Annual salary provides employees with consistent, predictable income throughout the year, offering financial stability and easier budgeting. On-demand pay allows workers to access earned wages immediately after completing work, improving cash flow and reducing reliance on credit. Choosing between annual salary and on-demand pay depends on individual financial needs and preferences for income flexibility.
Table of Comparison
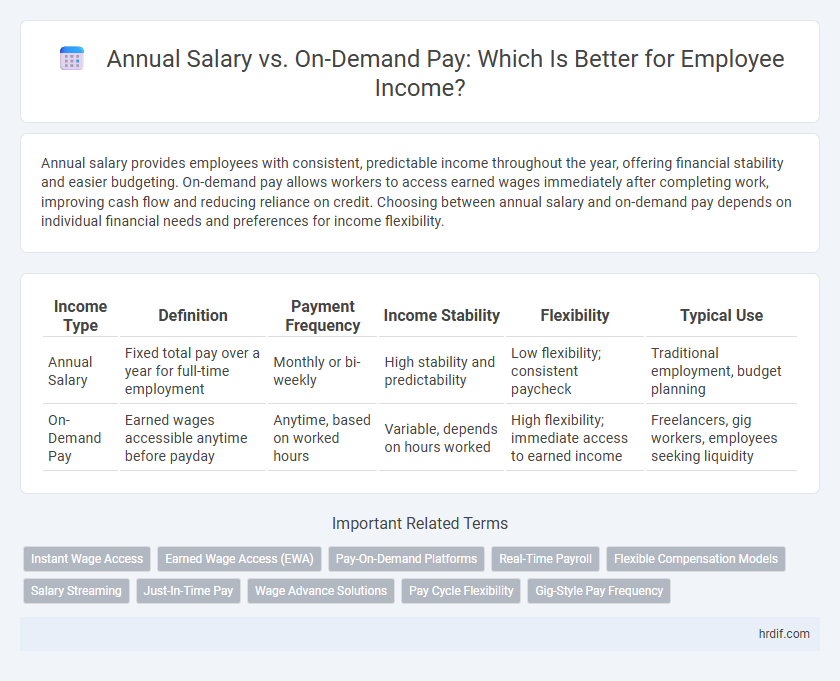
| Income Type | Definition | Payment Frequency | Income Stability | Flexibility | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Salary | Fixed total pay over a year for full-time employment | Monthly or bi-weekly | High stability and predictability | Low flexibility; consistent paycheck | Traditional employment, budget planning |
| On-Demand Pay | Earned wages accessible anytime before payday | Anytime, based on worked hours | Variable, depends on hours worked | High flexibility; immediate access to earned income | Freelancers, gig workers, employees seeking liquidity |
Understanding Annual Salary and On-Demand Pay
Annual salary provides employees with a fixed, predictable income, typically expressed as a yearly amount, ensuring financial stability and facilitating budget planning. On-demand pay, also known as earned wage access, allows workers to access a portion of their earned income before the traditional payday, offering greater flexibility and immediate liquidity. Understanding both compensation methods helps employees choose the option that best suits their financial needs and lifestyle preferences.
Key Differences Between Annual Salary and On-Demand Pay
Annual salary guarantees employees a fixed income over a year, providing financial stability and predictable budgeting. On-demand pay offers flexible access to earned wages before payday, improving cash flow and reducing financial stress. The key differences lie in payment frequency, income predictability, and employee financial control.
Pros and Cons of Annual Salary for Employees
Annual salary provides employees with financial stability by offering a consistent income and predictable budgeting throughout the year. However, it may limit earning potential during peak periods of high productivity or overtime, as pay remains fixed regardless of extra work hours. Employees on an annual salary might also lack flexibility compared to on-demand pay, which rewards actual hours worked and can adapt to fluctuating workloads.
Benefits and Drawbacks of On-Demand Pay
On-demand pay offers immediate access to earned wages, improving cash flow and reducing financial stress for employees, which can enhance job satisfaction and retention. However, relying on on-demand pay may lead to budgeting challenges and potential overspending due to the frequent access to funds before the traditional pay cycle ends. Unlike annual salary, on-demand pay lacks consistent income predictability, potentially complicating long-term financial planning for employees.
Financial Stability: Which Model Works Best?
Annual salary provides employees with consistent, predictable income, enhancing long-term financial stability by ensuring steady cash flow and facilitating budgeting. On-demand pay offers flexibility by allowing workers to access earned wages before payday, which can help manage immediate financial needs but may lead to irregular income patterns. For sustained financial security, annual salary models typically outperform on-demand pay systems by supporting routine expense planning and reducing financial stress.
Impact on Employee Satisfaction and Retention
Employees receiving annual salary enjoy consistent income stability, which significantly enhances job satisfaction and reduces turnover rates. On-demand pay offers flexibility and immediate access to earned wages, appealing to employees seeking cash flow control, but may introduce income unpredictability that affects long-term retention. Companies balancing both compensation models can optimize employee satisfaction by addressing diverse financial needs and improving overall retention metrics.
