Job seekers actively pursue new employment opportunities and are readily available for interviews, while passive talent is currently employed and not actively looking but may consider new offers if approached. Understanding the distinction between these candidate statuses helps employers tailor their recruitment strategies to engage each group effectively. Passive talent often requires personalized outreach and relationship-building, whereas job seekers respond well to direct job postings and immediate openings.
Table of Comparison
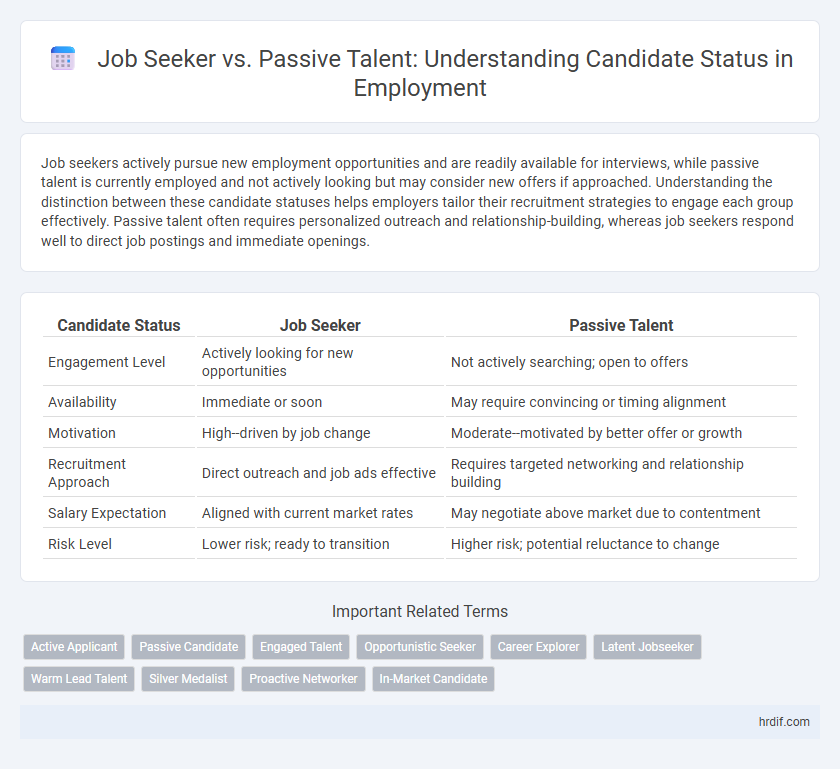
| Candidate Status | Job Seeker | Passive Talent |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement Level | Actively looking for new opportunities | Not actively searching; open to offers |
| Availability | Immediate or soon | May require convincing or timing alignment |
| Motivation | High--driven by job change | Moderate--motivated by better offer or growth |
| Recruitment Approach | Direct outreach and job ads effective | Requires targeted networking and relationship building |
| Salary Expectation | Aligned with current market rates | May negotiate above market due to contentment |
| Risk Level | Lower risk; ready to transition | Higher risk; potential reluctance to change |
Defining Job Seekers and Passive Talent
Job seekers actively pursue new employment opportunities by applying for jobs, attending interviews, and regularly updating their resumes on job platforms. Passive talent, on the other hand, is currently employed and not actively looking but remains open to new career opportunities if approached with the right offer. Understanding the distinction helps recruiters target candidates effectively by tailoring engagement strategies to the individual's job search behavior and professional status.
Key Differences Between Job Seekers and Passive Talent
Job seekers actively pursue new employment opportunities through applications and interviews, displaying a high level of engagement and urgency. Passive talent, conversely, is currently employed and not actively looking but may consider offers if approached with compelling opportunities. Understanding these distinctions helps recruiters tailor sourcing strategies to effectively attract and engage each candidate type.
Motivations: What Drives Job Seekers vs Passive Talent
Job seekers are primarily motivated by the urgency to secure employment, higher salaries, and career growth opportunities, often actively applying to multiple positions. Passive talent, while not actively looking, is driven by factors such as job satisfaction, work-life balance, and compelling offers that align with their long-term career goals. Understanding these motivations helps recruiters tailor their approach, addressing immediate needs for job seekers and leveraging personalized engagement for passive candidates.
Sourcing Strategies for Each Candidate Status
Job seekers actively apply for roles, making targeted job boards and career fairs effective sourcing strategies to quickly access motivated candidates. Passive talent, not currently seeking new opportunities, requires strategic networking, personalized outreach, and leveraging employee referrals to uncover hidden potential. Tailoring sourcing methods enhances engagement and improves recruitment outcomes for both candidate statuses.
Engagement Techniques for Active vs Passive Candidates
Active job seekers respond well to direct job postings, personalized outreach, and detailed role descriptions that highlight growth opportunities and company culture. Passive talent requires relationship-building engagement through networking events, social media interactions, and targeted content that showcases employer brand value and long-term career prospects. Utilizing data-driven talent analytics can optimize engagement strategies by tailoring communication based on candidate activity levels and professional interests.
