Permanent employees benefit from job security, consistent income, and company-provided benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Gig workers enjoy flexibility, the ability to choose projects, and often experience varied work environments, but they face income instability and lack employer-sponsored benefits. Businesses must weigh the advantages of a stable, committed workforce against the agility and cost-effectiveness provided by gig workers.
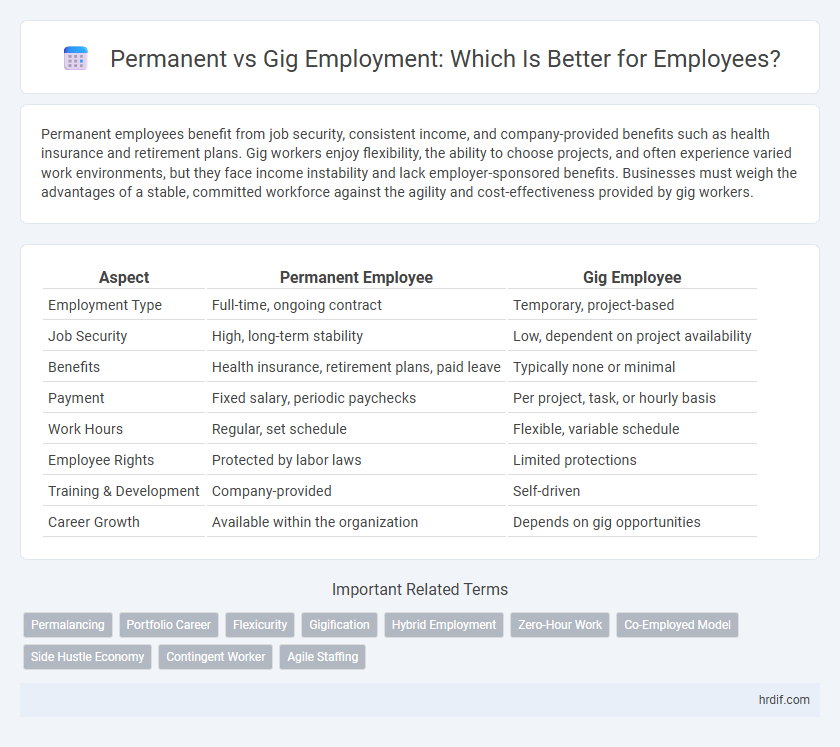
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Permanent Employee | Gig Employee |
|---|---|---|
| Employment Type | Full-time, ongoing contract | Temporary, project-based |
| Job Security | High, long-term stability | Low, dependent on project availability |
| Benefits | Health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave | Typically none or minimal |
| Payment | Fixed salary, periodic paychecks | Per project, task, or hourly basis |
| Work Hours | Regular, set schedule | Flexible, variable schedule |
| Employee Rights | Protected by labor laws | Limited protections |
| Training & Development | Company-provided | Self-driven |
| Career Growth | Available within the organization | Depends on gig opportunities |
Understanding Permanent Employment
Permanent employment offers employees job security with a fixed salary, benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave. It often involves long-term commitment to one organization, fostering career growth and skill development within a stable work environment. Understanding the stability and legal protections associated with permanent roles helps workers make informed career decisions.
Defining Gig Work in Today’s Market
Gig work in today's market refers to short-term, flexible, and project-based employment where individuals perform tasks or services for multiple clients or platforms without long-term commitments. Unlike permanent employment, gig workers often lack traditional benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, making financial and job security primary considerations. The rise of digital platforms has significantly expanded gig work opportunities, enabling a diverse workforce seeking autonomy and varied income streams.
Job Security: Permanent vs Gig Roles
Permanent roles provide greater job security with consistent income, benefits, and long-term career growth opportunities. Gig roles offer flexibility and variety but come with income unpredictability and limited access to benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Employees in permanent positions typically experience more stability, while gig workers face higher risks of job discontinuity.
Work-Life Balance in Both Models
Permanent employees typically benefit from a structured schedule and consistent income, which fosters a more stable work-life balance. Gig workers experience flexible hours that allow greater control over when and where they work, though income unpredictability can impact personal planning. Both models require careful management of time and resources to maintain a healthy balance between professional responsibilities and personal life.
Career Growth Opportunities Compared
Permanent employees often benefit from structured career growth opportunities, including promotions, professional development programs, and mentorship within the organization. Gig workers face limited long-term advancement prospects due to the temporary nature of contracts and the absence of formal career development pathways. Companies typically invest more in skill enhancement and internal mobility for permanent staff compared to gig workers.
Income Stability: Which Offers More?
Permanent employees benefit from consistent monthly salaries, providing reliable income stability and easier financial planning. Gig workers face fluctuating earnings due to irregular project availability, which can lead to income unpredictability and financial uncertainty. Employers often offer benefits and job security to permanent staff, further enhancing income consistency compared to gig roles.
