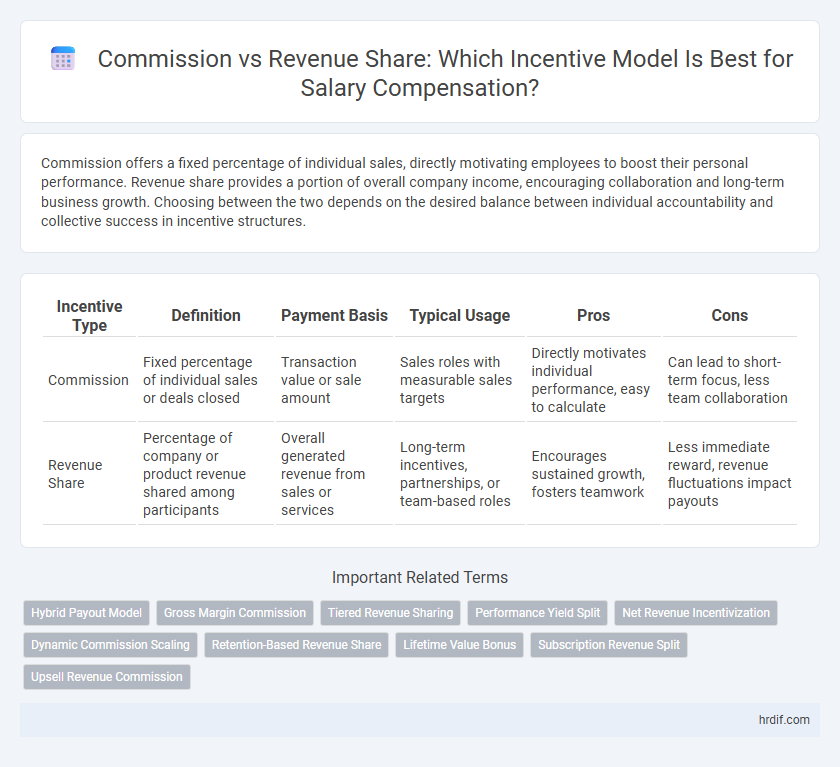
Commission offers a fixed percentage of individual sales, directly motivating employees to boost their personal performance. Revenue share provides a portion of overall company income, encouraging collaboration and long-term business growth. Choosing between the two depends on the desired balance between individual accountability and collective success in incentive structures.
Table of Comparison
| Incentive Type | Definition | Payment Basis | Typical Usage | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commission | Fixed percentage of individual sales or deals closed | Transaction value or sale amount | Sales roles with measurable sales targets | Directly motivates individual performance, easy to calculate | Can lead to short-term focus, less team collaboration |
| Revenue Share | Percentage of company or product revenue shared among participants | Overall generated revenue from sales or services | Long-term incentives, partnerships, or team-based roles | Encourages sustained growth, fosters teamwork | Less immediate reward, revenue fluctuations impact payouts |
Defining Commission and Revenue Share Incentives
Commission incentives involve a fixed percentage of sales revenue paid directly to employees based on their individual performance, creating a clear link between effort and earnings. Revenue share incentives distribute a portion of the company's total income among participants, aligning individual rewards with overall business success. Defining these incentives requires understanding their impact on motivation, sales behavior, and profitability to tailor compensation plans effectively.
Key Differences Between Commission and Revenue Share
Commission is typically a fixed percentage of individual sales generated by a salesperson, providing direct incentives tied to personal performance. Revenue share involves distributing a portion of overall company or product revenue among stakeholders, aligning incentives with collective business success. Commissions incentivize short-term sales targets, while revenue share promotes long-term growth and collaboration across teams.
Pros and Cons of Commission-Based Compensation
Commission-based compensation directly links employee earnings to sales performance, incentivizing high productivity and effort. It provides clear targets and motivates employees to close deals but can result in income instability and encourage aggressive selling tactics. Unlike revenue share models, commissions reward individual contributions more explicitly but may undermine teamwork and long-term customer relationships.
Pros and Cons of Revenue Share Models
Revenue share models align employee incentives with company growth, motivating individuals to drive long-term business success by earning a percentage of generated revenue. This approach fosters collaboration and encourages sustainable performance but may lead to unpredictable income fluctuations and challenges in attributing revenue accurately among team members. Companies must weigh the benefits of increased motivation and retention against the complexities of tracking revenue contributions and managing cash flow variability.
When Commission Incentives Work Best
Commission incentives work best in sales roles with clear, measurable transactions where individual performance directly drives revenue, such as retail or real estate. They motivate employees to exceed targets by tying compensation to specific sales outcomes, enhancing productivity and accountability. Commission structures excel when sales cycles are short and deal values are consistent, providing immediate financial rewards for sales success.
