Salary offers consistent monthly income with benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, providing financial stability and predictable cash flow. Gig income, while potentially higher per project, fluctuates based on workload and client availability, requiring careful budgeting and tax planning. Choosing between salary and gig income depends on personal preference for stability versus flexibility and income variability.
Table of Comparison
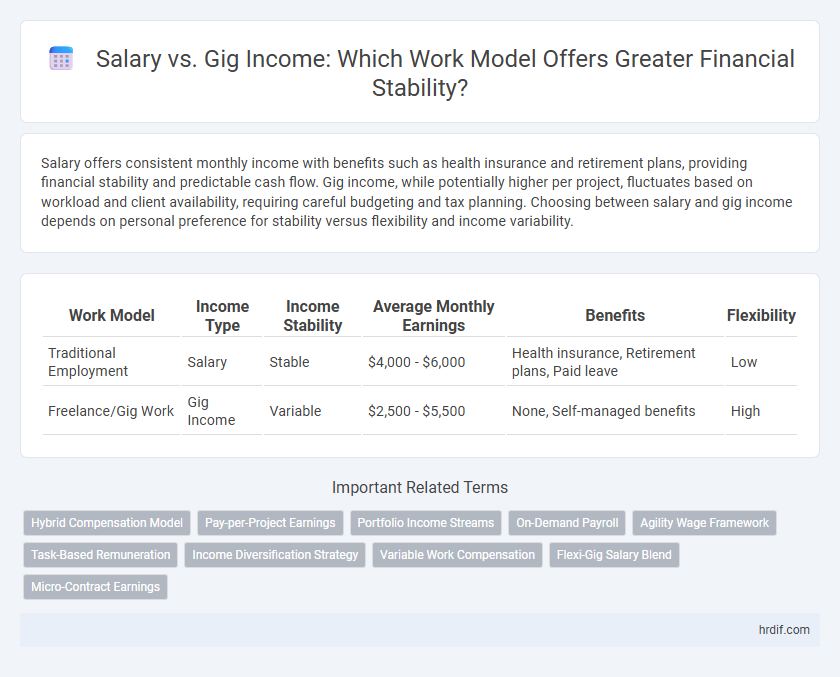
| Work Model | Income Type | Income Stability | Average Monthly Earnings | Benefits | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Employment | Salary | Stable | $4,000 - $6,000 | Health insurance, Retirement plans, Paid leave | Low |
| Freelance/Gig Work | Gig Income | Variable | $2,500 - $5,500 | None, Self-managed benefits | High |
Understanding Salary and Gig Income: Key Differences
Salary offers consistent, predictable income through fixed regular payments, providing financial stability and benefits like health insurance and retirement plans. Gig income fluctuates based on project availability and client demand, often lacking employer-provided benefits but offering flexibility and autonomy. Understanding these differences helps individuals choose a work model that aligns with their financial goals and lifestyle preferences.
Job Security: Traditional Salary vs. Gig Work
Traditional salary jobs offer consistent income and enhanced job security through benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and legal protections, which are often absent in gig work. Gig income can be unpredictable and varies based on project availability, leading to financial instability and limited access to employee benefits. Workers relying on gig income face higher risks of income fluctuation and lack long-term security compared to salaried employees.
Income Stability: Predictability vs. Flexibility
Salary provides consistent and predictable income, offering financial stability ideal for long-term planning and fixed expenses. Gig income offers flexibility with variable earnings, which can fluctuate significantly based on workload and market demand. Balancing salary's predictability with gig work's adaptable schedule is crucial for managing both stable cash flow and income growth opportunities.
Benefits and Perks: Salaried Roles vs. Gig Economy
Salaried roles typically offer consistent benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off, providing financial stability and security that gig income often lacks. Gig economy workers benefit from flexible schedules and diverse income streams but must manage their own healthcare, taxes, and retirement savings without employer assistance. The choice between salaried employment and gig work hinges on weighing guaranteed perks against autonomy and variable earnings potential.
Earning Potential: Cap Limits and Opportunities
Salary offers a fixed earning potential with predictable income and capped increases based on role and experience, providing financial stability but limited upside. Gig income presents variable earning opportunities without fixed caps, allowing individuals to scale earnings based on effort, skill demand, and market conditions. This flexibility can lead to higher maximum income, though it lacks the guaranteed consistency of salaried positions.
Work-Life Balance: Structured Jobs vs. Gig Flexibility
Traditional salaried positions offer a structured work environment with predictable hours and consistent income, which enhances work-life balance by providing routine and financial stability. Gig work provides flexibility to choose projects and schedule, allowing workers to tailor their hours to personal needs but often results in income variability and less predictable workloads. Balancing these elements involves considering the trade-off between steady paychecks and the autonomy to control work timing.
