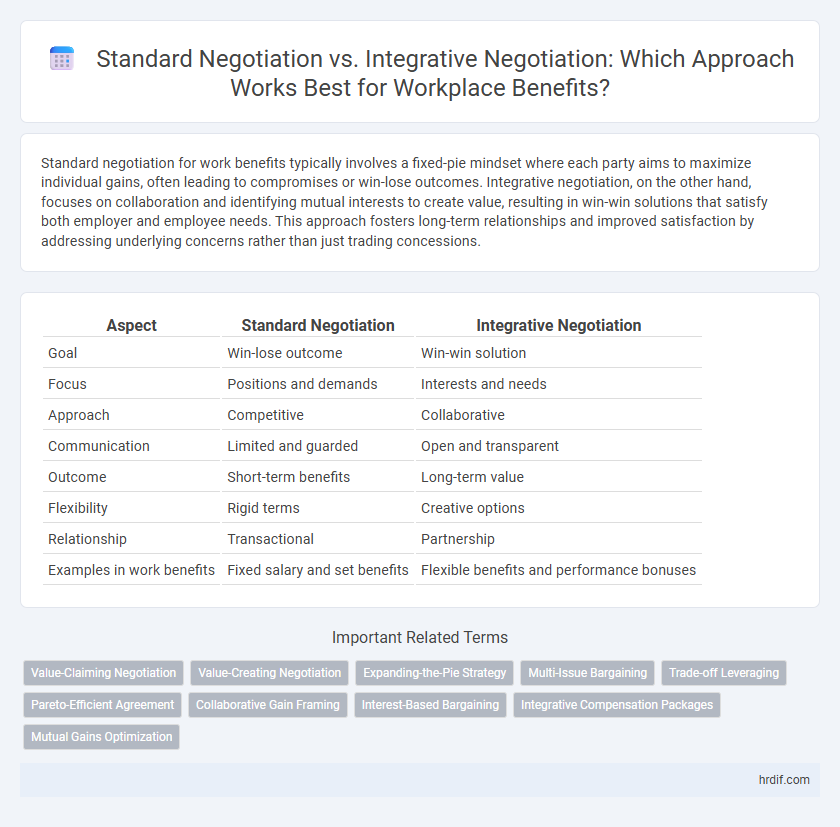
Standard negotiation for work benefits typically involves a fixed-pie mindset where each party aims to maximize individual gains, often leading to compromises or win-lose outcomes. Integrative negotiation, on the other hand, focuses on collaboration and identifying mutual interests to create value, resulting in win-win solutions that satisfy both employer and employee needs. This approach fosters long-term relationships and improved satisfaction by addressing underlying concerns rather than just trading concessions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Standard Negotiation | Integrative Negotiation |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Win-lose outcome | Win-win solution |
| Focus | Positions and demands | Interests and needs |
| Approach | Competitive | Collaborative |
| Communication | Limited and guarded | Open and transparent |
| Outcome | Short-term benefits | Long-term value |
| Flexibility | Rigid terms | Creative options |
| Relationship | Transactional | Partnership |
| Examples in work benefits | Fixed salary and set benefits | Flexible benefits and performance bonuses |
Understanding Standard vs Integrative Negotiation
Standard negotiation often involves a competitive, zero-sum approach where each party aims to maximize their own benefits, typically resulting in compromises that may not fully satisfy either side. Integrative negotiation focuses on collaboration, seeking mutually beneficial solutions by understanding the underlying interests and priorities of both parties to create added value. In the context of work benefits, integrative negotiation can lead to more comprehensive and sustainable agreements, improving employee satisfaction and organizational outcomes.
Key Principles of Standard Negotiation in the Workplace
Standard negotiation in the workplace centers on distributive bargaining where parties compete over fixed resources, such as salary or benefits. Key principles include clear goal setting, understanding the counterpart's position, and leveraging tactics like anchoring and concession-making. Emphasizing a win-lose outcome, this approach often limits the scope of mutual gains compared to integrative negotiation strategies.
Core Concepts of Integrative Negotiation for Employees
Integrative negotiation for work benefits focuses on collaboration, aiming to create win-win outcomes by addressing the underlying interests of both employers and employees. Key concepts include joint problem-solving, open communication, and exploring multiple options to satisfy mutual needs. This approach contrasts with standard negotiation, which often centers on dividing fixed resources and positional bargaining.
Comparing Outcomes: Standard vs Integrative Approaches
Standard negotiation often results in fixed outcomes focused on individual gains, typically limiting collaboration and leading to compromises that may leave parties partially satisfied. Integrative negotiation emphasizes mutual interests and creative problem-solving, producing outcomes that maximize joint value and improve long-term workplace relationships. Data shows integrative approaches increase employee satisfaction and retention by aligning benefits with shared goals and fostering trust.
Benefits Negotiation: Win-Lose or Win-Win?
Standard negotiation in work benefits often results in a win-lose outcome, where one party gains at the expense of the other, leading to limited collaboration and potential resentment. Integrative negotiation focuses on win-win solutions by identifying shared interests and creating value, fostering long-term relationships and mutual satisfaction in benefit agreements. Emphasizing integrative strategies enhances employee engagement and retention through flexible benefit packages tailored to both employer and employee needs.
