Fixed salary provides a stable and predictable income stream, offering financial security and consistent budgeting ease. In contrast, gig economy rates fluctuate based on demand and workload, leading to variable earnings that may require more flexible financial planning. Choosing between the two depends on individual risk tolerance and the need for income stability versus earning potential variability.
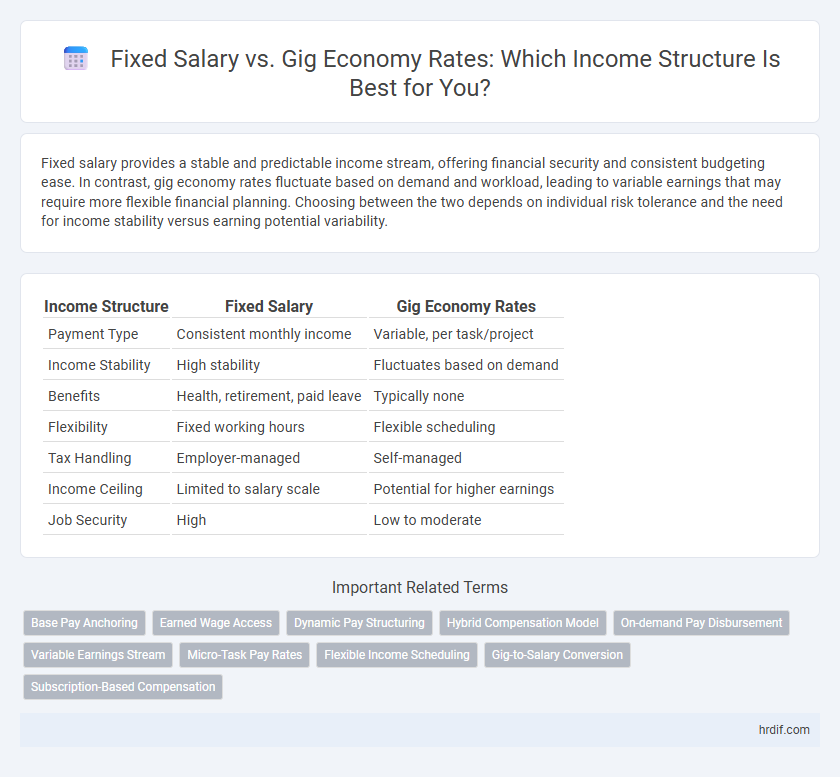
Table of Comparison
| Income Structure | Fixed Salary | Gig Economy Rates |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Type | Consistent monthly income | Variable, per task/project |
| Income Stability | High stability | Fluctuates based on demand |
| Benefits | Health, retirement, paid leave | Typically none |
| Flexibility | Fixed working hours | Flexible scheduling |
| Tax Handling | Employer-managed | Self-managed |
| Income Ceiling | Limited to salary scale | Potential for higher earnings |
| Job Security | High | Low to moderate |
Defining Fixed Salary and Gig Economy Earnings
Fixed salary represents a predetermined, consistent income paid regularly regardless of hours worked, often including benefits like health insurance and retirement plans. Gig economy earnings vary based on task completion, project demand, and hours worked, creating income fluctuations without traditional employee benefits. Understanding these differences is crucial for workers evaluating financial stability and long-term planning in diverse employment models.
Pros and Cons of Fixed Salary Jobs
Fixed salary jobs provide consistent monthly income, ensuring financial stability and easier budgeting, which is ideal for long-term financial planning and securing loans. They often include benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, contributing to overall job security and employee wellbeing. However, fixed salaries may limit earning potential and flexibility compared to gig economy rates, where income can fluctuate based on workload and market demand.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gig Economy Rates
Gig economy rates offer flexible income opportunities, enabling workers to choose projects and hours, which suits those seeking autonomy and variable workloads. However, these rates often lack stability and benefits found in fixed salaries, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and predictable monthly earnings. The variability in gig pay can result in financial uncertainty, making long-term budgeting and financial planning more challenging compared to traditional fixed salary structures.
Income Stability: Fixed Salary vs. Gig Work
Fixed salary provides predictable monthly income and benefits, ensuring financial stability and easier budgeting. Gig economy rates fluctuate based on demand, projects, and hours worked, causing irregular cash flow and income uncertainty. Workers relying on gig work often face challenges in planning long-term expenses due to this variability.
Earning Potential Comparison: Salary vs. Gig
Fixed salary offers consistent monthly income with predictable budgeting and financial security, while gig economy rates vary based on project volume and market demand, potentially leading to fluctuating earnings. Gig workers often have higher earning potential during peak periods but face income instability and lack of benefits compared to salaried employees. A clear comparison shows salaried roles prioritize stable income streams, whereas gig economy roles emphasize flexible but variable compensation.
