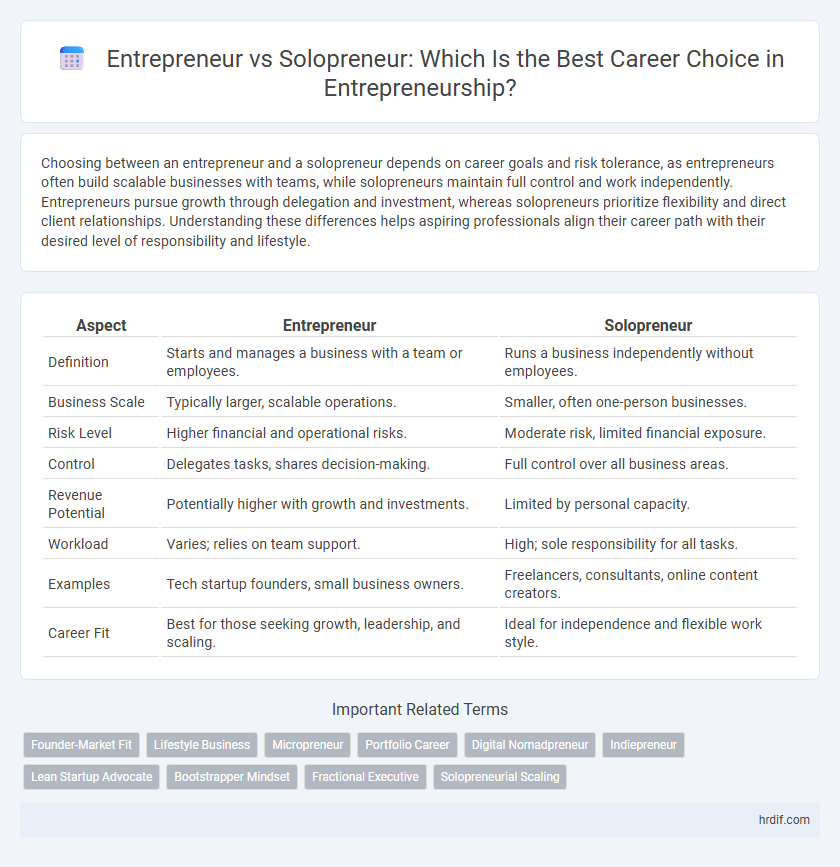
Choosing between an entrepreneur and a solopreneur depends on career goals and risk tolerance, as entrepreneurs often build scalable businesses with teams, while solopreneurs maintain full control and work independently. Entrepreneurs pursue growth through delegation and investment, whereas solopreneurs prioritize flexibility and direct client relationships. Understanding these differences helps aspiring professionals align their career path with their desired level of responsibility and lifestyle.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Entrepreneur | Solopreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Starts and manages a business with a team or employees. | Runs a business independently without employees. |
| Business Scale | Typically larger, scalable operations. | Smaller, often one-person businesses. |
| Risk Level | Higher financial and operational risks. | Moderate risk, limited financial exposure. |
| Control | Delegates tasks, shares decision-making. | Full control over all business areas. |
| Revenue Potential | Potentially higher with growth and investments. | Limited by personal capacity. |
| Workload | Varies; relies on team support. | High; sole responsibility for all tasks. |
| Examples | Tech startup founders, small business owners. | Freelancers, consultants, online content creators. |
| Career Fit | Best for those seeking growth, leadership, and scaling. | Ideal for independence and flexible work style. |
Defining Entrepreneur and Solopreneur: Key Differences
Entrepreneurs build scalable companies by leveraging teams, external funding, and strategic growth, while solopreneurs primarily operate independently, focusing on personal expertise and control without seeking external investors. Entrepreneurs embrace risk through business expansion and market disruption, whereas solopreneurs prioritize stability and self-reliance by managing all aspects of their ventures. Understanding these distinctions helps career seekers align their goals with either high-growth ambitions or autonomous, hands-on business management.
Skills Required for Entrepreneurs vs Solopreneurs
Entrepreneurs require strong leadership and team management skills to effectively delegate tasks and drive company growth, while solopreneurs must excel in self-discipline, multitasking, and adaptability to manage all aspects of their business independently. Both career paths demand resilience and strategic thinking, but entrepreneurs typically develop advanced networking and fundraising abilities, whereas solopreneurs hone specialized skills closely tied to their niche. Mastery of digital marketing tools and financial literacy is critical across both roles for sustainable success.
Risk and Reward: Comparing Career Paths
Entrepreneurs often face higher financial risks by investing in scalable businesses with potential for significant rewards through equity growth and market expansion. Solopreneurs typically encounter lower initial risks, relying on personal skills and smaller investments, but their rewards remain limited by individual capacity and time constraints. Choosing between these paths depends on one's risk tolerance and desire for long-term wealth versus immediate control and flexibility.
Financial Potential: Earning as an Entrepreneur vs Solopreneur
Entrepreneurs typically have higher financial potential than solopreneurs due to the scalability of businesses involving multiple employees and investment opportunities. Solopreneurs often face income limitations as their earnings are directly tied to personal productivity and time constraints. Equity stakes, passive income streams, and investor-backed growth give entrepreneurs greater long-term wealth-building advantages compared to solopreneurs.
Work-Life Balance Considerations
Entrepreneurs often face intense demands balancing business growth with personal time, frequently working long hours to scale their ventures. Solopreneurs typically experience greater control over their schedules, allowing more flexibility to maintain a healthier work-life balance. Choosing between these paths depends on individual priorities for autonomy, income potential, and lifestyle integration.
