W2 employees receive consistent wages with taxes withheld by their employer, offering greater job security and access to benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Platform-based employees operate as independent contractors, managing their own taxes and lacking employee benefits, but they enjoy increased flexibility and control over their work schedule. Understanding the distinctions between W2 employment and platform-based roles is crucial for making informed career decisions and optimizing tax strategies.
Table of Comparison
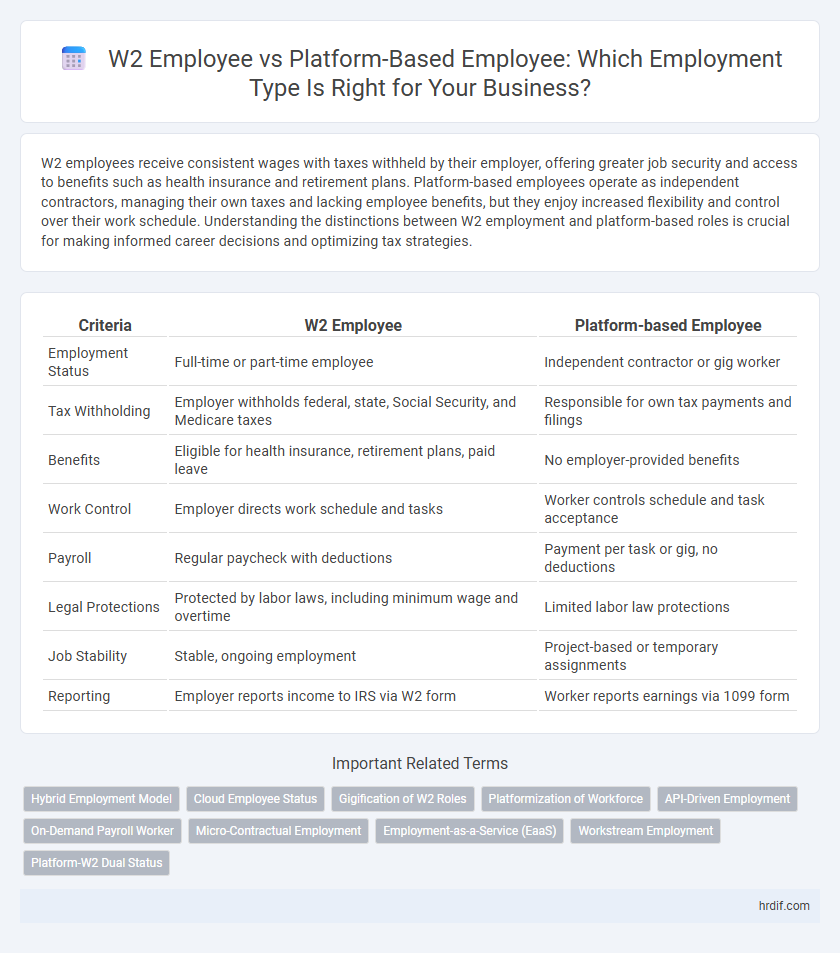
| Criteria | W2 Employee | Platform-based Employee |
|---|---|---|
| Employment Status | Full-time or part-time employee | Independent contractor or gig worker |
| Tax Withholding | Employer withholds federal, state, Social Security, and Medicare taxes | Responsible for own tax payments and filings |
| Benefits | Eligible for health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave | No employer-provided benefits |
| Work Control | Employer directs work schedule and tasks | Worker controls schedule and task acceptance |
| Payroll | Regular paycheck with deductions | Payment per task or gig, no deductions |
| Legal Protections | Protected by labor laws, including minimum wage and overtime | Limited labor law protections |
| Job Stability | Stable, ongoing employment | Project-based or temporary assignments |
| Reporting | Employer reports income to IRS via W2 form | Worker reports earnings via 1099 form |
Defining W2 Employees and Platform-Based Employees
W2 employees are individuals directly hired by a company, receiving a W-2 tax form that reflects employer-paid taxes, benefits, and wage withholding, ensuring consistent labor law protections and payroll administration. Platform-based employees work through digital platforms or gig economy services, often classified as independent contractors, responsible for their own taxes and lacking traditional employee benefits and legal protections. The distinction between W2 and platform-based employment impacts tax obligations, worker rights, and company liabilities.
Key Differences in Employment Structure
W2 employees have a traditional employment structure with fixed salaries, tax withholdings, and benefits administered by the employer, ensuring legal protections and consistent work schedules. Platform-based employees operate as independent contractors, often managing their own taxes and lacking standard benefits, with payment tied directly to tasks or projects completed via digital platforms. This distinction affects job security, control over work, and compliance with labor regulations.
Compensation: Salary vs. Gig Payments
W2 employees receive a fixed salary with guaranteed benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, ensuring financial stability and predictable income. Platform-based employees earn gig payments based on tasks completed, offering flexibility but with variable income and limited access to traditional employment benefits. The choice between these employment types impacts compensation structure, job security, and financial predictability for workers.
Benefits and Perks Comparison
W2 employees typically receive comprehensive benefits including health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and unemployment protection, which are mandated by employers and regulated by labor laws. Platform-based employees, classified often as independent contractors, generally lack access to standard benefits and must secure their own insurance, retirement savings, and absence coverage. The disparity in benefits impacts financial security, workplace stability, and tax obligations, making W2 employment preferable for those prioritizing structured support and legal protections.
