Onsite employees benefit from direct face-to-face collaboration, immediate access to resources, and a structured work environment that fosters team cohesion. Distributed employees enjoy greater flexibility, reduced commute times, and access to a wider talent pool, enhancing productivity through personalized workspaces. Balancing onsite and distributed work models requires clear communication strategies and technology infrastructure to maintain engagement and performance across diverse locations.
Table of Comparison
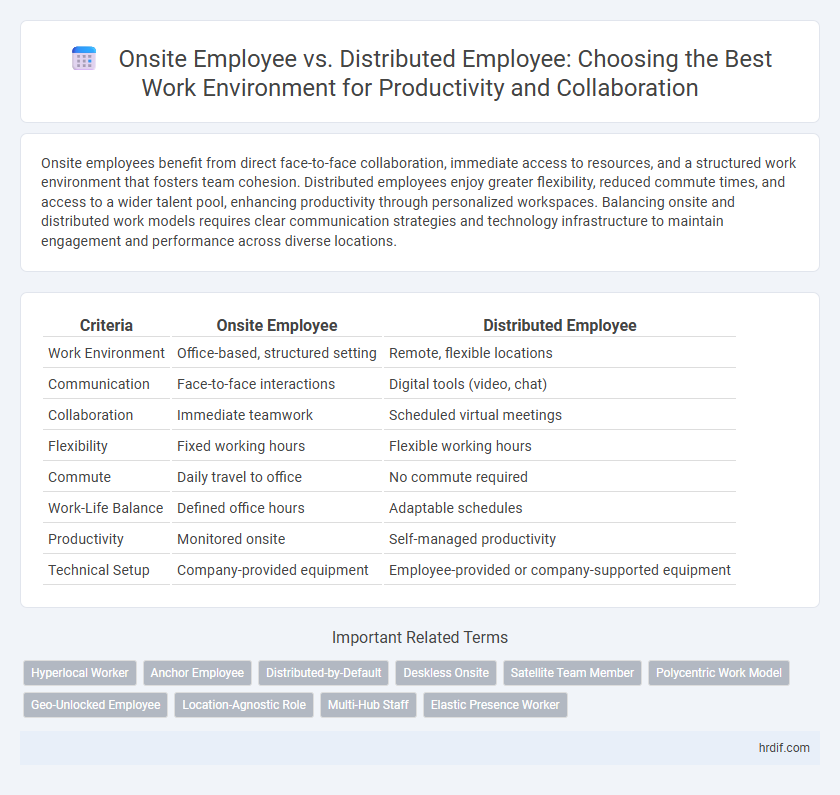
| Criteria | Onsite Employee | Distributed Employee |
|---|---|---|
| Work Environment | Office-based, structured setting | Remote, flexible locations |
| Communication | Face-to-face interactions | Digital tools (video, chat) |
| Collaboration | Immediate teamwork | Scheduled virtual meetings |
| Flexibility | Fixed working hours | Flexible working hours |
| Commute | Daily travel to office | No commute required |
| Work-Life Balance | Defined office hours | Adaptable schedules |
| Productivity | Monitored onsite | Self-managed productivity |
| Technical Setup | Company-provided equipment | Employee-provided or company-supported equipment |
Defining Onsite and Distributed Employees
Onsite employees work at a physical company location, engaging in face-to-face collaboration and utilizing on-premises resources that support immediate communication and teamwork. Distributed employees operate remotely from various geographic locations, leveraging digital tools and cloud-based platforms to maintain productivity and connectivity across different time zones. Defining these roles highlights the structural and technological distinctions influencing workflow, communication strategies, and management approaches within modern work environments.
Key Differences in Work Environment
Onsite employees benefit from direct access to physical office resources, face-to-face collaboration, and a structured daily routine that fosters immediate communication and team cohesion. Distributed employees enjoy flexible work hours, reduced commute times, and greater autonomy but may face challenges in synchronous interaction and maintaining work-life boundaries. The onsite environment typically supports real-time problem solving, whereas distributed setups rely heavily on digital tools and self-motivation to sustain productivity.
Productivity: Onsite vs Distributed Teams
Onsite employees benefit from immediate access to resources and direct collaboration, often resulting in faster decision-making and enhanced team synergy. Distributed employees leverage flexible schedules and diverse talent pools, which can boost productivity through personalized work environments and reduced commute times. Productivity in both setups depends heavily on effective communication tools, clear goals, and organizational support tailored to each work environment.
Communication and Collaboration Challenges
Onsite employees benefit from face-to-face interactions, enabling immediate feedback and spontaneous collaboration, which streamlines communication and decision-making. Distributed employees face challenges such as time zone differences, reliance on digital tools, and potential miscommunication, requiring intentional strategies to maintain synergy and inclusivity. Effective communication platforms and clear protocols become critical to bridging gaps and fostering teamwork in distributed work environments.
Impact on Employee Engagement and Wellbeing
Onsite employees often benefit from direct social interactions and immediate access to resources, which can enhance their engagement and sense of belonging, contributing positively to their wellbeing. Distributed employees experience greater flexibility and autonomy, leading to improved work-life balance but may face challenges such as isolation and communication barriers that can affect their emotional health. Organizations implementing hybrid models must prioritize inclusive communication strategies and mental health support to maintain high engagement and wellbeing across both onsite and distributed workforces.
