Hourly wage provides a straightforward payment structure based on the number of hours worked, offering consistent income for employees with varying skill levels. Skill-premium pay rewards specialized expertise and higher proficiency, leading to greater earning potential for individuals with advanced abilities. Employers use these compensation types to balance fair base compensation with incentives for skill development and performance improvement.
Table of Comparison
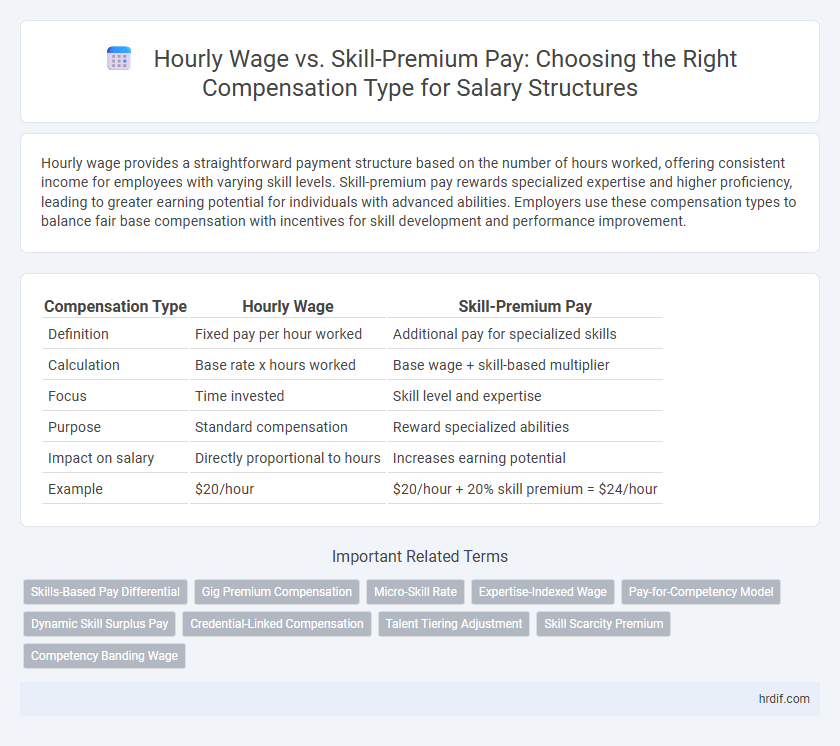
| Compensation Type | Hourly Wage | Skill-Premium Pay |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed pay per hour worked | Additional pay for specialized skills |
| Calculation | Base rate x hours worked | Base wage + skill-based multiplier |
| Focus | Time invested | Skill level and expertise |
| Purpose | Standard compensation | Reward specialized abilities |
| Impact on salary | Directly proportional to hours | Increases earning potential |
| Example | $20/hour | $20/hour + 20% skill premium = $24/hour |
Understanding Hourly Wage and Skill-Premium Pay
Hourly wage represents the fixed amount paid for each hour worked, providing straightforward compensation based on time. Skill-premium pay reflects additional earnings granted for specialized skills or higher proficiency, rewarding expertise beyond basic job requirements. Understanding the distinction helps employers design fair compensation strategies that motivate skill development and recognize employee value.
Key Differences Between Hourly and Skill-Premium Compensation
Hourly wage compensation is based solely on the number of hours worked, providing consistent pay regardless of skill level or job complexity. Skill-premium pay compensates employees based on their expertise, qualifications, and specialized skills, often resulting in higher earnings for advanced competencies. The key difference lies in hourly wages being time-dependent, while skill-premium pay emphasizes value creation through professional capabilities.
Benefits of Hourly Wage Compensation
Hourly wage compensation provides transparent, consistent pay directly linked to the number of hours worked, ensuring employees are fairly remunerated for their time. This model benefits workers with flexibility in scheduling and predictable income, which supports budgeting and financial planning. Hourly wages also simplify overtime calculations, offering additional earnings for extended work hours without complex pay structures.
Advantages of Skill-Premium Pay Structures
Skill-premium pay structures reward employees based on their expertise, driving higher motivation and retention in specialized roles. This compensation model encourages continuous learning and skill development, leading to increased productivity and innovation. Compared to hourly wages, skill-premium pay offers a competitive advantage by aligning pay with value-added capabilities and performance.
Impact on Employee Motivation and Retention
Hourly wage provides consistent, predictable income that appeals to employees valuing stability, while skill-premium pay rewards specialized expertise, boosting motivation by linking compensation directly to skill acquisition and performance. Research shows skill-premium pay enhances retention rates by fostering career development opportunities and increasing job satisfaction among high-skilled workers. Employers leveraging skill-based pay structures often experience lower turnover costs and higher workforce productivity due to improved employee engagement.