Flexibility and Budgeting: Salary vs On-Demand Pay
Annual salary provides employees with consistent income, enabling reliable budgeting and financial planning throughout the year. On-demand pay offers greater flexibility by allowing access to earned wages before the traditional payday, helping manage unexpected expenses without relying on credit. Choosing between annual salary and on-demand pay depends on prioritizing steady financial security versus adaptable access to funds.
Employer Perspectives: Cost and Administrative Factors
Employers often prefer annual salary structures as they simplify budgeting and reduce administrative overhead related to payroll processing and benefits management. On-demand pay, while appealing to employees for its flexibility, can increase operational costs due to the need for more frequent transactions and complex compliance requirements. Balancing cost-efficiency and administrative ease drives many organizations to maintain traditional salaried compensation models despite growing interest in on-demand payment systems.
Industry Trends: The Rise of On-Demand Pay
On-demand pay is rapidly transforming employee income structures, with 40% of U.S. companies offering this flexible compensation option as of 2024. Industry trends reveal that workers increasingly prefer access to earnings between paychecks to manage financial emergencies and reduce reliance on credit. Surveys indicate on-demand pay improves employee retention by up to 30%, signaling a major shift from traditional annual salary models toward more dynamic income solutions.
Choosing the Right Compensation Model for Your Career
Annual salary offers financial stability with consistent monthly income, making it ideal for employees seeking predictable cash flow and long-term benefits like retirement plans and health insurance. On-demand pay provides flexibility by allowing access to earned wages before the typical payday, supporting better cash management and reducing financial stress. Selecting the right compensation model depends on your career goals, lifestyle needs, and preference for income predictability versus financial agility.
Related Important Terms
Instant Wage Access
Instant Wage Access allows employees to receive a portion of their earned income before the traditional annual salary payout, providing greater financial flexibility and reducing reliance on loans or credit. This on-demand pay model enhances cash flow management and improves overall employee satisfaction by aligning income access with immediate expenses.
Earned Wage Access (EWA)
Earned Wage Access (EWA) offers employees real-time access to wages before the traditional payday, enhancing financial flexibility compared to a fixed annual salary. This on-demand pay model improves cash flow management and reduces reliance on high-interest loans, benefiting both employees and employers by promoting financial well-being and reducing turnover.
Pay-On-Demand Platforms
Pay-On-Demand platforms offer employees instant access to earned wages before the traditional paycheck date, providing financial flexibility and reducing reliance on high-interest loans. Comparing annual salary with on-demand pay reveals that while the former guarantees a fixed income, on-demand pay enhances cash flow management but may involve fees or reduced overall earnings if misused.
Real-Time Payroll
Real-time payroll systems enable employees to access on-demand pay, offering greater financial flexibility compared to traditional annual salary disbursements. This shift enhances employee satisfaction by providing instant access to earned wages, reducing reliance on fixed pay cycles and improving cash flow management.
Flexible Compensation Models
Flexible compensation models increasingly favor on-demand pay, allowing employees to access earned wages instantly rather than waiting for traditional annual salary disbursements. This approach enhances financial flexibility, reduces stress, and aligns income with individual cash flow needs compared to static annual salary structures.
Salary Streaming
Salary streaming enables employees to access earned wages in real-time rather than waiting for annual salary disbursement, enhancing financial flexibility and reducing reliance on traditional payday cycles. On-demand pay systems integrate with payroll to provide incremental income access, contrasting with fixed annual salary structures that offer stability but less immediate liquidity.
Just-In-Time Pay
Just-In-time pay, a form of on-demand pay, allows employees to access earned wages immediately rather than waiting for the traditional annual salary cycle, enhancing financial flexibility and reducing reliance on high-interest loans. This payment method improves cash flow management and supports workers facing unexpected expenses, contrasting with fixed annual salaries that offer predictable but less adaptable income streams.
Wage Advance Solutions
Annual salary provides employees with consistent, predictable income, fostering financial stability and long-term planning; wage advance solutions, however, offer flexible on-demand pay access that helps manage unexpected expenses and reduce reliance on costly loans. Integrating wage advance options into traditional compensation structures enhances employee satisfaction and financial wellness by bridging income gaps between pay periods.
Pay Cycle Flexibility
Annual salary provides stable, predictable income with fixed pay periods, while on-demand pay offers employees the flexibility to access earned wages anytime, enhancing cash flow management and financial wellness. Pay cycle flexibility through on-demand pay reduces reliance on traditional biweekly or monthly pay schedules, catering to diverse financial needs and improving overall employee satisfaction.
Gig-Style Pay Frequency
Gig-style pay frequency offers employees flexible income by providing payment immediately after task completion, contrasting with the fixed, predictable nature of annual salaries which aggregate earnings over a year. This model supports financial agility for workers who prioritize short-term cash flow and variable workload over consistent monthly paychecks.
Annual Salary vs On-Demand Pay for employee income. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com