Strategies for Negotiating Work Benefits
Standard negotiation strategies for work benefits often emphasize positional bargaining where each party defends their interests, focusing on fixed resources such as salary or vacation days. Integrative negotiation strategies prioritize collaborative problem-solving to create value, exploring options like flexible work hours, professional development opportunities, and wellness programs to meet both employee and employer needs. Effective negotiation involves understanding employee priorities, leveraging data on industry benchmarks, and employing active listening to generate mutually beneficial agreements.
Common Pitfalls in Standard Negotiation Tactics
Standard negotiation tactics often lead to common pitfalls such as rigid positional bargaining, which limits creative solutions for work benefits. This approach frequently results in win-lose scenarios, causing dissatisfaction and undermining long-term employer-employee relationships. In contrast, integrative negotiation encourages collaborative problem-solving that maximizes mutual gains and addresses underlying interests effectively.
Advantages of Integrative Negotiation for Career Growth
Integrative negotiation promotes collaboration and mutual gain, enabling employees to explore creative solutions that address both personal career aspirations and organizational goals. By fostering open communication and trust, it enhances long-term relationships, leading to opportunities for skill development, mentorship, and increased responsibility. This approach supports sustainable career growth by aligning work benefits with individual performance and professional advancement.
Practical Examples: Standard vs Integrative in Benefit Talks
Standard negotiation in work benefits often involves fixed positions, such as splitting a limited budget for health insurance coverage or vacation days, where each party aims to maximize individual gain. Integrative negotiation, by contrast, explores underlying interests, like combining flexible work hours with professional development opportunities, creating value for both employer and employee. For instance, instead of negotiating solely for salary increases, an integrative approach might result in enhanced benefits packages that satisfy financial needs while improving work-life balance.
Choosing the Right Negotiation Approach for Work Benefits
Standard negotiation often centers on fixed positions and compromises, which can limit the potential for maximizing employee work benefits. Integrative negotiation emphasizes collaboration and value creation, leading to tailored solutions that better address both employer and employee needs. Selecting the appropriate approach depends on the complexity of the benefits and the willingness of parties to explore mutually advantageous outcomes.
Related Important Terms
Value-Claiming Negotiation
Standard negotiation often centers on value-claiming tactics where each party aims to maximize their own benefits, typically resulting in competitive, zero-sum outcomes. Integrative negotiation, by contrast, seeks to create additional value by exploring mutual interests and collaborative solutions, but may require more trust and open communication to move beyond mere value-claiming approaches.
Value-Creating Negotiation
Standard negotiation often revolves around fixed positions and distributive bargaining, limiting the potential for mutual gains in work benefits. Integrative negotiation emphasizes collaborative problem-solving and value-creating strategies, enabling both employers and employees to expand the benefits package through shared interests and creative solutions.
Expanding-the-Pie Strategy
Standard negotiation often relies on a fixed-pie assumption, limiting work benefits to a zero-sum game where one party's gain is another's loss. Integrative negotiation utilizes the Expanding-the-Pie strategy by identifying shared interests and creating additional value, enabling both employers and employees to achieve enhanced work benefits without sacrificing either party's needs.
Multi-Issue Bargaining
Standard negotiation typically involves single-issue bargaining with fixed positions, leading to competitive outcomes, while integrative negotiation employs multi-issue bargaining to explore mutual gains and create value across work benefits. By addressing multiple dimensions such as salary, health insurance, and flexible hours simultaneously, integrative negotiation enhances opportunities for collaborative solutions that satisfy both employer and employee interests.
Trade-off Leveraging
Standard negotiation often involves fixed trade-offs where each party aims to maximize their own benefits, typically resulting in compromises that limit overall value. Integrative negotiation leverages trade-offs by identifying shared interests and creating value, allowing both parties to achieve better work benefits through collaborative problem-solving and resource expansion.
Pareto-Efficient Agreement
Standard negotiation often results in a zero-sum outcome where one party's gain is another's loss, limiting the potential for a Pareto-efficient agreement. Integrative negotiation emphasizes collaborative problem-solving and value creation, increasing the likelihood of achieving work benefits that optimize mutual gains without disadvantaging either party.
Collaborative Gain Framing
Standard negotiation often centers on fixed positions and compromises, leading to limited value creation between parties. Integrative negotiation utilizes collaborative gain framing by emphasizing mutual interests and expanding the benefits pool, resulting in more innovative and mutually advantageous work benefits agreements.
Interest-Based Bargaining
Standard negotiation often centers on positional bargaining, where each party defends fixed demands, limiting creative solutions for work benefits. Interest-Based Bargaining emphasizes understanding underlying needs and shared goals, facilitating collaborative agreements that improve employee satisfaction and organizational outcomes.
Integrative Compensation Packages
Integrative negotiation in work benefits focuses on creating customized compensation packages that address the unique needs and priorities of both employees and employers, fostering collaboration and long-term satisfaction. Unlike standard negotiation, which often involves fixed trade-offs, integrative approaches expand value by combining salary, bonuses, flexible work arrangements, and professional development opportunities.
Mutual Gains Optimization
Standard negotiation typically revolves around fixed resources and competitive positions, often resulting in win-lose outcomes, whereas integrative negotiation emphasizes collaboration and creative problem-solving to expand the value for all parties involved, optimizing mutual gains. By prioritizing shared interests and open communication, integrative negotiation fosters sustainable agreements that enhance work benefits and employee satisfaction.
Standard negotiation vs Integrative negotiation for work benefits. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com