Employers determining salary policies must balance market rate benchmarks with geo-adjusted pay to attract and retain talent effectively. Market rate reflects industry-standard compensation based on job role and experience, while geo-adjusted pay accounts for local cost of living and regional economic conditions. Implementing a geo-adjusted pay strategy ensures competitive salaries that reflect both market demand and the financial realities of the employee's location.
Table of Comparison
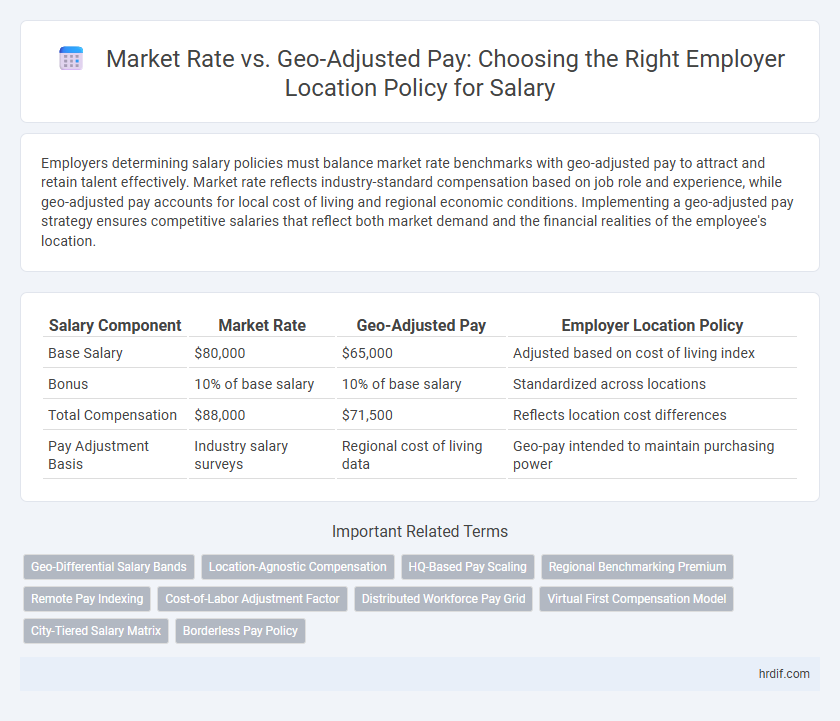
| Salary Component | Market Rate | Geo-Adjusted Pay | Employer Location Policy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Salary | $80,000 | $65,000 | Adjusted based on cost of living index |
| Bonus | 10% of base salary | 10% of base salary | Standardized across locations |
| Total Compensation | $88,000 | $71,500 | Reflects location cost differences |
| Pay Adjustment Basis | Industry salary surveys | Regional cost of living data | Geo-pay intended to maintain purchasing power |
Understanding Market Rate Compensation
Understanding market rate compensation requires analyzing industry salary benchmarks and competitor pay scales to attract skilled talent effectively. Market rate reflects the standard pay for a particular role within a specific sector, regardless of geographic location, ensuring consistency and fairness. Employers must balance these rates with geo-adjusted pay strategies to maintain competitiveness while accounting for cost-of-living differences across regions.
What is Geo-Adjusted Pay?
Geo-adjusted pay is a compensation strategy where an employee's salary is modified based on the cost of living and market conditions in their specific geographic location. Employers implement geo-adjustments to balance competitive pay with regional economic factors, ensuring fairness while managing labor costs effectively. This approach contrasts with market rate pay, which is set according to industry standards regardless of location, potentially leading to disparities in employee purchasing power.
Key Differences Between Market Rate and Geo-Adjusted Pay
Market rate reflects the standard compensation based on industry benchmarks and job roles without considering employee location, driving competitive pay aligned with national or global standards. Geo-adjusted pay modifies salary according to the cost of living and local economic conditions in the employee's geographic area, ensuring fairness and budget efficiency for employers. Key differences include the impact on talent attraction and retention, with market rate promoting uniformity and geo-adjusted pay enabling location-specific flexibility.
The Impact of Remote Work on Salary Structures
Remote work has shifted salary structures by prompting employers to reconsider market rate versus geo-adjusted pay policies. Companies adopting geo-adjusted pay reduce compensation based on an employee's lower cost of living location, potentially saving costs but risking talent retention. Market rate pay ensures uniform salaries regardless of location, promoting equity and competitiveness but increasing overall payroll expenses.
Benefits of Market Rate Salary Policies
Market rate salary policies align employee compensation with industry standards, ensuring competitive pay that attracts top talent regardless of location. Offering market rate salaries helps employers maintain workforce quality and reduces turnover by providing equitable compensation. These policies simplify payroll management and enhance the company's reputation as a fair employer in the global marketplace.
Advantages of Geo-Adjusted Pay Models
Geo-adjusted pay models enhance employer competitiveness by aligning salaries with local living costs, ensuring equitable compensation across regions. They support talent retention and satisfaction by reflecting economic realities of specific locations, reducing geographic pay disparities. This approach optimizes payroll budgets while fostering a geographically diverse workforce, enabling access to broader talent pools.
