Salary offers consistent monthly income and benefits, providing financial stability for freelancers prioritizing predictability. Gig income varies significantly based on project availability and client demand, appealing to those seeking flexibility and diverse work opportunities. Balancing salary and gig income can optimize earnings while managing risk in a freelance career.
Table of Comparison
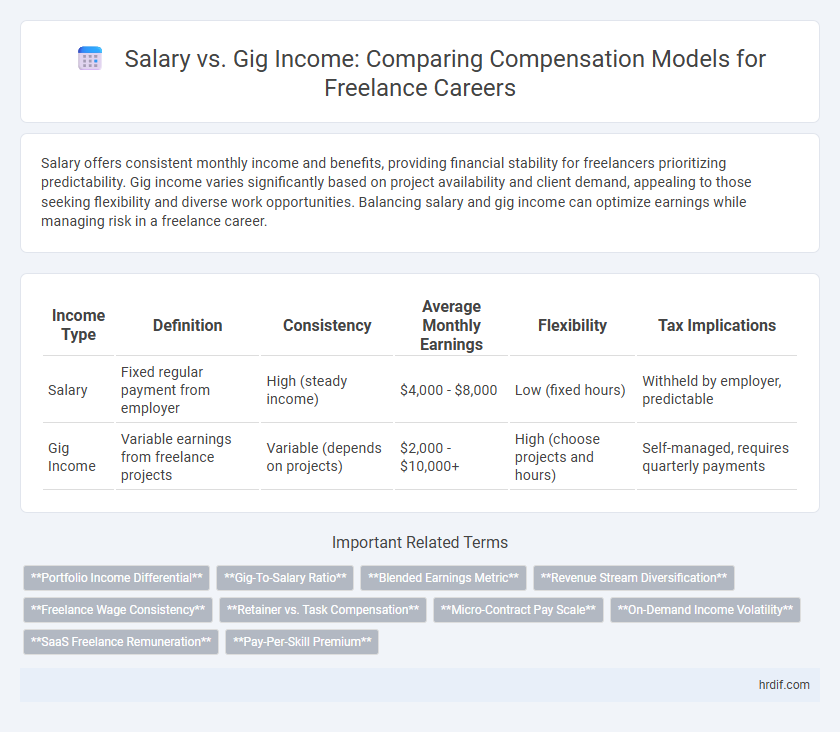
| Income Type | Definition | Consistency | Average Monthly Earnings | Flexibility | Tax Implications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salary | Fixed regular payment from employer | High (steady income) | $4,000 - $8,000 | Low (fixed hours) | Withheld by employer, predictable |
| Gig Income | Variable earnings from freelance projects | Variable (depends on projects) | $2,000 - $10,000+ | High (choose projects and hours) | Self-managed, requires quarterly payments |
Understanding Salary and Gig Income: Key Differences
Salary provides a consistent and predictable income with fixed payments typically issued monthly or biweekly, offering financial stability and benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Gig income varies significantly based on project availability, client demand, and workload, often lacking traditional employee benefits but allowing greater flexibility and control over work schedules. Freelancers must balance the security of a salaried job against the potential earnings and independence offered by gig work, considering factors like tax implications and income volatility.
Financial Stability: Salary Jobs vs Gig Work
Salaried positions offer consistent monthly income and benefits like healthcare and retirement plans, providing financial stability essential for long-term planning. Gig income varies widely based on project availability and market demand, leading to irregular cash flow and increased financial uncertainty. Freelancers balancing gig work may require robust budgeting strategies and emergency funds to mitigate income volatility.
Flexibility and Control Over Earnings
Freelance careers offer greater flexibility and control over earnings compared to traditional salaried positions, allowing individuals to set their own rates and choose projects that fit their schedules. Gig income fluctuates based on workload and demand, providing opportunities to increase earnings through multiple clients and diversified tasks. Salary roles provide consistent income but lack the adaptability and earning potential tied directly to effort and market conditions inherent in freelance work.
Predictability of Income: Pros and Cons
Salary offers predictable, consistent income through fixed paychecks, enabling easier financial planning and stability for freelancers. Gig income varies greatly based on project availability and client demand, resulting in fluctuating earnings that can challenge budgeting and long-term financial security. However, gig income flexibility allows freelancers to scale work volume and potentially increase overall earnings during high-demand periods.
Benefits and Deductions: What’s Included?
Salary income typically includes benefits such as health insurance, retirement contributions, and paid leave, with automatic tax deductions like Social Security and Medicare withheld by the employer. Gig income from freelance careers usually lacks these employer-provided benefits, requiring freelancers to manage their own health coverage, retirement savings, and estimated tax payments. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurately comparing net earnings and overall financial security between salaried and gig-based work.
Tax Implications for Salaried Employees and Gig Workers
Salaried employees often face predictable tax withholdings and employer-managed deductions, simplifying year-end filing but potentially limiting deductibility options. Gig workers encounter complex tax obligations, including self-employment taxes and quarterly estimated payments, requiring meticulous record-keeping of income and business expenses to maximize deductions. Understanding differences in tax treatment between W-2 income and 1099 earnings is crucial for optimizing tax liability in freelance careers.
