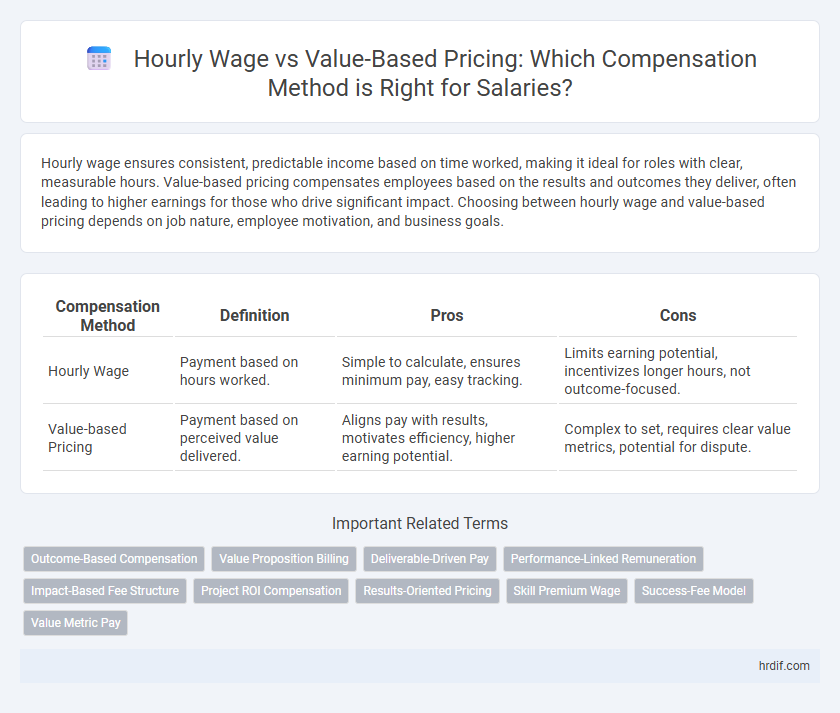
Hourly wage ensures consistent, predictable income based on time worked, making it ideal for roles with clear, measurable hours. Value-based pricing compensates employees based on the results and outcomes they deliver, often leading to higher earnings for those who drive significant impact. Choosing between hourly wage and value-based pricing depends on job nature, employee motivation, and business goals.
Table of Comparison
| Compensation Method | Definition | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hourly Wage | Payment based on hours worked. | Simple to calculate, ensures minimum pay, easy tracking. | Limits earning potential, incentivizes longer hours, not outcome-focused. |
| Value-based Pricing | Payment based on perceived value delivered. | Aligns pay with results, motivates efficiency, higher earning potential. | Complex to set, requires clear value metrics, potential for dispute. |
Understanding Hourly Wage Compensation
Hourly wage compensation provides a straightforward payment model based on the exact number of hours worked, ensuring consistent income for employees and easy tracking for employers. This method benefits workers in roles where time commitment is critical, such as retail, healthcare, and customer service industries. Understanding hourly wage structures allows businesses to manage labor costs effectively while offering employees a predictable earnings framework.
What is Value-Based Pricing in Careers?
Value-based pricing in careers sets compensation based on the employee's contribution to the company's value rather than hourly work hours, aligning pay with measurable outcomes and business impact. This method incentivizes productivity and innovation by rewarding skills, expertise, and the quality of results over time spent on tasks. Employers adopting value-based pricing often see higher employee motivation and retention due to direct correlation between performance and earnings.
Key Differences Between Hourly Wage and Value-Based Pricing
Hourly wage compensates employees based on the exact time spent on tasks, providing predictable income but limiting earning potential to hours worked. Value-based pricing rewards professionals according to the perceived value or outcome delivered, often leading to higher income variability tied to project success. Key differences include payment structure, risk distribution between worker and client, and incentive alignment toward efficiency and results rather than time spent.
Pros and Cons of Hourly Wage Compensation
Hourly wage compensation offers straightforward pay based on actual hours worked, providing transparency and simplicity for both employers and employees. This method ensures consistent income but may discourage efficiency since earnings are tied directly to time rather than output or results. However, hourly wages lack flexibility in rewarding high performance or incentivizing innovation compared to value-based pricing models.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing aligns compensation with the actual value delivered to clients, promoting motivation for high-quality work and client satisfaction. This method can lead to higher earnings for employees when their contributions directly enhance business outcomes, but it carries the risk of income variability and challenges in accurately measuring value. Unlike hourly wage compensation, value-based pricing incentivizes efficiency and innovation but requires clear metrics and strong negotiation skills to implement effectively.
