Traditional contract negotiation often involves in-person discussions centered on predefined terms such as salary, benefits, and job responsibilities. Remote work policy negotiation introduces new priorities, including flexibility, communication expectations, and technology support to ensure productivity outside the office. Employers and employees must balance these evolving factors to create agreements that reflect modern work environments and individual needs.
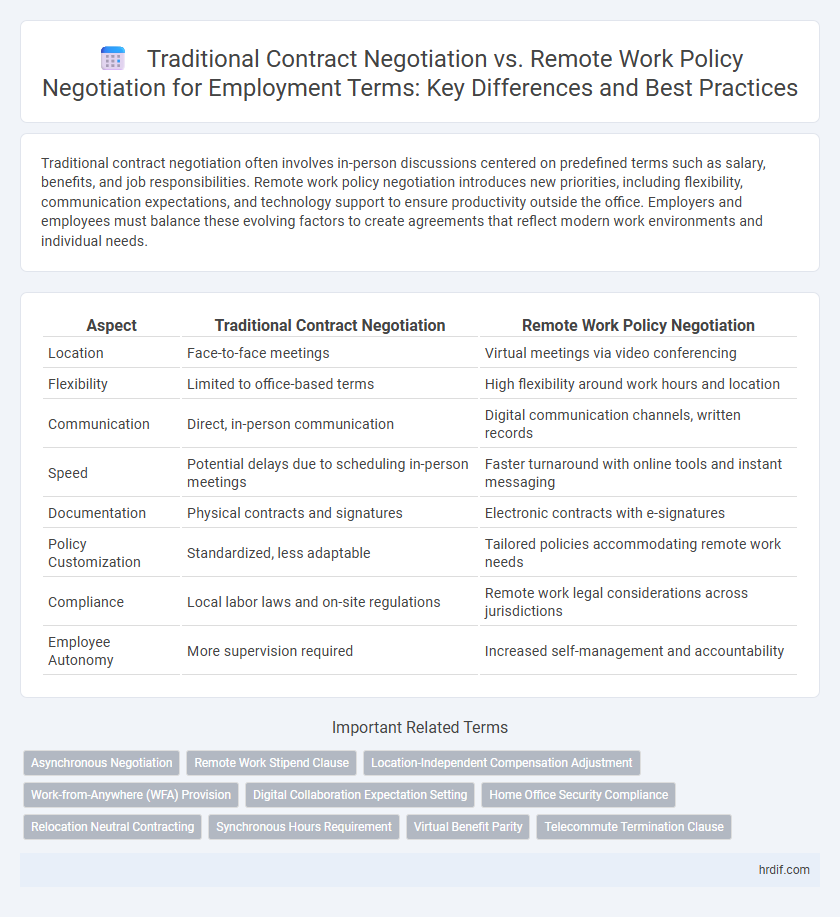
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Contract Negotiation | Remote Work Policy Negotiation |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Face-to-face meetings | Virtual meetings via video conferencing |
| Flexibility | Limited to office-based terms | High flexibility around work hours and location |
| Communication | Direct, in-person communication | Digital communication channels, written records |
| Speed | Potential delays due to scheduling in-person meetings | Faster turnaround with online tools and instant messaging |
| Documentation | Physical contracts and signatures | Electronic contracts with e-signatures |
| Policy Customization | Standardized, less adaptable | Tailored policies accommodating remote work needs |
| Compliance | Local labor laws and on-site regulations | Remote work legal considerations across jurisdictions |
| Employee Autonomy | More supervision required | Increased self-management and accountability |
Introduction: Evolving Employment Terms in a Digital Era
Traditional contract negotiation relies heavily on face-to-face interactions and physical documentation, often resulting in prolonged timelines and limited flexibility. Remote work policy negotiation for employment terms integrates digital communication tools, enabling real-time collaboration and adaptive agreements that reflect the dynamic nature of hybrid work environments. Emphasizing clarity in remote work expectations, such as availability, cybersecurity, and performance metrics, is crucial to addressing the evolving demands of the digital workforce.
