Salary provides a fixed, predictable income that ensures financial stability for employees in traditional full-time roles. Fractional compensation in job sharing divides the total salary between multiple employees, reflecting their part-time contributions while offering flexibility and cost efficiency for employers. This approach balances workload distribution with proportional remuneration, optimizing resources without compromising employee earnings.
Table of Comparison
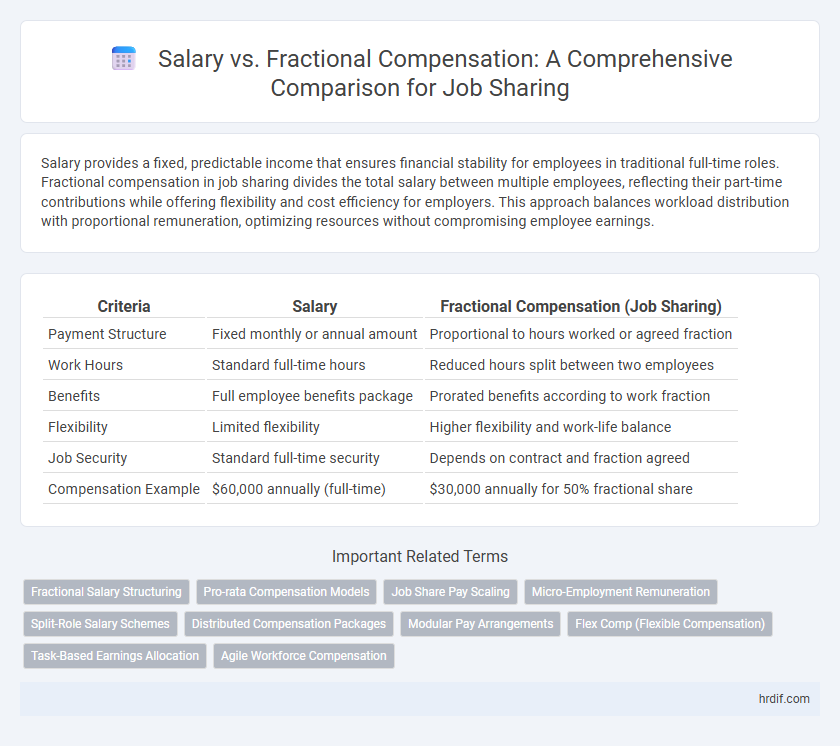
| Criteria | Salary | Fractional Compensation (Job Sharing) |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Structure | Fixed monthly or annual amount | Proportional to hours worked or agreed fraction |
| Work Hours | Standard full-time hours | Reduced hours split between two employees |
| Benefits | Full employee benefits package | Prorated benefits according to work fraction |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility | Higher flexibility and work-life balance |
| Job Security | Standard full-time security | Depends on contract and fraction agreed |
| Compensation Example | $60,000 annually (full-time) | $30,000 annually for 50% fractional share |
Understanding Salary and Fractional Compensation
Understanding salary versus fractional compensation is crucial for job sharing agreements where the total salary is divided proportionally based on work hours or responsibilities. Salary typically refers to a fixed annual amount paid for a full-time position, while fractional compensation allocates a fraction of that salary according to the employee's part-time contribution. This structure ensures fair remuneration aligned with workload, promoting transparency in shared roles.
Defining Job Sharing Arrangements
Job sharing arrangements involve splitting one full-time position between two or more employees, with salary or fractional compensation reflecting the shared responsibilities and hours worked. Fractional compensation aligns pay proportionally to the time committed, offering cost efficiency and flexibility for employers while maintaining fair remuneration for employees. Defining clear salary parameters and role expectations ensures transparency and equitable distribution of workload in job sharing agreements.
Key Differences Between Salary and Fractional Compensation
Salary provides a fixed, consistent income regardless of hours worked, while fractional compensation allocates payment based on the actual portion of time or tasks completed in job sharing arrangements. Salary benefits include steady financial predictability and employer-covered benefits, whereas fractional compensation offers flexibility and aligns earnings directly with work contribution. Key differences involve payment structure, benefits eligibility, and financial certainty, which impact both employer cost management and employee income stability.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Salary Models
Traditional salary models offer predictable income and often include benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, providing financial stability for employees. However, these models can lack flexibility, making it difficult to accommodate part-time or job-sharing arrangements, and may discourage collaboration due to fixed individual compensation. The rigidity of traditional salaries can result in inefficiencies and decreased job satisfaction when workload or personal circumstances change.
Benefits of Fractional Compensation in Job Sharing
Fractional compensation in job sharing offers increased flexibility by aligning pay with actual hours worked, promoting work-life balance and reducing burnout. This approach enables companies to attract diverse talent pools and retain skilled employees by providing customized salary structures that match fractional roles. Cost-effectiveness is enhanced as employers save on full-time salary overheads while maintaining productivity through shared responsibilities.