Career Growth: Climbing the Ladder vs Building a Portfolio
Salary-based careers offer structured career growth through clear promotion paths and incremental raises, providing long-term financial stability and professional development. Gig income in freelance careers emphasizes building a diverse portfolio and client base, fostering entrepreneurial skills and flexibility but often lacking predictable upward progression. Focusing on salary supports steady advancement within established organizations, while gig income prioritizes self-driven growth and varied project experience.
Work-Life Balance: Steady Job or Flexible Gigs?
Steady salaries provide consistent income that supports predictable budgeting and financial stability, fostering a balanced work-life routine essential for freelancers prioritizing security. Gig income offers flexible scheduling, allowing freelancers to tailor work hours around personal commitments but can introduce income variability that challenges long-term planning. Choosing between salary and gig income hinges on balancing financial predictability with the desire for scheduling freedom in freelance careers.
Job Security: Traditional Employment vs Freelance Uncertainty
Traditional employment offers consistent salary payments and job security through benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, providing financial stability for workers. Freelance careers, reliant on gig income, experience fluctuating earnings with uncertain client demand and no guaranteed benefits, increasing financial risk for freelancers. Understanding these contrasts is crucial for professionals weighing stable income against flexible but unpredictable gig opportunities.
Long-Term Financial Planning: Salary vs Gig Income
Long-term financial planning favors stable salaried positions due to predictable income, consistent benefits, and retirement contributions offered by employers. Gig income, while potentially lucrative short-term, often lacks financial security and complicates budgeting for expenses like healthcare, taxes, and retirement savings. Freelancers relying on gig income must implement rigorous saving strategies and diversify income streams to achieve financial stability comparable to salaried employees.
Related Important Terms
Portfolio Income Differential
Portfolio income differential highlights the variability between stable salary earnings and fluctuating gig income in freelance careers, where portfolio income often depends on diverse project completions and client payments. Freelancers experience higher income volatility compared to salaried employees, as their earnings from gig work rely on inconsistent job availability and portfolio performance.
Gig-To-Salary Ratio
The Gig-To-Salary Ratio measures the proportion of income freelancers earn from gig work compared to a traditional salary, highlighting financial stability and earning potential within freelance careers. A higher ratio indicates greater reliance on gig income, influencing budgeting strategies and long-term financial planning for independent professionals.
Blended Earnings Metric
The Blended Earnings Metric combines both salary and gig income to provide a comprehensive view of a freelancer's total earnings, capturing the variability and flexibility inherent in independent careers. This metric enables more accurate financial planning and benchmarking by integrating stable salary components with fluctuating gig revenues.
Revenue Stream Diversification
Freelancers benefit from revenue stream diversification by combining steady salary income with variable gig earnings, reducing financial risk and increasing overall income stability. Balancing a fixed salary with multiple gig opportunities enhances cash flow flexibility and mitigates reliance on a single income source.
Freelance Wage Consistency
Freelance wage consistency often fluctuates compared to salaried positions due to the variable nature of project availability and client demand, impacting predictable monthly income. Salary offers steady, reliable payments that provide financial stability absent in gig-based freelance careers.
Retainer vs. Task Compensation
Retainer compensation provides freelancers with predictable, recurring income by securing ongoing work from clients, while task-based pay offers flexibility through payments per individual project or assignment. Opting for retainers often ensures financial stability and long-term client relationships, whereas task compensation allows greater control over workload and the potential to maximize earnings per completed task.
Micro-Contract Pay Scale
Micro-contract pay scales in freelance careers often result in variable gig income, typically ranging from $50 to $500 per project depending on the industry and complexity, contrasting with fixed monthly salaries that provide stable and predictable earnings. Freelancers managing multiple micro-contracts can accumulate an income comparable to or exceeding traditional salaries, but income volatility remains a significant challenge.
On-Demand Income Volatility
Freelance careers face significant on-demand income volatility compared to traditional salaries, as gig income fluctuates based on project availability and client demand. This variability challenges consistent financial planning and often requires freelancers to build substantial savings or diversify income streams to manage lean periods effectively.
SaaS Freelance Remuneration
SaaS freelance remuneration often surpasses traditional salary due to its performance-based pricing models and ongoing subscription revenues, enabling freelancers to scale income through multiple client contracts simultaneously. Unlike fixed salaries, gig income in SaaS freelancing fluctuates with customer acquisition and retention metrics, rewarding expertise in product customization and value delivery.
Pay-Per-Skill Premium
Freelancers command a pay-per-skill premium, often earning significantly more than traditional salaried employees by leveraging specialized expertise in high-demand niches. This targeted compensation model rewards proficiency and adaptability, enabling gig workers to maximize income through project-based engagements rather than fixed salaries.
Salary vs Gig Income for freelance careers Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com