Job Roles Best Suited for Each Compensation Type
Hourly wage compensation best suits entry-level and routine job roles such as retail clerks, warehouse workers, and customer service representatives, where tasks are clearly defined and performance is easily quantifiable. Skill-premium pay benefits specialized roles like software engineers, data scientists, and healthcare professionals, where advanced knowledge, technical expertise, and problem-solving abilities drive added value. Employers often link skill-premium pay to certifications, experience, and productivity, rewarding employees who contribute significantly to organizational innovation and efficiency.
How Employers Determine Skill-Premium Pay Rates
Employers determine skill-premium pay rates by assessing the specialized expertise, certifications, and experience an employee brings beyond basic job requirements. Market demand for specific skills and the complexity of tasks directly influence the incremental pay above the standard hourly wage. Data from industry benchmarks, competitor salaries, and internal performance metrics also play a key role in setting competitive skill-premium compensation.
The Influence of Market Demand on Compensation Choices
Market demand heavily influences compensation choices, where high-demand skills often garner skill-premium pay rather than standard hourly wages. Employers tend to offer skill-based premiums to attract and retain specialized talent in competitive job markets. This compensation strategy aligns pay with the scarcity and value of specific expertise, optimizing workforce investment.
Legal Considerations: Hourly vs Skill-Based Pay
Legal considerations for hourly wage versus skill-premium pay emphasize compliance with minimum wage laws and overtime regulations under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Employers must ensure that skill-based pay structures do not result in compensation below statutory wage thresholds, while accurately tracking hours to avoid wage disputes. Proper documentation and transparent pay policies help mitigate legal risks related to misclassification and inconsistent wage calculations.
Choosing the Right Compensation Model for Your Career
Choosing between hourly wage and skill-premium pay depends on your career goals and expertise level. Hourly wages offer predictable income based on the number of hours worked, ideal for entry-level roles or jobs with consistent demand. Skill-premium pay rewards specialized skills and experience, driving higher compensation for professionals in technical or niche fields where expertise significantly impacts value.
Related Important Terms
Skills-Based Pay Differential
Skill-premium pay reflects higher compensation for employees whose specialized skills directly enhance performance and productivity, differentiating it clearly from standard hourly wages that compensate time rather than expertise. This pay differential incentivizes advanced competencies by aligning salary with the value of specific skills critical to organizational success.
Gig Premium Compensation
Gig premium compensation often exceeds standard hourly wages by incorporating skill-based pay rates that reward expertise and efficiency in project delivery. This hybrid model attracts highly skilled freelancers by offering competitive earnings aligned with specialized abilities rather than solely time spent.
Micro-Skill Rate
Micro-skill rate compensation offers a targeted premium pay structure that rewards employees based on specific skill acquisitions rather than broad hourly wage increments. This approach promotes efficiency by aligning salary with demonstrable expertise, allowing organizations to incentivize skill development more precisely than traditional hourly wage models.
Expertise-Indexed Wage
Expertise-indexed wage models prioritize skill proficiency over standard hourly rates by assigning compensation based on demonstrated expertise and productivity levels. This approach often results in a higher skill-premium pay compared to traditional hourly wage structures, aligning employee earnings with their specialized capabilities and value contribution.
Pay-for-Competency Model
The Pay-for-Competency Model emphasizes skill-premium pay, where compensation is directly linked to employees' demonstrated expertise and proficiency rather than hours worked. This approach incentivizes higher performance and skill development by rewarding specialized competencies, often resulting in more equitable and motivating salary structures compared to traditional hourly wage systems.
Dynamic Skill Surplus Pay
Dynamic Skill Surplus Pay adjusts hourly wage rates based on real-time demand for specialized skills, enabling employers to reward proficiency beyond standard compensation structures. This adaptive model ensures that employees with high-demand, niche expertise receive premium pay that better reflects their market value compared to traditional flat hourly wages.
Credential-Linked Compensation
Credential-linked compensation often results in a higher skill-premium pay compared to standard hourly wage, reflecting the increased value of specialized certifications and qualifications. Employers allocate a premium to credentialed employees to incentivize advanced expertise and ensure competitive compensation aligned with industry standards.
Talent Tiering Adjustment
Talent tiering adjustment frequently differentiates compensation by integrating skill-premium pay, which rewards advanced expertise beyond the base hourly wage. This approach aligns salary structures with employee proficiency levels, enhancing motivation and retention through targeted financial incentives.
Skill Scarcity Premium
Skill-premium pay offers higher compensation than basic hourly wages by directly reflecting the scarcity and specialized expertise required for certain roles, incentivizing talent with rare qualifications. Companies leverage skill scarcity premiums to attract and retain highly skilled workers, ensuring competitive advantage in markets where specialized competencies are in short supply.
Competency Banding Wage
Competency banding wage structures allocate pay based on skill levels and job complexity, offering higher skill-premium pay compared to standard hourly wages that compensate solely for time worked. This approach rewards employees with specialized competencies, promoting career development and aligning compensation with expertise rather than hours logged.
Hourly Wage vs Skill-Premium Pay for compensation type. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com