Market rate salaries are determined by industry standards and competitive benchmarks, reflecting the value of a position regardless of location. Geo-adjusted salaries account for regional cost-of-living differences, aiming to provide equitable purchasing power across various geographic areas. Balancing these approaches is crucial for pay standardization to ensure fairness while attracting and retaining talent in diverse markets.
Table of Comparison
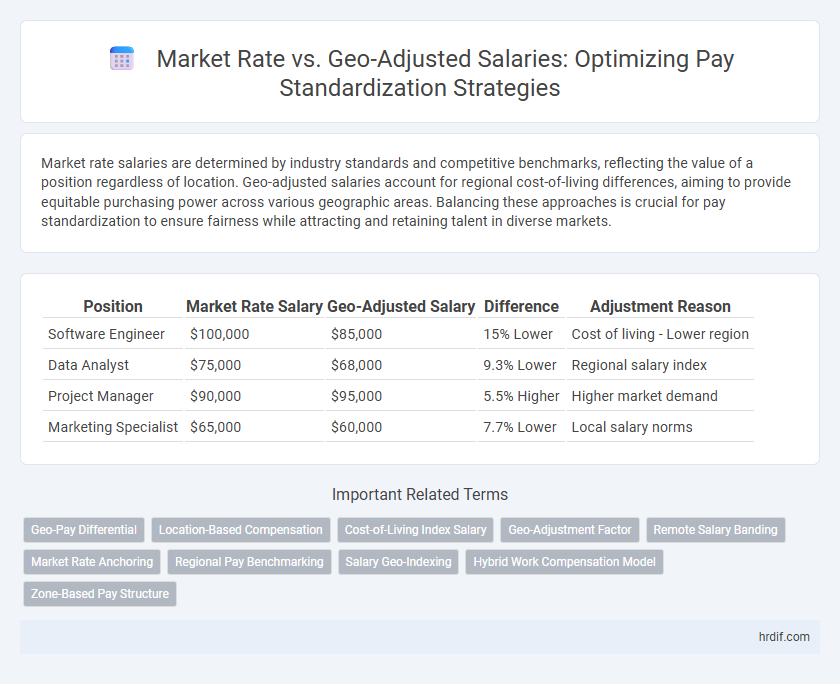
| Position | Market Rate Salary | Geo-Adjusted Salary | Difference | Adjustment Reason |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Software Engineer | $100,000 | $85,000 | 15% Lower | Cost of living - Lower region |
| Data Analyst | $75,000 | $68,000 | 9.3% Lower | Regional salary index |
| Project Manager | $90,000 | $95,000 | 5.5% Higher | Higher market demand |
| Marketing Specialist | $65,000 | $60,000 | 7.7% Lower | Local salary norms |
Understanding Market Rate and Geo-Adjusted Salaries
Market rate salaries reflect compensation benchmarks based on industry standards and role-specific demand within a broader economic region, ensuring competitive pay aligned with talent availability. Geo-adjusted salaries modify these base rates considering local cost of living, housing, and economic conditions to maintain equitable purchasing power across different locations. Understanding the distinction between market rate and geo-adjusted salaries is crucial for organizations aiming to standardize pay while attracting and retaining talent in diverse geographic regions.
Why Companies Use Market Rate Salary Benchmarks
Companies use market rate salary benchmarks to align employee compensation with industry standards, ensuring competitiveness in talent acquisition and retention. These benchmarks reflect the typical pay for specific roles within a given market, helping organizations maintain equity and avoid underpaying or overpaying staff. Market rate data supports informed salary decisions by accounting for supply and demand trends, regional cost of living, and economic conditions.
The Case for Geo-Adjusted Pay Structures
Geo-adjusted pay structures align salaries with local cost of living and economic conditions, promoting equitable compensation across diverse regions. Market rate salaries often overlook regional disparities, leading to overpayment in low-cost areas and underpayment in high-cost locations. Implementing geo-adjusted pay ensures competitive, fair, and sustainable salary standards that attract and retain talent effectively.
Key Differences: Market Rate vs. Geo-Adjusted Salaries
Market rate salaries are determined by industry standards and competitor pay within a specific job market, reflecting the true value of skills and experience regardless of location. Geo-adjusted salaries modify these base figures according to the cost of living and economic conditions in different geographic areas to maintain equity and affordability. This differentiation ensures pay standardization aligns with both market competitiveness and regional financial realities.
Pros and Cons of Market Rate Compensation
Market rate compensation aligns salaries with industry standards, attracting top talent by offering competitive pay based on skill and experience levels. It simplifies budgeting and salary benchmarking but may overlook cost-of-living variations, potentially disadvantaging employees in high-expense areas. This approach can lead to geographic pay disparities, impacting employee satisfaction and retention in diverse locations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Geo-Adjusted Salaries
Geo-adjusted salaries offer the advantage of aligning employee pay with local living costs, promoting fairness in diverse economic regions and aiding companies in managing payroll budgets effectively. This approach can lead to challenges such as potential employee dissatisfaction in high-cost areas or talent retention issues in lower-cost regions where pay may feel inadequate compared to market rates. Balancing geo-adjusted pay with market rate standards is essential to maintain competitive compensation, employee motivation, and equitable workforce distribution.