Tax Obligations and Withholding
W2 employees have tax obligations managed by their employer, including automatic withholding of federal, state, and Social Security taxes, ensuring compliance without additional burden. Platform-based employees, often classified as independent contractors, must handle their own tax obligations by paying estimated quarterly taxes and self-employment taxes, increasing the complexity of tax management. The distinction impacts withholding responsibilities and tax reporting requirements, making employer-controlled W2 status more straightforward in payroll compliance.
Job Security and Stability
W2 employees benefit from consistent salaries, comprehensive benefits, and legal protections, ensuring greater job security and stability compared to platform-based employees. Platform-based employees often face variable income, lack of traditional benefits, and fewer legal safeguards, resulting in less predictable employment conditions. Employers and workers prioritize job stability when choosing between W2 employment and gig platform arrangements.
Flexibility and Work-Life Balance
W2 employees often experience more structured work hours and defined roles, which can limit flexibility but provide predictable income and benefits. Platform-based employees enjoy greater control over their schedules, enhancing work-life balance by allowing them to choose projects and work times suited to personal needs. However, this flexibility may come with variable income and fewer traditional employment protections.
Career Growth Opportunities
W2 employees typically benefit from structured career growth opportunities through formal training programs, mentorship, and clear promotion paths within the organization. Platform-based employees often face limited career advancement due to the gig economy's focus on task completion rather than long-term development. Employers offering W2 status tend to invest more in employee skill development, leading to enhanced career progression and stability.
Legal Protections and Workers’ Rights
W2 employees benefit from comprehensive legal protections, including minimum wage, overtime pay, unemployment insurance, and workers' compensation, ensured by federal and state labor laws. Platform-based employees, often classified as independent contractors, typically lack these protections and are excluded from benefits like health insurance, paid leave, and collective bargaining rights. This classification significantly impacts job security and workers' rights, as W2 status mandates employer compliance with labor standards, while platform workers face limited legal safeguards.
Choosing the Right Employment Type
Choosing the right employment type involves evaluating the benefits and limitations of W2 employees versus platform-based employees. W2 employees receive consistent wages, tax withholdings, and access to company benefits such as healthcare, retirement plans, and paid leave, which provide financial security and legal protections. In contrast, platform-based employees often enjoy flexible schedules and freelance opportunities but lack traditional benefits and face variable income and tax responsibilities.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Employment Model
The hybrid employment model blends the stability of W2 employees, who receive benefits and tax withholdings, with the flexibility of platform-based employees, allowing companies to optimize workforce scalability and compliance. This approach leverages the advantages of both employment types by offering core workers traditional employment protections while engaging platform-based talent for project-specific or gig tasks.
Cloud Employee Status
W2 employees receive consistent payroll, benefits, and tax withholding directly from their employer, ensuring full compliance with IRS regulations for cloud workforce management. Platform-based employees operate as independent contractors through digital platforms, offering flexibility but requiring separate tax filings and lacking traditional employment benefits.
Gigification of W2 Roles
W2 employees typically receive consistent wages, benefits, and tax withholdings managed by a single employer, while platform-based employees operate as independent contractors engaging in gig work through online platforms, offering flexibility but less job security. The gigification of W2 roles blends the stability of traditional employment with the flexibility of gig economy models, enabling employers to adapt workforce needs dynamically while providing employees with varied work opportunities.
Platformization of Workforce
Platform-based employees experience increased flexibility and task variety through digital platforms that connect them directly with employers, reshaping traditional employment models. This platformization of the workforce leverages technology to optimize labor allocation, often shifting responsibilities and benefits typically associated with W2 employees to the platform providers.
API-Driven Employment
W2 employees receive standardized payroll processing, tax withholdings, and benefits managed directly by the employer, ensuring compliance and stability within traditional employment frameworks. Platform-based employees leverage API-driven employment solutions enabling seamless integration of work assignments, real-time contract automation, and transparent payment processing, optimizing workforce management across decentralized platforms.
On-Demand Payroll Worker
W2 employees receive regular wages with tax withholding and benefits, ensuring compliance with labor laws, while platform-based on-demand payroll workers operate as independent contractors, offering flexibility but often lacking standard employment protections and benefits. Choosing between these employment types impacts payroll management, tax responsibilities, and worker classification under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA).
Micro-Contractual Employment
Micro-contractual employment offers flexible work arrangements compared to traditional W2 employee status, enabling platform-based employees to engage in short-term, task-specific roles without long-term commitments. Unlike W2 employees who receive standardized benefits and tax withholdings, platform-based micro-contractors manage their own taxes and lack employer-provided benefits, emphasizing autonomy but requiring proactive financial planning.
Employment-as-a-Service (EaaS)
Employment-as-a-Service (EaaS) leverages platform-based employee models to provide flexible workforce solutions, contrasting with traditional W2 employee arrangements that involve direct employer control and standardized benefits. Platform-based employees benefit from on-demand engagement and scalable labor pools, optimizing operational efficiency for businesses seeking agile employment types.
Workstream Employment
W2 employees under Workstream Employment receive consistent payroll processing, tax withholding, and benefits administration directly managed by the employer, ensuring compliance with labor laws and streamlined HR operations. Platform-based employees operate as independent contractors, lacking traditional employee benefits and tax withholdings, offering businesses flexibility but requiring careful classification to avoid legal risks.
Platform-W2 Dual Status
Platform-W2 dual status employees benefit from both W2 employment stability, including tax withholding and benefits, and platform-based flexibility, enabling access to diverse gig opportunities. This hybrid model optimizes workforce adaptability and compliance, balancing employer control with independent contractor autonomy.
W2 Employee vs Platform-based Employee for employment type Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com