Salary structures will need to evolve as Universal Basic Income (UBI) becomes more prominent, potentially redefining traditional employment compensation. Future jobs may offer hybrid models combining guaranteed UBI with performance-based salaries to ensure financial stability and motivation. This shift could reduce income inequality while encouraging innovation and flexibility in the workforce.
Table of Comparison
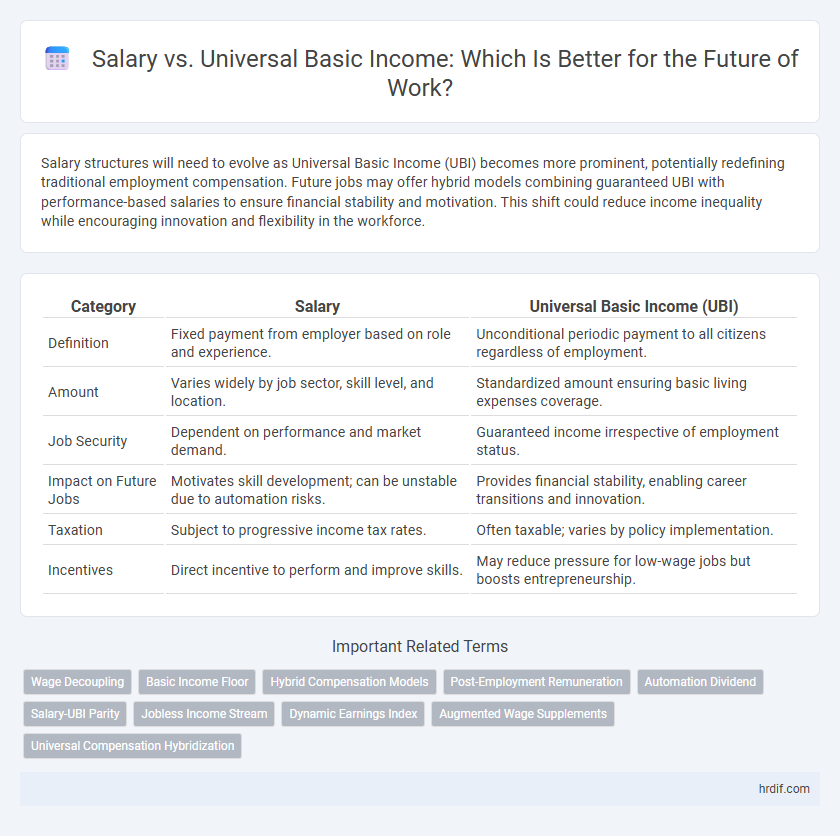
| Category | Salary | Universal Basic Income (UBI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed payment from employer based on role and experience. | Unconditional periodic payment to all citizens regardless of employment. |
| Amount | Varies widely by job sector, skill level, and location. | Standardized amount ensuring basic living expenses coverage. |
| Job Security | Dependent on performance and market demand. | Guaranteed income irrespective of employment status. |
| Impact on Future Jobs | Motivates skill development; can be unstable due to automation risks. | Provides financial stability, enabling career transitions and innovation. |
| Taxation | Subject to progressive income tax rates. | Often taxable; varies by policy implementation. |
| Incentives | Direct incentive to perform and improve skills. | May reduce pressure for low-wage jobs but boosts entrepreneurship. |
Comparing Salary Systems and Universal Basic Income
Salary systems incentivize individual performance and skill development by linking pay directly to job roles and responsibilities. Universal Basic Income (UBI) provides a fixed, unconditional payment to all citizens, aiming to reduce poverty and income inequality regardless of employment status. Comparing these models reveals that salary systems drive productivity and economic growth, while UBI offers financial security and flexibility in a rapidly evolving job market impacted by automation.
How UBI Could Transform Future Workforce Compensation
Universal Basic Income (UBI) could revolutionize future workforce compensation by providing a guaranteed financial baseline, reducing dependency on traditional salary structures. This shift may encourage innovation and entrepreneurship as individuals gain financial security without relying solely on job-based income. By decoupling income from employment, UBI has the potential to address job displacement caused by automation and AI, fostering a more resilient and adaptable economy.
The Pros and Cons of Traditional Salaries vs. UBI
Traditional salaries provide a stable income linked to specific job roles, ensuring predictable cash flow and incentivizing performance, but they can create financial insecurity during unemployment or job transitions. Universal Basic Income (UBI) offers a guaranteed minimum income regardless of employment, promoting economic security and reducing poverty, yet it may diminish work incentives and strain public budgets. Balancing the predictability of salaries with UBI's social safety nets presents a complex challenge for future labor markets and policy frameworks.
Economic Security: Salary Employment vs. Universal Basic Income
Salary employment provides consistent income tied to job performance, offering economic security through predictable wages and benefits like health insurance and retirement plans. Universal Basic Income delivers unconditional cash payments to all individuals, reducing poverty and income volatility but may lack the incentives that come with traditional employment. Evaluating economic security involves balancing guaranteed baseline support from UBI against the structured financial stability and growth potential provided by salaried jobs.
Impact on Career Choices: Salary Jobs or Guaranteed Income?
Salary jobs offer clear financial incentives tied to skill development and performance, influencing career choices toward specialized, high-demand industries. Universal Basic Income (UBI) provides a safety net that may encourage more risk-taking and entrepreneurship by decoupling income from employment. This shift in financial security could reshape job market dynamics, promoting innovation but potentially reducing the motivation for traditional salaried positions.