Impact on Employee Attraction and Retention
Market rate salaries reflect the average compensation for specific roles within an industry, while geo-adjusted salaries account for regional cost of living differences to ensure fair pay. Offering geo-adjusted salaries enhances employee attraction by providing competitive, location-appropriate compensation that aligns with local economic conditions. This approach improves retention by demonstrating equity and recognizing individual financial needs, reducing turnover in diverse geographic locations.
Equity and Fairness in Salary Standardization
Market rate salaries reflect the average compensation for specific roles within an industry, while geo-adjusted salaries account for local cost of living variations to maintain equity across regions. Pay standardization strategies integrating both approaches ensure fairness by balancing competitive market compensation with geographic economic realities. This alignment reduces disparities and supports consistent employee valuation regardless of location.
Implementing Pay Standardization Across Locations
Implementing pay standardization across locations requires balancing market rate data with geo-adjusted salary benchmarks to ensure equitable compensation. Companies leveraging comprehensive geographic cost-of-living indexes and regional market salary surveys can optimize pay structures while maintaining competitiveness and fairness. Integrating these insights supports consistency in employee compensation, reduces pay disparities, and enhances talent retention globally.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Salary Standardization
Market rate salaries are increasingly being blended with geo-adjusted pay models to address cost-of-living disparities while maintaining competitive compensation. Future trends indicate the rise of hybrid salary frameworks leveraging AI-driven analytics to balance local economic factors with global talent market demands. Such evolution aims to standardize pay more equitably across regions, enhancing employee retention and organizational agility.
Related Important Terms
Geo-Pay Differential
Geo-pay differentials adjust salaries based on regional cost of living and labor market conditions, ensuring equitable compensation aligned with local economic realities. This approach balances market rate benchmarks with geographic salary variations, promoting fair pay standardization across diverse locations.
Location-Based Compensation
Market rate salaries reflect prevailing wages within specific industries but often overlook regional cost-of-living differences, while geo-adjusted salaries tailor compensation based on location to ensure equitable pay standards. Incorporating location-based compensation strategies enhances talent retention by aligning salaries with local economic conditions and living expenses.
Cost-of-Living Index Salary
Market rate salaries reflect industry standards based on job roles and experience, while geo-adjusted salaries incorporate the Cost-of-Living Index to align compensation with regional expenses, ensuring pay equity across diverse locations. Utilizing geo-adjusted salaries helps companies standardize pay by balancing market competitiveness with local economic conditions, reducing employee turnover and promoting financial fairness.
Geo-Adjustment Factor
Geo-adjustment factors modify salaries based on regional cost-of-living variations to ensure equitable compensation across different locations, reflecting local economic conditions rather than solely market rates. Incorporating geo-adjusted salaries helps organizations maintain competitive pay standards while addressing disparities caused by geographic cost differences.
Remote Salary Banding
Remote salary banding leverages geo-adjusted salaries to align compensation with local cost-of-living variations while maintaining competitiveness within the global market rate framework. This approach ensures equitable pay standards by balancing regional economic factors and industry benchmarks, optimizing talent acquisition and retention in distributed workforce environments.
Market Rate Anchoring
Market rate anchoring establishes salary benchmarks based on industry-specific compensation data, ensuring competitive pay aligned with skills and experience. This approach promotes pay equity by standardizing salaries according to prevailing market conditions rather than geographic location variations.
Regional Pay Benchmarking
Regional pay benchmarking is critical for maintaining competitive and equitable salaries by aligning compensation with localized market rates and economic conditions. Geo-adjusted salaries account for cost of living variations, ensuring pay standardization that reflects regional purchasing power and attracts top talent across diverse locations.
Salary Geo-Indexing
Salary geo-indexing adjusts compensation based on regional cost of living metrics, ensuring pay aligns with local market rates and economic conditions. This approach promotes equitable pay standards by balancing national salary benchmarks with geographic cost variations to attract and retain talent across diverse locations.
Hybrid Work Compensation Model
Market rate salaries reflect industry standards based on role and experience, while geo-adjusted salaries account for cost-of-living differences across locations to ensure equitable pay. The hybrid work compensation model blends these approaches by setting base salaries aligned with market rates and adjusting pay based on employees' geographic location and remote work patterns, promoting both fairness and competitiveness.
Zone-Based Pay Structure
Market rate salaries reflect the prevailing compensation levels in a specific industry and role, while geo-adjusted salaries account for cost-of-living variations across different locations, ensuring equitable pay standards. A zone-based pay structure categorizes regions into distinct zones with tailored salary bands, optimizing compensation fairness and operational budgeting across geographic areas.
Market Rate vs Geo-adjusted Salaries for pay standardization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com