Salary provides employees with a predictable, fixed income that simplifies financial planning and ensures steady earnings each pay period. On-demand pay offers flexibility by allowing workers to access earned wages before the regular payday, which can help manage unexpected expenses and improve cash flow. Choosing between salary and on-demand pay depends on an individual's need for income stability versus immediate access to funds.
Table of Comparison
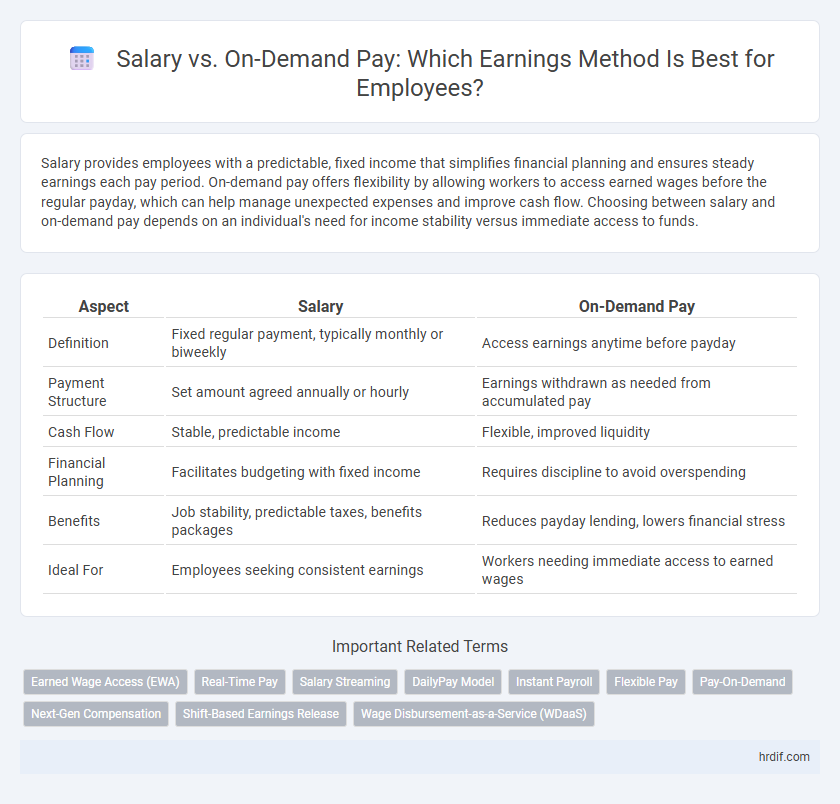
| Aspect | Salary | On-Demand Pay |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed regular payment, typically monthly or biweekly | Access earnings anytime before payday |
| Payment Structure | Set amount agreed annually or hourly | Earnings withdrawn as needed from accumulated pay |
| Cash Flow | Stable, predictable income | Flexible, improved liquidity |
| Financial Planning | Facilitates budgeting with fixed income | Requires discipline to avoid overspending |
| Benefits | Job stability, predictable taxes, benefits packages | Reduces payday lending, lowers financial stress |
| Ideal For | Employees seeking consistent earnings | Workers needing immediate access to earned wages |
Understanding Salary: The Traditional Pay Model
Salary represents a fixed, regular payment typically disbursed monthly or biweekly, ensuring consistent income regardless of hours worked. This traditional pay model provides financial stability and predictable budgeting for employees, contrasting with the variability of on-demand pay systems. Employers often prefer salary arrangements to streamline payroll processes and foster long-term employee commitment.
What is On-Demand Pay?
On-demand pay allows employees to access a portion of their earned wages before the traditional payday, providing greater financial flexibility and reducing reliance on high-interest loans. Unlike a fixed salary paid on a set schedule, on-demand pay offers real-time access to earnings based on hours worked or tasks completed. This payment model helps improve cash flow management and supports workers facing unexpected expenses without waiting for the end of the pay period.
Key Differences between Salary and On-Demand Pay
Salary offers a fixed, predictable income paid regularly, providing financial stability and ease of budgeting, regardless of hours worked or immediate cash needs. On-demand pay allows employees to access earned wages before the scheduled payday, increasing financial flexibility and helping manage unexpected expenses without waiting for the traditional pay cycle. Key differences include payment frequency, control over cash flow, and impact on employee financial wellbeing and motivation.
Pros and Cons of Salary-Based Earnings
Salary-based earnings provide employees with predictable and stable income, facilitating financial planning and budgeting. However, this fixed payment structure may limit earning potential compared to on-demand pay systems, which offer flexibility and access to wages as work is completed. Employers benefit from salary models through simplified payroll administration but face challenges in motivating performance without direct correlation to hours worked.
Benefits and Drawbacks of On-Demand Pay
On-demand pay offers employees immediate access to earned wages, improving cash flow and reducing financial stress compared to traditional salary schedules. This payment flexibility can enhance employee satisfaction and retention but may incur higher administrative costs and potential budgeting challenges for employers. However, reliance on frequent payouts might diminish incentives for long-term financial planning among workers.
