Full-time employees offer consistent availability and deeper integration within company culture, ensuring long-term commitment and alignment with business goals. Fractional employees provide specialized expertise on a part-time basis, allowing flexibility and cost-efficiency for projects requiring niche skills without the overhead of full employment. Choosing between full-time and fractional employees depends on the organization's need for ongoing support versus targeted, short-term contributions.
Table of Comparison
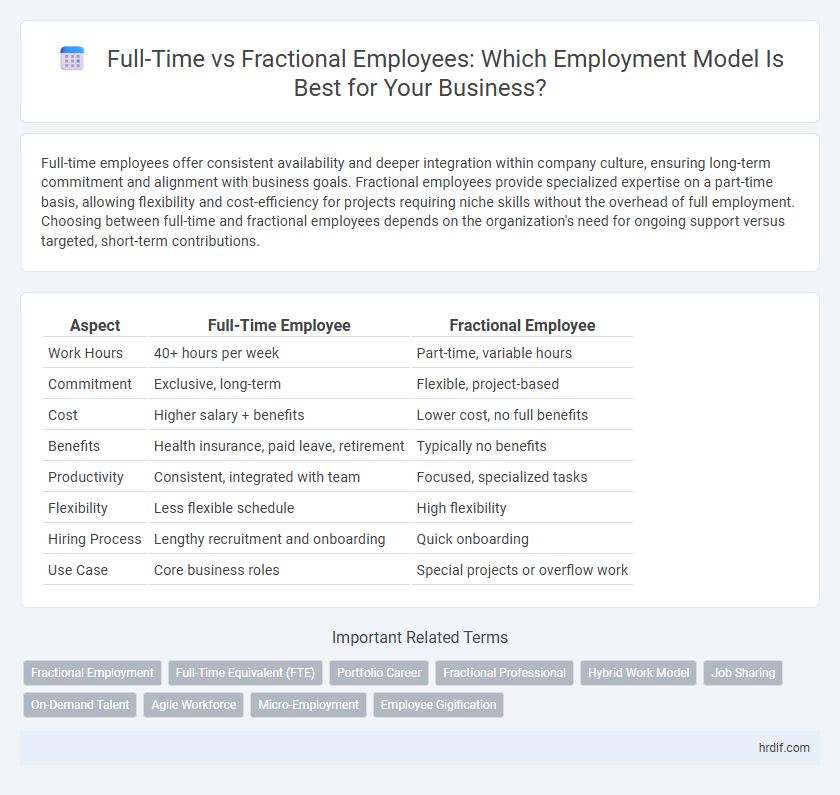
| Aspect | Full-Time Employee | Fractional Employee |
|---|---|---|
| Work Hours | 40+ hours per week | Part-time, variable hours |
| Commitment | Exclusive, long-term | Flexible, project-based |
| Cost | Higher salary + benefits | Lower cost, no full benefits |
| Benefits | Health insurance, paid leave, retirement | Typically no benefits |
| Productivity | Consistent, integrated with team | Focused, specialized tasks |
| Flexibility | Less flexible schedule | High flexibility |
| Hiring Process | Lengthy recruitment and onboarding | Quick onboarding |
| Use Case | Core business roles | Special projects or overflow work |
Understanding Full-Time Employment
Full-time employment typically involves working 35 to 40 hours per week with access to comprehensive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave. Employers often prefer full-time employees for their long-term commitment and consistent productivity, supporting business stability and growth. Understanding the legal implications of full-time status, including labor laws and tax obligations, is crucial for both employers and employees.
What Is Fractional Employment?
Fractional employment refers to a work arrangement where employees dedicate a portion of their time to a company, often balancing multiple roles across different organizations, unlike full-time employment that demands exclusive, continuous work hours. This model provides flexibility and cost-efficiency for businesses seeking specialized skills without the commitment of full-time salaries and benefits. Fractional employees typically focus on specific projects or strategic roles, enabling companies to scale expertise on demand while maintaining operational agility.
Key Benefits of Full-Time Roles
Full-time employees benefit from consistent income, comprehensive health insurance, and paid leave, which enhance financial stability and well-being. They often receive career development opportunities, such as training programs and promotions, fostering long-term growth within the company. Employers also tend to offer full-time roles greater job security and retirement plans, increasing overall employee satisfaction and loyalty.
Advantages of Fractional Positions
Fractional employees offer businesses increased flexibility and cost-efficiency by enabling access to specialized skills without the expenses associated with full-time salaries and benefits. This arrangement supports scaling workforce capacity according to project demands, reducing overhead while maintaining high productivity. Companies benefit from diverse expertise and improved adaptability in a dynamic market, making fractional roles ideal for strategic growth.