Flexibility and Stability: UBI Compared to Regular Salaries
Universal Basic Income offers greater financial flexibility than traditional salaries by providing a consistent income regardless of employment status, allowing individuals to pursue gig economy jobs and freelance work without the pressure of fixed monthly earnings. Regular salaries provide stability through predictable paychecks tied to a specific role but often lack adaptability to fluctuating market demands or personal career shifts. UBI's model supports economic resilience amid automation and changing job landscapes, enhancing freedom while maintaining a baseline financial security.
Incentivizing Innovation: Universal Basic Income or Salaried Roles?
Salaried roles provide targeted incentives by rewarding specific skills and productivity, driving innovation through performance-based motivation. Universal Basic Income (UBI) offers financial security that can encourage creative risk-taking by reducing economic pressure on individuals. Balancing UBI with salary structures may foster an environment where innovation thrives alongside stable economic support.
Adapting to Automation: Salary Structures vs. UBI Solutions
Adapting to automation, salary structures must evolve to address job displacement and income inequality by incorporating flexible compensation models and performance-based incentives. Universal Basic Income (UBI) offers a complementary solution by providing a guaranteed financial safety net, enabling individuals to pursue reskilling and entrepreneurship without the immediate pressure of job loss. Integrating adaptive salary frameworks with UBI programs can create a more resilient economic system that supports workers amid rapid technological changes.
Social Equity: Redefining Fair Pay with UBI and Salaries
Universal Basic Income (UBI) offers a foundational financial safety net, promoting social equity by ensuring minimum income regardless of job status, while traditional salaries continue to reflect skills and job performance. Integrating UBI can reduce income disparities, support marginalized communities, and address the unpredictability of automation-driven job markets. Redefining fair pay involves balancing UBI's unconditional support with merit-based salary structures to create a more inclusive and equitable economic future.
The Future of Work: Which Model Ensures Better Livelihoods?
Salary models provide predictable income based on skills and job performance, supporting financial stability for specialized roles in the evolving job market. Universal Basic Income (UBI) offers a safety net that addresses automation-displaced workers by guaranteeing a minimum income regardless of employment status. Evaluating the future of work indicates a hybrid approach combining stable salaries with UBI may best ensure economic security and livelihood resilience amid technological advances.
Related Important Terms
Wage Decoupling
Wage decoupling highlights the growing disparity between traditional salary structures and the implementation of Universal Basic Income (UBI) as automation and AI reshape future job markets. UBI offers a fixed income independent of employment status, potentially reducing reliance on fluctuating wages tied to increasingly automated roles.
Basic Income Floor
Universal Basic Income (UBI) provides a guaranteed basic income floor that ensures financial stability regardless of employment status, addressing the volatility of future job markets and automation risks. This income floor supplements or replaces fluctuating traditional salaries, offering a safety net that supports economic security and reduces poverty in evolving labor landscapes.
Hybrid Compensation Models
Hybrid compensation models blend traditional salary structures with Universal Basic Income (UBI) to address income stability amid evolving job markets driven by automation and gig economy growth. These models ensure a baseline financial security through UBI while rewarding performance and skills via variable salary components, enhancing workforce adaptability and motivation.
Post-Employment Remuneration
Post-employment remuneration through Universal Basic Income (UBI) offers a stable financial foundation independent of traditional salary structures, addressing job displacement caused by automation and gig economy shifts. This model ensures consistent income security, reducing economic volatility often associated with intermittent or contract-based employment.
Automation Dividend
Automation Dividend offers a transformative approach to income distribution by reallocating wealth generated from automated systems, potentially surpassing traditional salary models in stability and inclusivity. This mechanism ensures equitable financial support regardless of job automation, mitigating employment displacement and promoting economic resilience.
Salary-UBI Parity
Salary-UBI parity addresses the balance between fixed wages and guaranteed income, ensuring financial stability as automation reshapes job markets. An optimized salary structure combined with Universal Basic Income can mitigate income inequality while supporting workforce adaptability and economic resilience.
Jobless Income Stream
Universal Basic Income (UBI) offers a stable jobless income stream that can supplement or replace traditional salaries, addressing income insecurity amid increasing automation and job displacement. By providing consistent financial support, UBI enables individuals to sustain basic needs without relying solely on employment-based salaries.
Dynamic Earnings Index
The Dynamic Earnings Index tracks fluctuations in salary trends relative to Universal Basic Income (UBI) proposals, highlighting potential shifts in worker compensation models as automation and gig economy roles expand. As future jobs evolve, this index underscores how variable earnings may complement or challenge fixed UBI schemes in maintaining economic stability for diverse labor sectors.
Augmented Wage Supplements
Augmented Wage Supplements are designed to bridge the gap between traditional salary structures and Universal Basic Income, providing targeted financial support that adapts to evolving job markets influenced by automation and AI. This model ensures workers receive a baseline income from UBI while augmenting earnings based on skill development, productivity, and job complexity, promoting economic stability and workforce adaptability.
Universal Compensation Hybridization
Universal Compensation Hybridization integrates fixed salaries with Universal Basic Income (UBI) to create a flexible income framework that ensures financial stability amid automation and evolving job markets. This approach balances traditional paycheck structures with guaranteed baseline earnings, fostering economic security and encouraging workforce adaptability in future employment landscapes.
Salary vs Universal Basic Income for future jobs Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com