Traditional Contract Negotiation: Face-to-Face Fundamentals
Traditional contract negotiation relies heavily on face-to-face interactions, fostering trust and immediate feedback through nonverbal cues such as body language and tone. This in-person approach facilitates clearer communication, rapid conflict resolution, and stronger relationship-building between employers and employees. Negotiators can better gauge reactions and adapt strategies dynamically, enhancing the effectiveness of reaching mutually beneficial employment terms.
Remote Work Policy Negotiation: New Norms and Expectations
Remote work policy negotiation has redefined employment terms by emphasizing flexibility, clear communication, and technology integration, shifting away from traditional contract negotiation's rigid frameworks. Employers and employees prioritize establishing expectations around availability, cybersecurity, and performance metrics to address remote work challenges effectively. This evolving negotiation landscape enhances mutual understanding and supports work-life balance, reflecting the new norms in employment agreements.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Remote Negotiations
Traditional contract negotiation typically involves in-person meetings where face-to-face interactions facilitate immediate feedback and nuanced communication, enhancing trust and rapport. Remote work policy negotiation relies heavily on digital communication tools, requiring clear, concise documentation and often more structured, asynchronous exchanges to prevent misunderstandings. Key differences include the mode of communication, the pace of negotiation, and the emphasis on written clarity to ensure alignment on employment terms in remote settings.
Communication Channels: In-Person Meetings vs Virtual Platforms
Traditional contract negotiation relies heavily on in-person meetings, enabling direct communication that fosters immediate feedback and non-verbal cue recognition critical for trust-building. Remote work policy negotiation leverages virtual platforms such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Slack, facilitating flexible scheduling and recorded conversations but sometimes reducing the richness of interpersonal interactions. Effective negotiation requires adapting communication channels to ensure clarity, active engagement, and understanding of employment terms regardless of the medium used.
Core Clauses: Salary, Benefits, and Flexibility
Traditional contract negotiation typically centers on fixed salary figures, standardized benefits packages, and limited flexibility in working hours or location. Remote work policy negotiation demands explicit agreements on salary adjustments based on remote work costs, tailored benefits for home office setups, and enhanced flexibility clauses reflecting varied work schedules. Employers must carefully balance these core clauses to attract talent while maintaining operational efficiency and legal compliance.
Power Dynamics: Shifting Leverage in Remote Discussions
Traditional contract negotiation often centers on in-person interactions where physical presence reinforces established power hierarchies between employer and employee. Remote work policy negotiation shifts leverage by empowering employees with flexibility and autonomy, diminishing the employer's ability to assert dominance through direct oversight. Digital communication platforms equalize engagement, allowing for more balanced dialogue and recalibrated power dynamics in employment terms discussions.
Legal and Compliance Considerations in Remote Settings
Remote work policy negotiation demands stricter adherence to diverse jurisdictional labor laws and data privacy regulations compared to traditional contract negotiation, where terms primarily focus on localized employment statutes. Ensuring compliance with international tax laws, cybersecurity mandates, and remote work-specific health and safety standards is critical to mitigate legal risks. Employers must incorporate clear provisions addressing remote work expectations, including monitoring policies and intellectual property protections, to uphold regulatory compliance in decentralized work environments.
Strategies for Success: Adapting Negotiation Techniques
Traditional contract negotiation relies heavily on in-person interactions, enabling nuanced reading of body language and immediate feedback, which helps build trust and resolve conflicts swiftly. Remote work policy negotiation requires leveraging digital communication tools to maintain clarity, setting clear expectations, and fostering transparency to overcome the absence of physical presence. Successful adaptation involves combining active listening techniques with structured agendas and frequent check-ins, ensuring alignment on employment terms despite the challenges of virtual environments.
Future Trends: The Hybrid Model and Ongoing Negotiations
Future trends in negotiation emphasize the hybrid model, blending traditional contract negotiation with remote work policy discussions to create flexible employment terms. Negotiators increasingly prioritize dynamic frameworks that accommodate both in-person and remote workflows, addressing employee preferences and organizational needs. Ongoing negotiations focus on balancing productivity, compliance, and work-life integration to optimize hybrid employment agreements.