Financial Impact on Employers and Employees
Salary offers employers predictable labor costs and simplifies budget planning, while fractional compensation in job sharing provides flexibility by aligning pay with actual hours worked. For employees, full salaries ensure steady income and benefits, whereas fractional compensation may reduce earnings but can improve work-life balance and reduce burnout. Employers must weigh the cost efficiency of fractional pay against potential administrative complexities and the impact on employee satisfaction and retention.
Flexibility and Work-Life Balance Considerations
Job sharing with fractional compensation offers enhanced flexibility, allowing employees to better manage personal commitments while maintaining professional responsibilities. Traditional salary models typically require full-time hours, limiting opportunities for work-life balance. Fractional pay structures support a healthier integration of work and personal life, promoting increased job satisfaction and reduced burnout.
Legal and Payroll Implications
Salary and fractional compensation in job sharing present distinct legal and payroll challenges, particularly in compliance with labor laws and tax regulations. Employers must ensure accurate pro-rata salary calculations and benefits allocation to avoid disputes and penalties related to wage laws and employee entitlements. Payroll systems need to accommodate variable compensation structures while maintaining Transparent record-keeping for audits and government reporting requirements.
Choosing the Right Compensation Model for Job Sharing
Choosing the right compensation model for job sharing depends on balancing fairness and motivation, with salary offering stability and fractional compensation aligning pay directly with hours worked. Salary ensures consistent income and benefits, attracting candidates seeking financial security, while fractional compensation allows flexibility and cost savings by compensating employees based on their actual contribution. Evaluating factors like workload distribution, employee preferences, and budget constraints helps determine the most effective approach for sustaining productivity and satisfaction in job-sharing arrangements.
Future Trends in Job Compensation Structures
Future trends in job compensation structures indicate a growing shift from traditional salary models to fractional compensation to accommodate job sharing arrangements, enhancing flexibility and cost efficiency for employers. Fractional compensation enables precise alignment of pay with the proportion of work performed, promoting equitable remuneration while supporting diverse workforce needs. Increasing adoption of digital tools and data analytics facilitates transparent tracking of contribution levels, driving more dynamic and performance-based compensation frameworks.
Related Important Terms
Fractional Salary Structuring
Fractional salary structuring in job sharing allocates compensation based on the exact portion of work performed, aligning payments with individual contributions rather than a fixed full-time salary. This approach enhances financial transparency and ensures equitable remuneration proportional to hours worked, promoting flexibility and optimizing workforce costs.
Pro-rata Compensation Models
Pro-rata compensation models in job sharing allocate salary based on the fraction of hours worked, ensuring equitable pay proportional to actual contributions. This approach contrasts with fixed salary models by providing flexibility and cost-efficiency for employers while maintaining fair income for employees in shared roles.
Job Share Pay Scaling
Job share pay scaling adjusts total compensation proportionally based on the percentage of hours worked, ensuring salary aligns fairly with individual contributions in a shared role. Fractional compensation offers flexibility by dividing salary and benefits according to each job sharer's workload, promoting equitable pay distribution and cost efficiency.
Micro-Employment Remuneration
Micro-employment remuneration through fractional compensation offers precise alignment with actual work contributions, enhancing cost efficiency compared to traditional fixed salaries in job sharing arrangements. This model allows for flexible income distribution among multiple employees, optimizing payroll expenses while maintaining workforce productivity.
Split-Role Salary Schemes
Split-role salary schemes enable employers to allocate fractional compensation proportionally across shared job roles, enhancing flexibility while maintaining equitable pay distribution. This approach optimizes salary budgeting by aligning remuneration with individual workload contributions in job sharing arrangements.
Distributed Compensation Packages
Distributed compensation packages in job sharing balance salary by dividing total pay proportionally among employees, optimizing cost efficiency while maintaining equitable remuneration. This fractional compensation structure enhances flexibility and supports collaborative workforce models without sacrificing financial fairness.
Modular Pay Arrangements
Modular pay arrangements in job sharing enable companies to tailor fractional compensation precisely to work contributions, improving transparency and equity compared to fixed salaries. This approach aligns pay with hours worked and responsibilities shared, fostering flexibility and motivation within collaborative roles.
Flex Comp (Flexible Compensation)
Fractional compensation in job sharing offers tailored Flex Comp models that align pay with actual hours worked, enhancing cost-efficiency and employee satisfaction. Salaries provide fixed income but lack the adaptability of Flex Comp systems, which optimize compensation based on productivity and shared responsibilities.
Task-Based Earnings Allocation
Task-based earnings allocation in job sharing allows salary to be distributed proportionally according to the specific duties completed, promoting fairness and transparency. This method contrasts with fractional compensation, which divides pay based on time or role percentage, potentially overlooking the value of individual task contributions.
Agile Workforce Compensation
Salary structures in Agile Workforce Compensation emphasize fixed payments, while Fractional Compensation enables proportional earnings tied to actual workload and contributions in job sharing models. This approach promotes flexibility, cost-efficiency, and aligns compensation with agile team dynamics and project outcomes.
Salary vs Fractional Compensation for job sharing. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com