resilience.
Fixed-to-Gig Ratio
Fixed-to-Gig Ratio evaluates the balance between a stable salary and variable gig pay, highlighting how a higher ratio ensures consistent income security while a lower ratio offers greater flexibility and potential earnings. Employers leverage this metric to optimize workforce budgeting, aligning compensation models with project demand and talent retention strategies.
Gig Economy Premium
Gig economy workers often receive a premium on pay rates compared to traditional salaried employees, reflecting the flexibility and lack of benefits inherent in gig roles. This gig pay premium can range from 10% to 30% higher per hour to compensate for job insecurity and absence of paid leave.
Scheduled Pay Stability
Salary offers scheduled pay stability through fixed, predictable income regardless of workload fluctuations, ensuring consistent financial security for employees. Gig pay varies with the number of tasks completed, leading to irregular earnings and less predictable financial planning.
Contractor Pay Leakage
Contractor pay leakage occurs when gig workers receive less overall compensation due to unpaid overtime, unbilled hours, and lack of benefits compared to salaried employees. This hidden cost reduces effective earnings and undermines the financial stability typically associated with traditional salary models.
Microtask Wage Benchmark
Microtask wage benchmarks reveal that salaried employment offers consistent income stability compared to gig pay, where earnings fluctuate based on task availability and completion speed. Salary models ensure predictable monthly compensation, whereas gig pay varies significantly, often lacking benefits or minimum wage guarantees.
Anytime Pay Access
Salary offers consistent, predictable income with benefits like paid leave and retirement plans, while gig pay provides flexible, task-based earnings without guaranteed stability. Anytime pay access in gig work enhances cash flow control by allowing workers to withdraw earned wages instantly, contrasting traditional salaried roles where pay is typically disbursed on fixed schedules.
Salary vs Gig Pay for employment model. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com