Related Important Terms
Asynchronous Negotiation
Asynchronous negotiation in remote work policy allows participants to exchange proposals and feedback without simultaneous presence, enhancing flexibility compared to traditional contract negotiation, which typically requires real-time discussions. This approach optimizes decision-making efficiency by accommodating different time zones and work schedules, reducing pressure and promoting thoughtful responses during employment terms negotiation.
Remote Work Stipend Clause
Traditional contract negotiation typically centers on salary, benefits, and work hours, whereas remote work policy negotiation increasingly emphasizes remote work stipend clauses to cover home office expenses, internet costs, and equipment needs. Including a detailed remote work stipend clause ensures clarity on financial support and employee eligibility, enhancing transparency and reducing disputes in remote employment agreements.
Location-Independent Compensation Adjustment
Traditional contract negotiation typically involves fixed salary structures tied to geographic location, whereas remote work policy negotiation emphasizes location-independent compensation adjustments that reflect an employee's productivity and market value rather than physical office presence. Companies adopting remote work policies increasingly implement dynamic pay models to attract top talent regardless of location, balancing cost efficiency with competitive remuneration.
Work-from-Anywhere (WFA) Provision
Traditional contract negotiation often centers on fixed workplace terms and in-person agreements, while remote work policy negotiation--especially with Work-from-Anywhere (WFA) provisions--requires addressing geographic flexibility, time zone coordination, and compliance with diverse labor laws. Emphasizing WFA terms demands detailed clauses on data security, expense reimbursement, and performance metrics adapted to decentralized work environments.
Digital Collaboration Expectation Setting
Traditional contract negotiation often involves in-person discussions with limited digital tools, focusing on fixed terms and face-to-face agreement finalization. In contrast, remote work policy negotiation leverages digital collaboration platforms to set clear expectations on communication, availability, and deliverables, enabling flexible and transparent employment terms tailored to virtual environments.
Home Office Security Compliance
Traditional contract negotiation often involves face-to-face discussions emphasizing general employment terms, whereas remote work policy negotiation prioritizes Home Office Security Compliance to ensure data protection and secure access protocols. Emphasizing encryption standards, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits in remote work agreements addresses risks unique to distributed work environments.
Relocation Neutral Contracting
Traditional contract negotiation often centers on relocation clauses tied to physical office presence, while remote work policy negotiation emphasizes relocation-neutral contracting to accommodate flexible geographic work arrangements. Relocation neutral contracts prioritize employee autonomy and reduce logistical barriers, fostering broader talent acquisition and retention without imposing mandatory moves.
Synchronous Hours Requirement
Traditional contract negotiation typically mandates strict synchronous hours requirements, ensuring all parties discuss and agree on employment terms in real-time, fostering immediate feedback and clarification. In contrast, remote work policy negotiation often emphasizes flexibility in synchronous hours, balancing employee autonomy with core collaboration periods to optimize productivity and work-life balance.
Virtual Benefit Parity
Traditional contract negotiation often centers on in-person discussions emphasizing salary and role specifics, while remote work policy negotiation prioritizes Virtual Benefit Parity to ensure equitable access to resources, communication tools, and career development opportunities regardless of location. Emphasizing Virtual Benefit Parity in remote negotiations drives fairness by aligning benefits such as healthcare, equipment stipends, and professional growth with those enjoyed by on-site employees.
Telecommute Termination Clause
Traditional contract negotiation typically involves in-person discussions to finalize terms, with telecommute termination clauses often standardized for office-based roles; remote work policy negotiation requires tailored telecommute termination clauses addressing flexibility, performance metrics, and technology security to protect employer and employee interests. The specificity of remote work telecommute termination clauses includes conditions for equipment return, data privacy, and agreed notice periods, reflecting the unique challenges of managing distributed teams.
Traditional contract negotiation vs remote work policy negotiation for employment terms. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com