Benefits of Hiring Job Seekers vs Passive Talent
Hiring job seekers offers immediate availability and openness to new opportunities, which accelerates the recruitment process and reduces hiring downtime. Passive talent, while often possessing higher expertise and industry experience, may require more time and resources to engage and convince to transition. Employers benefit from job seekers' readiness to adapt quickly, whereas passive talent brings innovation potential and long-term value through deep organizational knowledge.
Challenges in Attracting Passive Talent
Attracting passive talent presents challenges as these candidates are not actively seeking new opportunities and may have limited engagement with job platforms. Employers must leverage personalized outreach, employer branding, and targeted networking to capture their interest. The difficulty lies in identifying and persuading passive talent to consider a transition despite current job satisfaction.
Matching Employer Expectations with Candidate Status
Job seekers actively pursue new opportunities, aligning their skills and experience with employer expectations for immediate availability and engagement. Passive talent, while not actively looking, often matches higher-level roles or niche skills that employers prioritize for strategic growth. Effective matching involves understanding the candidate's current employment status to tailor recruitment approaches and meet organizational needs precisely.
The Role of Employer Branding in Talent Attraction
Employer branding significantly influences whether job seekers or passive talent engage with a company as potential candidates. Strong employer branding attracts active job seekers by showcasing compelling career opportunities and company culture, while also enticing passive talent by building trust and recognition even when they are not actively searching. Prioritizing authentic employee experiences and consistent messaging enhances talent attraction across both candidate statuses.
Optimizing Recruitment Approaches for Diverse Candidates
Understanding the distinction between job seekers actively pursuing opportunities and passive talent not currently looking is crucial for optimizing recruitment strategies. Tailoring outreach to passive talent through personalized engagement and employer branding enhances access to high-quality candidates who may not respond to traditional job postings. Leveraging data-driven insights and targeted communication increases recruitment efficiency and diversifies candidate pools by addressing the unique motivations of both active and passive candidates.
Related Important Terms
Active Applicant
Active applicants actively pursue job opportunities by regularly applying to open positions, showcasing updated resumes, and engaging with recruiters. Unlike passive talent, who remains employed and not actively searching, active job seekers demonstrate higher availability and immediate interest in new employment options.
Passive Candidate
Passive candidates possess valuable industry experience and are often currently employed, making them less likely to respond to traditional job postings but highly sought after for strategic talent acquisition. Employers targeting passive talent leverage personalized outreach and talent relationship management to engage these individuals who may not actively seek new opportunities yet represent a high potential for retention and growth.
Engaged Talent
Engaged talent represents candidates who are actively participating in talent communities or employer branding activities, bridging the gap between job seekers actively applying and passive talent not currently pursuing new opportunities. Companies leveraging engaged talent strategies witness higher retention and faster hiring cycles by nurturing relationships with individuals showing interest but not actively job hunting.
Opportunistic Seeker
Opportunistic seekers are job candidates who selectively explore new opportunities without actively searching, balancing current employment stability with potential career advancements. Their status contrasts with active job seekers who pursue roles aggressively, making opportunistic talent valuable for strategic recruitment targeting timely engagement and personalized offers.
Career Explorer
Career explorers seek roles aligning with growth and skill development, often maintaining active job search status, contrasting with passive talent who stay employed but open to opportunities discreetly. Understanding this distinction helps employers tailor recruitment strategies to engage dynamic career explorers effectively.
Latent Jobseeker
Latent jobseekers, often classified under passive talent, are employees not actively applying for jobs but open to new opportunities when approached, representing a crucial segment for recruiters targeting high-quality candidates. Understanding the distinction between active job seekers and latent jobseekers helps organizations tailor engagement strategies to attract top talent who may not appear in traditional applicant pools.
Warm Lead Talent
Warm Lead Talent represents candidates who have shown interest but are not actively seeking new opportunities, blending qualities of both job seekers and passive talent. These individuals offer high engagement potential and can be nurtured through personalized communication to convert into successful hires.
Silver Medalist
Silver Medalist candidates represent a unique status between active Job Seekers and Passive Talent, as they have demonstrated strong potential but were not selected initially and remain open to new opportunities. Employers targeting Silver Medalists can leverage this group's proven skills and familiarity with the company, reducing recruitment time and cost compared to engaging passive talent without prior assessment.
Proactive Networker
Proactive networkers as job seekers actively engage in industry events and online platforms to uncover new opportunities, demonstrating high motivation and readiness for change. In contrast, passive talent typically remains employed and less visible, relying on recruiters or internal referrals, yet proactive networkers maintain continuous relationship-building to access hidden job markets.
In-Market Candidate
In-market candidates actively seeking new job opportunities demonstrate higher engagement and readiness to transition compared to passive talent, who are currently employed and not openly exploring roles but may respond to compelling offers. Companies targeting in-market candidates often experience shorter hiring cycles and improved retention rates due to the candidates' proactive job search behavior and clear availability.
Job Seeker vs Passive Talent for candidate status Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com