Salary vs On-Demand Pay: Impact on Financial Stability
A fixed salary provides consistent monthly income, ensuring predictable cash flow and aiding in long-term financial planning. On-demand pay offers flexible access to earned wages before payday, helping address immediate cash needs but potentially leading to inconsistent monthly earnings. Choosing between salary and on-demand pay impacts financial stability by balancing steady income with liquidity convenience, influencing budgeting and debt management strategies.
Employee Preferences: Salary or On-Demand Pay?
Employees increasingly favor on-demand pay over traditional salary structures due to the flexibility it offers in accessing earned wages anytime, which enhances financial stability and reduces stress. According to recent surveys, 65% of workers prefer on-demand pay for its immediate liquidity, while 35% still value the predictability of a fixed salary. Employers adopting on-demand pay models report higher employee satisfaction and retention rates, highlighting a significant shift in workforce compensation preferences.
Employer Perspectives: Salary vs On-Demand Pay Models
Employers prefer salary models for predictable budgeting and simplified payroll management, ensuring consistent cash flow and easier financial forecasting. On-demand pay offers flexibility and may improve employee satisfaction and retention but introduces variable payroll costs and increased administrative complexity. Balancing fixed salary expenses with the dynamic nature of on-demand pay helps employers optimize compensation strategies while maintaining operational efficiency.
How Salary and On-Demand Pay Affect Job Satisfaction
Salary provides consistent and predictable income, fostering financial stability and higher overall job satisfaction. On-demand pay offers immediate access to earned wages, reducing financial stress and increasing employee morale, particularly for those facing urgent expenses. Combining both payment methods can optimize earnings flexibility and enhance job satisfaction by balancing stability with accessibility.
The Future of Earnings: Will On-Demand Pay Replace Salary?
On-demand pay offers instant access to earned wages, providing flexibility that contrasts traditional salary structures with fixed monthly payments. This shift enhances financial well-being by reducing reliance on credit and improving cash flow management for employees. Despite its advantages, salary remains prevalent due to predictable income stability and benefits, suggesting a future where on-demand pay complements rather than replaces conventional salary models.
Related Important Terms
Earned Wage Access (EWA)
Earned Wage Access (EWA) offers employees immediate access to wages already earned, improving financial flexibility compared to traditional fixed salary schedules. This on-demand pay model reduces reliance on payday loans and enhances cash flow management, leading to increased employee satisfaction and reduced turnover.
Real-Time Pay
Real-time pay provides employees immediate access to earned wages, improving financial flexibility compared to traditional salary systems that require waiting for scheduled paydays. This on-demand pay model supports cash flow management and reduces reliance on costly short-term credit options.
Salary Streaming
Salary streaming enhances employee financial flexibility by allowing access to earned wages in real-time, contrasting with traditional fixed monthly salary schedules that may delay cash flow. This on-demand pay model improves liquidity, reduces reliance on credit, and supports better financial wellness compared to conventional salary structures.
DailyPay Model
The DailyPay model empowers employees by offering on-demand access to earned wages, enhancing cash flow flexibility compared to traditional fixed salary payments. This approach reduces financial stress and promotes better money management by allowing users to withdraw earnings as they accrue rather than waiting for scheduled paydays.
Instant Payroll
Instant payroll services provide employees with immediate access to earned wages, enhancing financial flexibility compared to traditional salary schedules that pay on fixed dates. This on-demand pay model reduces reliance on high-interest loans and improves cash flow management, supporting overall employee financial wellness.
Flexible Pay
Flexible pay options, such as on-demand pay, provide employees with immediate access to earned wages, enhancing financial control compared to traditional salaried income. This flexibility reduces reliance on fixed pay schedules, allowing workers to manage cash flow and meet urgent expenses efficiently.
Pay-On-Demand
Pay-On-Demand offers employees instant access to earned wages before the traditional payday, improving financial flexibility and reducing reliance on high-interest loans. This approach enhances cash flow management and supports timely bill payments, leading to increased employee satisfaction and retention compared to fixed salaries.
Next-Gen Compensation
Next-Gen Compensation shifts the focus from traditional salary models to flexible On-Demand Pay systems, enabling employees to access earned wages instantly, reducing financial stress and enhancing productivity. By integrating real-time earnings with payroll technology, companies foster financial wellness and adapt to dynamic workforce needs in a competitive market.
Shift-Based Earnings Release
Shift-based earnings release offers employees predictable income by providing payments tied directly to completed work shifts, contrasting with on-demand pay that allows immediate access to earned wages but may lead to fluctuating cash flow. Employers benefit from shift-based payments as they simplify payroll management and foster budget stability while supporting transparent earnings verification.
Wage Disbursement-as-a-Service (WDaaS)
Wage Disbursement-as-a-Service (WDaaS) offers a flexible alternative to traditional salary structures by enabling employees to access earned wages on-demand, improving cash flow and financial well-being. This innovative pay model reduces the delay between work performed and compensation received, enhancing overall employee satisfaction and retention rates compared to fixed salary payments.
Salary vs On-Demand Pay for earnings. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com