Job Security: Full-Time vs Fractional
Full-time employees benefit from greater job security due to consistent work hours, comprehensive benefits, and employment contracts that provide legal protections. Fractional employees work on a part-time or project basis, resulting in less stability and limited access to benefits, which can increase the risk of job loss. Employers often prioritize full-time roles for long-term retention, making them a more secure option compared to fractional employment.
Work-Life Balance Comparison
Full-time employees often experience structured work hours, which can lead to consistent routines but may limit flexibility, impacting work-life balance. Fractional employees benefit from flexible schedules that allow better management of personal and professional commitments, enhancing overall satisfaction. Studies show fractional roles reduce burnout rates by 30% compared to traditional full-time positions.
Compensation and Benefits Differences
Full-time employees typically receive a comprehensive benefits package including health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and bonuses, reflecting their consistent work schedule and full salary. Fractional employees, working part-time or on a project basis, often receive prorated compensation with limited or no access to company-sponsored benefits, focusing primarily on hourly or project-based pay rates. The disparity in compensation and benefits directly impacts employee retention, job satisfaction, and overall financial security within the workforce.
Career Growth Opportunities
Full-time employees often benefit from more robust career growth opportunities due to consistent access to training programs, mentorship, and internal promotions. Fractional employees may experience limited advancement prospects because their part-time involvement reduces exposure to organizational development initiatives. Companies typically invest more in full-time staff for long-term skill development, enhancing their potential for leadership roles.
Skills Development and Learning
Full-time employees often benefit from structured training programs and continuous professional development opportunities that foster long-term skill enhancement. Fractional employees, working part-time or on specific projects, can gain specialized skills through focused assignments and diverse industry exposure. Organizations leveraging both employment types can optimize skill development by balancing depth with breadth in learning experiences.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Career
Choosing between full-time and fractional employment depends on your career goals and lifestyle preferences. Full-time roles offer stability, benefits, and opportunities for advancement, while fractional positions provide flexibility, diverse project experience, and work-life balance. Assess your professional priorities to determine which employment type aligns best with your long-term career growth.
Related Important Terms
Fractional Employment
Fractional employment offers companies flexible access to specialized skills without the costs associated with full-time salaries, allowing for scalable workforce management. This model caters to project-based roles and part-time commitments, optimizing productivity while minimizing overhead expenses.
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE)
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) quantifies employee workload by comparing part-time hours to a full-time schedule, standardizing labor measurement across full-time and fractional employees. Utilizing FTE metrics enables businesses to optimize staffing efficiency, budget accurately, and align workforce capacity with organizational needs.
Portfolio Career
Full-time employees typically focus on a single employer with consistent hours and benefits, whereas fractional employees distribute their skills across multiple projects or companies, enabling a diverse portfolio career. This approach increases expertise in various industries, enhances flexibility, and supports income diversification for professionals pursuing dynamic career growth.
Fractional Professional
Fractional professionals offer businesses flexible, part-time expertise, enabling access to specialized skills without the cost of a full-time salary and benefits. This model allows companies to scale talent based on project needs, optimizing budget efficiency and fostering innovation through diverse expert input.
Hybrid Work Model
Full-time employees in a hybrid work model typically maintain consistent on-site and remote hours, ensuring full integration within company culture and team dynamics. Fractional employees, working part-time or project-based schedules, offer flexibility and cost efficiency while supporting specific business needs without full-time commitments.
Job Sharing
Job sharing allows two full-time employees to split one full-time position, providing flexibility and work-life balance without reducing overall productivity. Employers benefit from diverse skill sets and continuous coverage, while employees gain flexibility and shared responsibilities within a full-time framework.
On-Demand Talent
Full-time employees provide consistent availability and deeper integration into company culture, while fractional employees offer on-demand talent solutions that optimize costs and flexibility for specialized projects. Businesses leveraging fractional experts benefit from scalable workforce capabilities and targeted expertise without the long-term commitments of full-time hires.
Agile Workforce
Full-time employees provide consistent availability and deep organizational knowledge, essential for maintaining a stable Agile workforce focused on rapid delivery and team cohesion. Fractional employees offer specialized skills and flexible capacity, enabling Agile teams to scale adaptively while optimizing talent costs and project-specific needs.
Micro-Employment
Micro-employment offers a flexible alternative to traditional full-time roles by allowing employees to work fractional hours tailored to specific projects or tasks, maximizing productivity and cost efficiency. This model supports diverse workforce participation and enables businesses to scale talent dynamically without the commitments of full-time employment.
Employee Gigification
Full-time employees provide consistent availability and in-depth company knowledge, while fractional employees offer specialized skills and flexibility for project-based needs, driving agility in the evolving workplace landscape. The gigification of employment emphasizes on-demand talent, enabling businesses to scale workforce capabilities efficiently without long-term commitments.
Full-time vs Fractional for employee. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com