Flexibility and Work-Life Balance Considerations
Fixed salary offers stable income and predictable work hours, providing employees with consistent financial security and a structured routine that supports long-term work-life balance. Gig economy rates often fluctuate, allowing greater flexibility to choose when and how much to work, which can enhance work-life balance by accommodating personal schedules but may introduce income variability and financial uncertainty. Balancing the stability of a fixed salary with the adaptability of gig work is essential for optimizing both flexibility and sustainable work-life harmony.
Financial Security and Benefits Analysis
Fixed salary offers consistent monthly income, ensuring reliable financial security and access to benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave. Gig economy rates provide flexibility and potentially higher earnings per task but lack guaranteed income stability and often exclude comprehensive benefits packages. Evaluating income structure should balance predictable cash flow and essential benefits against variable pay and autonomy.
Career Growth Opportunities in Each Income Model
Fixed salary structures provide stable income and predictable career progression through promotions and annual raises, fostering long-term skill development within an organization. The gig economy offers flexible earning potential based on project demand but may lack formal growth pathways, requiring individuals to independently build their portfolios and networks for advancement. Career growth in fixed salaries often aligns with organizational hierarchy, whereas gig rates depend on market reputation and diverse client relationships.
Risk Factors in Fixed and Gig Income Structures
Fixed salary provides stable monthly income with predictable cash flow and employer-backed benefits, minimizing financial risk during economic downturns. Gig economy rates introduce income volatility due to fluctuating demand, inconsistent work availability, and lack of traditional benefits, increasing overall financial uncertainty. Workers reliant on gig income face higher risks of income gaps and insufficient social security coverage compared to fixed salary earners.
Choosing the Right Income Structure for Your Career
Fixed salary provides predictable monthly income and financial stability, ideal for long-term budgeting and benefits like health insurance and retirement plans. Gig economy rates offer flexibility and higher earning potential per task but come with income variability and lack of traditional employment benefits. Evaluating your risk tolerance, financial goals, and lifestyle preferences helps determine whether a fixed salary or gig-based earnings best align with your career objectives.
Related Important Terms
Base Pay Anchoring
Base pay anchoring stabilizes income expectations by establishing a consistent fixed salary, contrasting sharply with the fluctuating, task-based rates prevalent in the gig economy. This foundational wage framework enhances financial predictability and supports long-term planning, whereas gig rates often lead to variable income streams that lack uniformity.
Earned Wage Access
Earned Wage Access (EWA) offers flexible income solutions by allowing employees to access a portion of their earned wages before payday, contrasting with the fixed salary's predictable but inflexible pay structure. In gig economy models, variable rates and irregular earnings make EWA a crucial tool for managing cash flow and financial stability.
Dynamic Pay Structuring
Dynamic pay structuring balances fixed salary stability with gig economy rates' flexibility, enabling workers to optimize income based on workload and market demand. This hybrid approach enhances financial resilience by combining guaranteed base earnings with variable gig-based compensation tied to performance metrics.
Hybrid Compensation Model
The hybrid compensation model combines a stable fixed salary with variable gig economy rates, offering employees consistent income alongside performance-based earnings. This approach balances financial security with flexibility, optimizing overall income structure in dynamic work environments.
On-demand Pay Disbursement
Fixed salary offers stable, predictable income essential for financial planning, while gig economy rates provide flexible, task-based earnings that fluctuate with demand. On-demand pay disbursement in gig work enables immediate access to earned wages, enhancing cash flow management compared to traditional fixed salary schedules.
Variable Earnings Stream
Variable earnings streams in the gig economy offer flexibility and the potential for higher income through task-based pay, contrasting with the predictable, fixed salary that provides stable, consistent monthly earnings. Gig workers face income volatility due to fluctuating demand and hours worked, making their earnings less reliable compared to fixed salary employees who benefit from guaranteed compensation regardless of workload changes.
Micro-Task Pay Rates
Fixed salary provides predictable income stability, while micro-task pay rates in the gig economy offer flexible but often variable earnings depending on task availability and complexity. Micro-task platforms typically pay between $0.05 to $5 per task, leading to inconsistent total income compared to steady monthly salaries.
Flexible Income Scheduling
Fixed salary provides predictable monthly income and financial stability, while gig economy rates offer flexible income scheduling that allows workers to choose when and how much they earn based on available projects or shifts. This flexibility supports varied work-life balance preferences but can result in irregular earnings compared to the consistency of a set salary.
Gig-to-Salary Conversion
Gig-to-salary conversion requires analyzing inconsistent hourly gig economy rates against stable fixed salary structures to determine reliable income comparability. Evaluating factors such as variable gig demand, benefits, and tax implications enhances accurate forecasting of annual earnings when transitioning from gig work to salaried employment.
Subscription-Based Compensation
Subscription-based compensation offers predictable, recurring income streams that blend the stability of fixed salaries with the flexibility of gig economy rates. This hybrid model enhances financial security for workers while allowing businesses to scale payments according to ongoing service demand.
fixed salary vs gig economy rates for income structure Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com