Benefits and Perks: What Employees Get
Permanent employees typically receive comprehensive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave, and job security, which provide long-term financial stability and well-being. Gig workers often lack these traditional perks but gain flexibility in work hours and project choices, catering to diverse lifestyle needs. Employers offer permanent staff additional perks like professional development programs and performance bonuses that gig roles usually do not include.
Flexibility and Autonomy Differences
Permanent employees typically experience less flexibility in work hours and location due to fixed schedules and company policies, whereas gig workers enjoy greater autonomy by choosing projects, setting their own schedules, and working remotely. This autonomy allows gig workers to balance personal commitments and adapt work intensity based on individual preference. However, permanent roles often provide structured career development and stability that gig roles may lack.
Skills Development in Each Path
Permanent employees benefit from structured training programs and long-term skill development aligned with company goals, fostering deep expertise and career growth. Gig workers develop versatile, diverse skills by engaging in varied projects across industries, enhancing adaptability and rapid learning. Both paths offer unique opportunities for skills expansion, but permanent roles emphasize specialization while gig work prioritizes flexibility and broad experience.
Choosing the Right Fit for Your Career
Permanent employment offers stability, consistent income, and benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, making it ideal for career growth and long-term financial security. Gig work provides flexibility, diverse project experiences, and independence, appealing to those seeking variety and control over their schedule. Evaluating personal priorities, risk tolerance, and career goals helps determine whether a permanent role or gig opportunities align best with an individual's professional aspirations.
Related Important Terms
Permalancing
Permanent employees benefit from job security, consistent income, and employee benefits, while gig workers enjoy flexibility and diverse project opportunities; permalancing combines these advantages by allowing professionals to take on long-term, predictable freelance assignments that offer stability without traditional employment constraints. This emerging work model supports sustainable career growth by blending the independence of gig work with the reliability of permanent roles.
Portfolio Career
A portfolio career combines multiple gig roles and permanent positions, offering employees diversified income streams and skills development while ensuring flexibility and job security. This approach enables workers to balance stability from permanent employment with the autonomy and variety found in gig work, enhancing overall career resilience.
Flexicurity
Permanent employees benefit from job security and consistent income, while gig workers enjoy greater flexibility and autonomy; flexicurity policies aim to balance these by combining flexible labor markets with social security and active labor market policies to protect workers in both arrangements. This approach enhances adaptability, ensuring continuous employment opportunities and social protection regardless of contract type.
Gigification
Gigification transforms traditional employment by shifting roles from permanent contracts to flexible, project-based gigs, enabling companies to optimize workforce scalability and reduce long-term commitments. This trend accelerates the rise of freelance platforms and digital marketplaces, redefining the employee experience with an emphasis on autonomy, variable income, and skill-based task allocation.
Hybrid Employment
Hybrid employment combines the stability of permanent roles with the flexibility of gig work, allowing employees to balance consistent income and job security with diverse project opportunities. This model enhances workforce adaptability, optimizes talent utilization, and supports organizational agility in rapidly changing markets.
Zero-Hour Work
Zero-hour contracts, common in gig employment, provide flexibility but often lack guaranteed income and benefits, contrasting with permanent employees who receive stable pay, job security, and entitlement to employment rights. The rise of zero-hour work underlines the need for regulatory frameworks to protect worker rights while accommodating business needs in evolving labor markets.
Co-Employed Model
The Co-Employed Model blends benefits of permanent employment with the flexibility of gig work by engaging workers through a third-party employer of record, ensuring compliance with labor laws and mitigating risks for the hiring company. This hybrid approach optimizes workforce management by providing gig workers access to benefits and job security typical of permanent employees while maintaining operational agility.
Side Hustle Economy
Permanent employees benefit from stable income and traditional benefits, while gig workers in the side hustle economy enjoy flexible schedules and diverse income streams. The rise of gig platforms has transformed workforce dynamics, enabling employees to supplement earnings through freelance or part-time engagements without leaving permanent roles.
Contingent Worker
Contingent workers, including gig employees, offer flexible staffing solutions without long-term commitments, contrasting with permanent employees who provide stability and continuity through fixed contracts and benefits. Organizations leveraging contingent labor can quickly scale workforce capacity to meet fluctuating demands while managing costs more effectively than maintaining a fully permanent staff.
Agile Staffing
Agile staffing maximizes workforce flexibility by balancing permanent employees who ensure stability and institutional knowledge with gig workers who provide on-demand skills and rapid scalability. This dynamic approach enhances business responsiveness, reduces talent acquisition time, and optimizes labor costs in fluctuating market conditions.
Permanent vs Gig for employee. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com