Taxes and Financial Planning: Salary vs. Gig Income
Salary income offers predictable tax withholding and simplifies financial planning by allowing consistent budgeting and retirement contributions, while gig income requires careful quarterly tax payments and detailed expense tracking to optimize deductions. Self-employment taxes impact gig workers more heavily, necessitating advanced tax planning strategies to minimize liabilities. Effective financial management in gig work depends on disciplined saving and strategic investment to address irregular income flows and tax obligations.
Career Growth: Advancement in Jobs vs. Gig Paths
Salaried positions often provide structured career advancement with clear promotion paths, benefits, and skill development opportunities, fostering long-term professional growth. Gig income models offer flexibility but generally lack formal advancement systems, requiring individuals to proactively build reputations and networks to increase earnings. Career growth in salaried roles emphasizes stability and progressive responsibility, while gig work demands entrepreneurial skills and self-driven portfolio expansion.
Job Satisfaction: Fulfillment in Salaried vs. Gig Work
Salaried positions often provide consistent income and benefits that contribute to long-term job satisfaction and financial stability, fostering a sense of fulfillment through structured career growth. Gig workers experience greater flexibility and autonomy, which can enhance personal fulfillment by allowing them to pursue varied projects aligned with their passions. However, the unpredictability of gig income may lead to stress, impacting overall job satisfaction compared to the reliability of a fixed salary.
Choosing the Right Model: Salary vs. Gig Income
Choosing the right work model depends on financial stability, flexibility needs, and long-term goals. Salary offers consistent monthly income, benefits like health insurance, and retirement plans, ensuring security and predictability. Gig income provides variable earnings and schedule freedom, appealing to those valuing autonomy but requires careful budgeting due to income fluctuations.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Compensation Model
The hybrid compensation model combines the stability of a fixed salary with the flexibility and potential earnings of gig income, optimizing financial security and performance incentives. This approach allows employees to benefit from predictable base pay while capitalizing on variable gig-based opportunities that drive productivity and innovation.
Pay-per-Project Earnings
Pay-per-project earnings in gig work offer flexible income opportunities but often lack the stability and benefits associated with a fixed salary. Workers relying on gig income must manage irregular payment schedules and variable project availability, impacting consistent financial planning compared to salaried employment.
Portfolio Income Streams
Portfolio income streams from diverse gig roles often surpass traditional salary by offering scalable earnings and tax advantages through multiple independent contracts. Workers leveraging gig income benefit from flexible scheduling and income diversification, reducing reliance on a single employer's salary limitations.
On-Demand Payroll
On-demand payroll offers gig workers immediate access to earned wages, enhancing cash flow flexibility compared to traditional salaried employees who receive fixed monthly payments. This payment model aligns income with work performed, reducing financial stress and supporting dynamic work schedules prevalent in gig economies.
Agility Wage Framework
The Agility Wage Framework prioritizes flexible compensation structures by balancing fixed salary with variable gig income, optimizing workforce adaptability and financial stability. Emphasizing real-time skills and project contributions, this model enables employees to maximize earnings through diverse gig opportunities while maintaining a reliable baseline salary.
Task-Based Remuneration
Task-based remuneration offers flexibility by compensating workers per completed gig, often resulting in variable income compared to a fixed salary that provides consistent, predictable earnings. This model incentivizes productivity but may lack the financial stability and benefits associated with traditional salaried employment.
Income Diversification Strategy
Diversifying income through a combination of salary and gig work enhances financial stability by balancing steady paychecks with flexible earning opportunities. This income diversification strategy mitigates risks associated with job loss or fluctuating gig demand while maximizing total earnings.
Variable Work Compensation
Salary often provides a fixed, predictable income, while gig income offers variable work compensation tied directly to project completion and client demand fluctuations. This variability can lead to higher earning potential but also increased income instability compared to traditional salaried positions.
Flexi-Gig Salary Blend
Flexi-Gig salary blend combines the stability of a fixed salary with the flexibility and potential higher earnings of gig income, optimizing financial security and work-life balance. This hybrid model supports diverse revenue streams by integrating predictable paychecks with variable gig projects, enhancing overall income resilience.
Micro-Contract Earnings
Micro-contract earnings offer flexible income streams that often surpass traditional salary models in short-term profitability and project diversity. Gig income enables workers to leverage multiple platforms simultaneously, optimizing financial growth through skill-specific, high-demand tasks.
Salary vs Gig Income for work model. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com