When to Choose Revenue Sharing Over Commissions
Revenue sharing is ideal when aligning long-term incentives with company growth, as it ties compensation directly to overall revenue performance rather than individual sales volume. It works well for collaborative environments where multiple employees contribute to revenue generation, promoting teamwork and shared goals. Revenue sharing is preferable in startups or businesses with volatile sales cycles, providing a more stable and motivating incentive than commissions.
Impact on Employee Motivation and Retention
Commission structures provide direct financial rewards tied to individual sales performance, significantly boosting employee motivation by offering clear incentives for exceeding targets. Revenue share models foster a sense of ownership and long-term commitment, enhancing retention by aligning employee interests with the company's overall financial success. Combining both approaches can create a balanced incentive system that drives immediate results while supporting sustained employee engagement.
Commission vs Revenue Share: Earning Potential
Commission structures offer direct earnings based on individual sales volume, providing clear, immediate incentives to maximize performance. Revenue share models distribute profits proportionally, aligning long-term success with overall business growth and fostering collaborative efforts. Choosing between commission and revenue share impacts earning potential by balancing short-term rewards with sustainable income streams.
Structuring Effective Incentive Plans
Commission-based incentives offer direct compensation tied to individual sales performance, ensuring clear motivation for employees to close deals. Revenue share models align employee rewards with overall company profitability, fostering long-term commitment and collaboration. Structuring effective incentive plans requires balancing immediate sales-driven commissions with revenue-sharing benefits to maximize both individual performance and sustained business growth.
Which Model Suits Your Business or Career Stage?
Commission suits sales-driven roles where individual performance directly impacts earnings, ideal for early career stages seeking clear motivation and growth opportunities. Revenue share benefits established businesses or professionals with recurring income streams, aligning incentives with long-term success and partnership growth. Choosing the right model depends on your business stability, growth phase, and desired risk-reward balance.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Payout Model
A hybrid payout model combines commission and revenue share to maximize employee incentives by aligning individual sales performance with overall company growth, offering fixed percentages from direct sales and a portion of recurring revenue streams. This approach drives motivation through immediate rewards and long-term passive income, fostering sustained engagement and increased profitability.
Gross Margin Commission
Gross Margin Commission bases incentives on the profitability of sales rather than total revenue, ensuring alignment with company profit goals and encouraging cost-effective sales strategies. This approach rewards sales teams for generating higher-margin sales, optimizing overall business performance and sustainable growth.
Tiered Revenue Sharing
Tiered revenue sharing offers a scalable incentive structure where earnings increase proportionally with sales performance, motivating sustained growth and higher revenue generation. Unlike fixed commissions, this model aligns employee rewards with company profitability by distributing a percentage of revenue across multiple tiers, enhancing long-term engagement and earning potential.
Performance Yield Split
Commission structures provide a fixed percentage of sales as direct incentive, ensuring predictable earnings tied to individual performance, while revenue share models distribute a portion of overall profits, aligning incentives with company growth and long-term success. Performance yield splits optimize motivation by balancing immediate rewards from commissions with sustained benefits from revenue sharing, maximizing both sales drive and collaborative enterprise value.
Net Revenue Incentivization
Net revenue incentivization through commission offers sales agents a fixed percentage of generated revenue, aligning compensation directly with performance. Revenue share models distribute earnings proportionally across stakeholders based on net revenue contribution, fostering long-term partnership growth and motivation.
Dynamic Commission Scaling
Dynamic commission scaling adjusts sales incentives based on revenue milestones, increasing commission percentages as sales targets grow to maximize motivation. This model aligns individual earnings with company revenue performance, creating a scalable and performance-driven compensation structure.
Retention-Based Revenue Share
Retention-based revenue share aligns employee incentives with long-term company growth by rewarding sustained customer retention rather than one-time transactions. This model enhances employee motivation and loyalty, driving steady revenue streams and reducing turnover costs compared to traditional commission structures.
Lifetime Value Bonus
Commission structures typically reward sales performance with fixed percentages per transaction, whereas revenue share incentives align earnings with ongoing customer payments, enhancing long-term motivation. Lifetime Value Bonus models further optimize incentives by rewarding sustained customer profitability, driving both acquisition and retention efforts in sales strategies.
Subscription Revenue Split
Commission structures typically provide a fixed percentage of sales as an incentive, while revenue share models allocate a portion of ongoing subscription revenue, encouraging long-term partner engagement. Subscription revenue splits align stakeholder interests by rewarding consistent growth and customer retention, driving sustainable income over transactional sales.
Upsell Revenue Commission
Upsell revenue commission structures incentivize sales teams by offering a percentage based on incremental revenue generated from existing customers, aligning motivation directly with company growth in upsell activities. Compared to fixed commissions, revenue share models for upsells drive higher performance by rewarding sales representatives proportionally to the increased customer lifetime value.
Commission vs Revenue Share for incentive. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com