Challenges Employers Face with Geo-Based Pay
Employers face challenges with geo-based pay policies due to varying living costs and market rates across regions, complicating fair compensation benchmarks. Balancing competitive salaries while managing budget constraints requires precise data analysis and continuous market monitoring. Discrepancies in pay can lead to employee dissatisfaction or talent retention issues, especially when remote work blurs traditional location boundaries.
Equity Considerations in Employer Location Policies
Employers adopting geo-adjusted pay policies must balance market rate competitiveness with fairness to ensure equitable compensation across diverse locations. Equity considerations demand analyzing cost of living variations while preventing income disparities that disadvantage remote or rural employees. Transparent criteria and regular market benchmarking promote fairness and employee trust in location-based salary adjustments.
Strategies for Choosing the Right Pay Structure
Employers must evaluate market rate data alongside geographic cost-of-living variations to establish competitive yet equitable salary frameworks. Incorporating geo-adjusted pay facilitates talent acquisition and retention across diverse regions by reflecting local economic conditions without inflating compensation unsustainably. Strategic pay structures blend external market benchmarks with internal equity principles to balance fairness, budget constraints, and organizational goals effectively.
Future Trends in Compensation for Distributed Teams
Market rate salary benchmarks increasingly integrate geo-adjusted pay to reflect cost-of-living variations across regions, optimizing talent acquisition and retention for distributed teams. Future compensation trends emphasize dynamic pay models leveraging real-time economic data and employee location insights to ensure competitive and equitable remuneration. Employers adopting flexible, algorithm-driven salary frameworks enhance workforce satisfaction while managing labor costs effectively in a global talent landscape.
Related Important Terms
Geo-Differential Salary Bands
Geo-differential salary bands enable employers to adjust compensation based on regional cost of living and market demand, ensuring competitive pay aligned with local economic conditions. Incorporating geo-adjusted pay policies helps attract and retain talent by offering salaries that reflect geographic disparities rather than a uniform market rate, optimizing workforce budgeting and employee satisfaction.
Location-Agnostic Compensation
Location-agnostic compensation policies prioritize paying employees based on market rate benchmarks rather than adjusting salaries according to the employer's geographic location, promoting fairness and equity across diverse regions. Implementing this approach helps attract top talent globally and reduces disparities caused by local cost-of-living variations, aligning compensation with skill level and market demand.
HQ-Based Pay Scaling
HQ-based pay scaling sets salaries according to the company's headquarters location, often leading to standardized compensation regardless of local market rates or cost of living differences. This approach can simplify payroll but may result in pay disparities that affect talent attraction and retention in higher-cost or lower-cost regions.
Regional Benchmarking Premium
Employers adopting geo-adjusted pay policies often apply a Regional Benchmarking Premium to align salaries with local market rates, ensuring competitive compensation across diverse locations. This premium accounts for cost-of-living variations and regional talent demand, balancing equity and market competitiveness while managing payroll expenses effectively.
Remote Pay Indexing
Market rate compensation reflects prevailing wages within the employer's industry and region, while geo-adjusted pay adjusts salaries based on the employee's remote location to remain competitive and cost-effective. Implementing remote pay indexing enables companies to balance fair remuneration with regional economic standards, optimizing talent acquisition and retention.
Cost-of-Labor Adjustment Factor
Market rate salaries reflect average compensation for a role within a specific industry and region, while geo-adjusted pay incorporates a Cost-of-Labor Adjustment Factor to align wages with local living expenses and labor market conditions. Employers use this factor to balance competitive compensation with operational costs, ensuring fair pay that reflects geographic economic disparities.
Distributed Workforce Pay Grid
Market rate salary benchmarks reflect regional economic conditions and job demand, while geo-adjusted pay incorporates cost-of-living differences to ensure equitable compensation across distributed workforce locations. Implementing a geo-adjusted pay grid enables employers to attract and retain talent globally by balancing competitive salaries with local market conditions and living expenses.
Virtual First Compensation Model
Virtual First Compensation Model prioritizes pay based on job market rates in the employee's location while adjusting salary to local cost-of-living to maintain equity and attract remote talent. Employers adopting this approach balance competitive compensation with geographic economic factors, ensuring fair pay across diverse regions.
City-Tiered Salary Matrix
City-tiered salary matrices align employee compensation with localized market rates, ensuring competitive pay based on geographic cost of living and economic conditions. Employers adopting this geo-adjusted pay policy can optimize talent acquisition and retention by offering salaries reflecting city-tier distinctions rather than a uniform national rate.
Borderless Pay Policy
Borderless pay policy integrates market rate analysis with geo-adjusted pay strategies, enabling employers to offer competitive salaries based on the employee's location while maintaining equity and cost-efficiency. This approach balances local living costs with talent acquisition goals, ensuring businesses attract and retain top talent globally without geographic salary disparities.
Market Rate vs Geo-Adjusted Pay for employer location policy. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com