Technology and Infrastructure Requirements
Onsite employees require robust physical infrastructure, including high-speed wired internet, secured local servers, and dedicated workstations optimized for productivity. Distributed employees depend heavily on cloud-based collaboration platforms, virtual private networks (VPNs), and reliable home-office setups equipped with secure remote access tools to maintain seamless communication and data protection. Both environments necessitate advanced cybersecurity measures, but distributed models prioritize endpoint security and bandwidth stability to support real-time collaboration across varying networks.
Management Styles for Onsite and Distributed Teams
Management styles for onsite employees emphasize direct supervision, face-to-face communication, and immediate feedback to foster collaboration and maintain productivity within a physical workspace. Distributed employee management requires leveraging digital tools for asynchronous communication, trust-based autonomy, and results-oriented performance tracking to accommodate remote work environments. Effective management balances clear goal-setting and regular virtual check-ins to ensure alignment and engagement across distributed teams.
Recruitment and Talent Pool Access
Onsite employees offer structured collaboration and immediate access to office resources, streamlining recruitment by targeting local talent pools. Distributed employees expand access to a diverse global talent pool, enabling companies to recruit specialized skills regardless of geographic limitations. Balancing onsite and distributed hiring enhances talent acquisition strategies by combining localized expertise with broad-based skill availability.
Cost Implications for Employers
Onsite employees often incur higher cost implications for employers due to expenses related to office space, utilities, and physical resources. Distributed employees reduce overhead costs but may require investment in remote work technology and cybersecurity measures. Employers must balance these financial factors with productivity and collaboration needs when deciding between onsite and distributed workforce models.
Future Trends in Work Environments
Future trends in work environments indicate a growing shift towards hybrid models combining onsite and distributed employees, leveraging advanced collaboration technologies like virtual reality and AI-driven communication tools. Employers prioritize flexibility and employee well-being, recognizing that distributed teams increase access to global talent pools while onsite work fosters stronger team cohesion and innovation through face-to-face interactions. Data from Gartner predicts that by 2025, 70% of organizations will adopt hybrid work models, balancing productivity with employee satisfaction in a rapidly evolving workforce landscape.
Related Important Terms
Hyperlocal Worker
Onsite employees benefit from immediate collaboration and access to physical resources, fostering team cohesion within a centralized location, while distributed employees prioritize flexibility, working remotely across diverse geographic regions. Hyperlocal workers combine these advantages by operating remotely but within a specific local area, enabling quick onsite engagement when necessary and supporting localized business needs efficiently.
Anchor Employee
Anchor employees in onsite work environments foster stronger team cohesion and immediate collaboration, enhancing productivity through face-to-face interactions and real-time problem-solving. Distributed employees offer flexibility and access to a wider talent pool, but anchor employees provide the critical in-person presence that stabilizes company culture and drives seamless communication.
Distributed-by-Default
Distributed-by-default employees leverage flexible, remote work environments that enhance productivity, reduce commuting time, and broaden access to global talent pools, fostering diverse and inclusive teams. This model utilizes cloud-based collaboration tools, prioritizes asynchronous communication, and supports work-life balance, making it a sustainable approach for modern organizations.
Deskless Onsite
Deskless onsite employees typically perform tasks requiring physical presence, such as frontline service or manufacturing roles, benefiting from immediate access to equipment and real-time communication with supervisors. Distributed employees, often remote, rely on digital tools and virtual collaboration, which may limit hands-on engagement but increase flexibility and reduce commuting constraints.
Satellite Team Member
Satellite team members, as a subset of distributed employees, work remotely from various geographic locations while maintaining close collaboration through digital tools, enhancing organizational flexibility and talent diversification. Unlike onsite employees who operate within a central physical office, satellite employees leverage technology to contribute effectively without requiring daily physical presence, optimizing both work-life balance and operational efficiency.
Polycentric Work Model
The Polycentric Work Model emphasizes local autonomy, positioning onsite employees within centralized offices to leverage face-to-face collaboration, while distributed employees operate remotely across diverse regions to access localized talent and adapt to specific market needs. Balancing onsite and distributed workforces under this model enhances organizational flexibility, promotes cultural alignment, and improves productivity by tailoring work environments to regional employee strengths and preferences.
Geo-Unlocked Employee
Geo-unlocked employees leverage flexible geographic locations to enhance productivity and access diverse talent pools, contrasting onsite employees who are confined to a physical office space. This distributed work model supports dynamic collaboration across time zones, fostering innovation and operational agility.
Location-Agnostic Role
Onsite employees typically benefit from immediate access to office resources and face-to-face collaboration, enhancing team dynamics and real-time problem solving, while distributed employees in location-agnostic roles leverage digital tools and flexible schedules to increase productivity and job satisfaction across diverse geographical areas. Companies adopting location-agnostic roles optimize talent acquisition by removing geographic constraints, promoting inclusivity, and reducing overhead costs associated with physical office spaces.
Multi-Hub Staff
Multi-hub staff leverage a blend of onsite and distributed employee models to optimize collaboration, combining the benefits of physical office presence with remote flexibility across multiple geographic locations. This strategy enhances productivity by enabling seamless communication and resource sharing while accommodating diverse work preferences and local market dynamics.
Elastic Presence Worker
Elastic Presence Workers adapt seamlessly between onsite and remote environments, leveraging flexible workspaces and digital collaboration tools to maintain productivity and engagement. Their elastic presence optimizes resource allocation by balancing in-office interactions with distributed work, enhancing both team cohesion and individual autonomy.
Onsite Employee vs Distributed Employee for work environment Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com