Scalability: Growth Opportunities in Each Path
Entrepreneurs pursue scalable business models with potential for exponential growth by building teams, securing investments, and expanding operations across markets. Solopreneurs prioritize control and autonomy, often limiting scalability due to reliance on individual capacity and time constraints. Evaluating growth opportunities depends on long-term vision, risk tolerance, and preference for managing a solo versus collaborative enterprise.
Decision-Making and Autonomy
Entrepreneurs often face complex decision-making processes involving team dynamics and market risks, while solopreneurs maintain full autonomy, making all strategic choices independently. The ability to control every aspect of the business grants solopreneurs flexibility but demands comprehensive skill sets and resilience. Choosing between these paths hinges on one's preference for collaborative leadership versus self-reliant autonomy in career development.
Resources and Support Systems Needed
Entrepreneurs typically require extensive resources, including access to capital, a diverse team, and robust support systems such as mentorship and networking opportunities to scale their ventures effectively. Solopreneurs often rely on limited resources, leveraging digital tools and outsourcing to manage business operations independently with minimal external support. Choosing between entrepreneur and solopreneur paths depends on one's ability to secure and manage resources and the preference for collaborative or autonomous work environments.
Personality Fit: Which Path Suits You?
Entrepreneurs thrive in collaborative environments, leveraging strong leadership and delegation skills to build scalable businesses, while solopreneurs excel through independence, self-discipline, and direct control over all aspects of their ventures. Personality traits such as comfort with risk, desire for autonomy, and communication style critically influence whether the dynamic, team-oriented entrepreneur role or the self-reliant solopreneur path is a better career fit. Understanding your natural tendencies toward teamwork versus solo accountability helps align your career choice with long-term satisfaction and success in the entrepreneurial landscape.
Long-Term Career Impact and Exit Strategies
Entrepreneurs typically build scalable businesses with long-term growth potential and diverse exit strategies such as acquisitions, public offerings, or mergers, creating substantial wealth opportunities. Solopreneurs often prioritize autonomy and direct control, focusing on sustainable income streams with exit options limited to business handover or gradual scale-down. Evaluating career impact involves weighing scalability ambitions against personal management preferences and risk tolerance for future transitions.
Related Important Terms
Founder-Market Fit
Founder-market fit significantly influences career success by aligning an entrepreneur's skills and passions with market demands, whereas solopreneurs prioritize autonomy and niche expertise. Choosing between entrepreneur and solopreneur paths depends on matching personal strengths to business models that maximize growth potential and market resonance.
Lifestyle Business
Choosing between entrepreneur and solopreneur hinges on the desired lifestyle business model, with entrepreneurs often seeking scalable ventures that require building teams, while solopreneurs prioritize autonomy and direct control with minimal overhead. Lifestyle businesses led by solopreneurs emphasize work-life balance and sustainable income without the pressure of rapid growth or external funding.
Micropreneur
Micropreneurs focus on building small-scale, sustainable businesses that prioritize work-life balance and niche markets, distinguishing them from traditional entrepreneurs who often seek rapid growth and large-scale expansion. Choosing a micropreneur career allows individuals to maintain autonomy, minimize risk, and foster close customer relationships while leveraging digital tools for efficient business operations.
Portfolio Career
Choosing between entrepreneur and solopreneur paths heavily influences the success of a portfolio career, as entrepreneurs typically build scalable businesses requiring teams and external funding, while solopreneurs maintain full control by managing multiple income streams independently. Portfolio careers thrive with solopreneurs leveraging diverse projects and skills for flexibility, whereas entrepreneurs invest in growth and market expansion to create larger enterprises.
Digital Nomadpreneur
Entrepreneurs often build scalable businesses with teams and extensive resources, while solopreneurs operate independently, managing all aspects of their ventures alone, offering more flexibility for a digital nomadpreneur lifestyle. Embracing solopreneurship enables digital nomadpreneurs to leverage remote work tools, maintain mobility, and create income streams aligned with their travel-focused career goals.
Indiepreneur
Entrepreneurs typically build scalable businesses with teams and external funding, while solopreneurs focus on independent ventures managed solo, often championed by indiepreneurs who prioritize creative freedom and direct control over their career trajectory. Indiepreneurs blend the best of both worlds by leveraging digital tools to scale personal brands and monetize niche markets without relying on traditional corporate structures.
Lean Startup Advocate
Entrepreneurs typically lead scalable ventures with a focus on building teams and seeking external funding, while solopreneurs prioritize autonomy and direct control over all aspects of their business, often bootstrapping operations. Lean Startup methodology, emphasizing validated learning and iterative product development, supports both career paths by minimizing risks and accelerating market fit.
Bootstrapper Mindset
Entrepreneurs typically build scalable businesses with teams, leveraging external funding and resources, while solopreneurs operate independently, emphasizing self-reliance and control. A bootstrapper mindset thrives in solopreneurship by maximizing limited resources, minimizing expenses, and prioritizing organic growth without external investment.
Fractional Executive
Fractional executives offer specialized leadership on a part-time basis, making solopreneurship an ideal career path for professionals seeking autonomy and flexible work arrangements without the overhead of building a full enterprise. Entrepreneurs often pursue scalable ventures with larger teams, while solopreneurs leverage fractional executive roles to deliver high-impact expertise to multiple clients simultaneously.
Solopreneurial Scaling
Solopreneurs scale their businesses by leveraging automation, outsourcing, and digital tools to maintain control while expanding revenue streams without traditional team structures. Unlike entrepreneurs who rely on building large teams and external funding, solopreneurs prioritize agility and sustainable growth through personalized branding and direct customer engagement.
Entrepreneur vs Solopreneur for career choice. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com