Choosing the Right Compensation Method for Your Career
Choosing between hourly wage and value-based pricing significantly impacts career growth and financial outcomes. Hourly wage ensures predictable income based on time worked, ideal for roles with consistent tasks and clear time demands. Value-based pricing aligns compensation with the perceived value of work delivered, often benefiting professionals in creative, consulting, or specialized fields by rewarding impact rather than hours spent.
Impact on Earnings: Hourly vs. Value-Based Pay
Hourly wage compensates employees based on time worked, providing predictable income but limiting earning potential during high-value projects. Value-based pricing links pay to the outcome or value delivered, enabling higher earnings when results exceed expectations and encouraging efficiency. This method aligns compensation with performance, often leading to greater income variability but increased rewards for impactful contributions.
Industries Suited for Hourly Wage vs. Value-Based Pricing
Industries like retail, hospitality, and manufacturing often use hourly wage compensation due to predictable task durations and standardized roles, facilitating straightforward payroll management. In contrast, sectors such as consulting, creative agencies, and software development benefit from value-based pricing, aligning compensation with project outcomes and client ROI to incentivize performance and innovation. This method suits industries with variable project scopes and deliverables where the value delivered surpasses time spent.
Negotiation Strategies for Each Compensation Method
Negotiation strategies for hourly wage emphasize transparency in hours worked and justifying rate increases based on experience and market comparisons, while value-based pricing negotiations focus on quantifying the client's return on investment and demonstrating the unique value delivered. When discussing hourly wage, leveraging detailed time tracking and industry benchmarks strengthens bargaining power, whereas value-based pricing benefits from presenting case studies and projected outcomes to align compensation with results. Understanding these distinctions enables professionals to tailor their negotiation approach to maximize compensation effectively.
Future Trends in Job Compensation Models
Future trends in job compensation models emphasize a shift from traditional hourly wage systems to value-based pricing, where pay aligns with the actual value delivered rather than time spent. Companies increasingly adopt value-based pricing to incentivize productivity and innovation, reflecting market demand and individual contribution more accurately. This approach supports flexible, outcome-driven work environments, fostering talent retention and business growth in evolving industries.
Related Important Terms
Outcome-Based Compensation
Outcome-based compensation aligns employee pay with measurable results, offering a performance-driven alternative to fixed hourly wages. This method incentivizes productivity and quality by directly linking earnings to the value created, optimizing motivation and business outcomes.
Value Proposition Billing
Value-based pricing for compensation prioritizes the actual value delivered to the client rather than hours worked, aligning salary with measurable outcomes and client ROI. This method enhances motivation and profitability by rewarding employees based on the impact and results they generate, rather than just time spent.
Deliverable-Driven Pay
Deliverable-driven pay emphasizes value-based pricing by compensating employees or contractors based on completed project outcomes rather than hours worked, aligning earnings directly with deliverables' impact and quality. This method often enhances motivation and efficiency, contrasting with hourly wage models that prioritize time spent over actual results or value delivered.
Performance-Linked Remuneration
Performance-linked remuneration integrates value-based pricing by aligning compensation with the actual worth created, rather than fixed hourly wages, incentivizing higher productivity and outcome-driven results. This method enhances motivation and rewards employees based on measurable contributions, fostering a results-oriented work environment.
Impact-Based Fee Structure
Impact-based fee structures prioritize value-driven compensation by aligning hourly wages with measurable outcomes, enhancing motivation and productivity. This approach shifts focus from time spent to the actual impact delivered, optimizing salary expenditure and incentivizing high-performance results.
Project ROI Compensation
Project ROI compensation models based on value-based pricing align employee pay with the financial success of projects, incentivizing higher performance and innovation compared to fixed hourly wages. This method maximizes return on investment by directly correlating compensation with project outcomes and client value delivered.
Results-Oriented Pricing
Results-oriented pricing aligns compensation with the actual value delivered, offering a clear advantage over hourly wage models by directly incentivizing performance and outcome efficiency. This method enhances motivation and drives higher productivity, as payments correspond to measurable results rather than elapsed time.
Skill Premium Wage
Skill Premium Wage reflects higher hourly rates paid to employees with specialized expertise compared to standard hourly wages, emphasizing the direct correlation between skill level and compensation. Value-based pricing, by contrast, aligns pay with the perceived value created for the client or company, often resulting in more variable income tied to project outcomes rather than fixed hourly rates.
Success-Fee Model
The success-fee model ties compensation directly to project outcomes, aligning hourly wage calculations with measurable value creation rather than fixed time input. This approach incentivizes performance and ensures payment reflects the tangible benefits delivered to the employer or client.
Value Metric Pay
Value metric pay aligns employee compensation with measurable business outcomes, often leading to higher motivation and performance compared to fixed hourly wages. This method ties earnings directly to delivered value, fostering productivity and incentivizing innovation in salary structures.
Hourly Wage vs Value-based Pricing for compensation method. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com