Entrepreneurs typically aim to grow their businesses on a larger scale, focusing on expansion, investment, and market dominance, while micropreneurs prioritize maintaining a small, manageable business that offers flexibility and work-life balance. Micropreneurs often leverage niche markets and personalized customer relationships, avoiding the pressures of rapid growth and extensive scaling. Business scale is a defining factor distinguishing entrepreneurs' pursuit of growth from micropreneurs' emphasis on sustainability and autonomy.
Table of Comparison
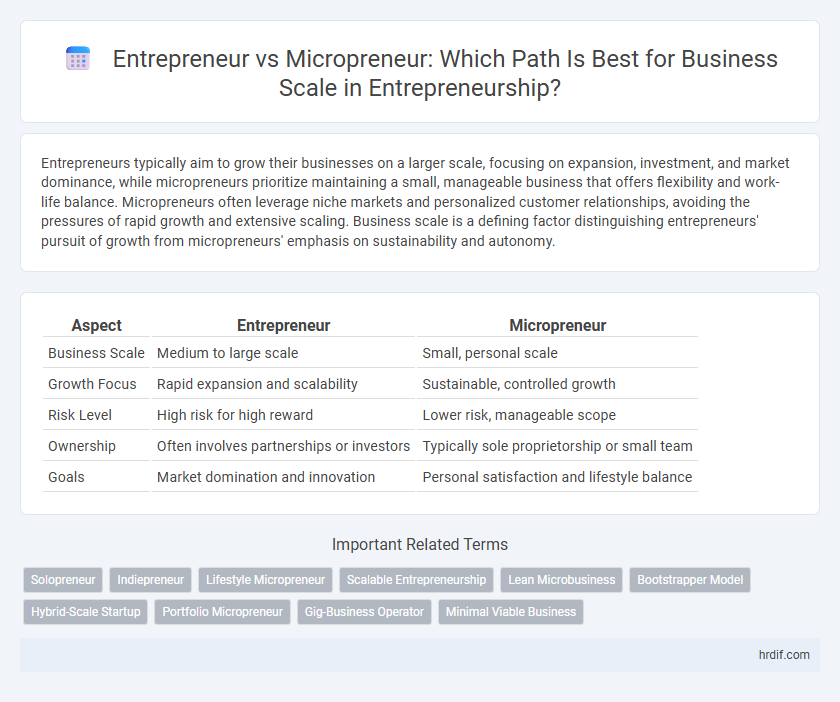
| Aspect | Entrepreneur | Micropreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Business Scale | Medium to large scale | Small, personal scale |
| Growth Focus | Rapid expansion and scalability | Sustainable, controlled growth |
| Risk Level | High risk for high reward | Lower risk, manageable scope |
| Ownership | Often involves partnerships or investors | Typically sole proprietorship or small team |
| Goals | Market domination and innovation | Personal satisfaction and lifestyle balance |
Defining Entrepreneur and Micropreneur: Key Differences
An entrepreneur typically seeks to build scalable businesses with high growth potential, often aiming to innovate and expand rapidly. In contrast, a micropreneur prioritizes maintaining a small, manageable business that offers lifestyle flexibility and sustainability over aggressive growth. Key differences lie in their business scale, growth objectives, and operational scope, with entrepreneurs focusing on market disruption and micropreneurs on niche stability.
Business Scale: Growth Mindset vs. Lifestyle Focus
Entrepreneurs prioritize scalable business models aimed at rapid growth, leveraging innovation and external funding to maximize market reach and revenue. Micropreneurs focus on maintaining a sustainable lifestyle business, emphasizing autonomy, work-life balance, and steady, manageable income without aggressive expansion. The key distinction lies in the growth mindset driving entrepreneurs versus the lifestyle-oriented goals shaping micropreneurs' business scale decisions.
Risk Appetite: Ambition Versus Control
Entrepreneurs usually pursue high-growth ventures, embracing significant risk to achieve ambitious market expansion and scalability. Micropreneurs prioritize maintaining control and sustainability, often opting for smaller-scale businesses with manageable risk levels. This difference in risk appetite shapes their distinct approaches to business scale and long-term objectives.
Resource Management: Team Building or Solo Journey
Entrepreneurs typically build scalable teams to optimize resource management, leveraging diverse skills for business growth, while micropreneurs often prefer a solo journey, managing resources independently to maintain agility and control. Effective team building in entrepreneurship enables delegation and innovation, crucial for scaling operations. In contrast, micropreneurs prioritize personalized management and close control over resources, favoring quality and flexibility over expansion.
Funding Strategies: Venture Capital or Bootstrapping
Entrepreneurs often pursue large-scale funding through venture capital to accelerate growth and expand market reach rapidly. Micropreneurs typically rely on bootstrapping, using personal savings and minimal external funding to maintain control and sustain a manageable business size. Choosing between venture capital and bootstrapping significantly impacts business scalability, financial risk, and operational flexibility.
Operational Scope: Local Niche vs. Global Expansion
Entrepreneurs typically aim for global expansion, leveraging scalable business models and broad market reach to maximize growth potential and impact. Micropreneurs focus on operational scope within a local niche, prioritizing sustainable, community-based business activities and personalized customer relationships. This distinction influences their strategic decisions, resource allocation, and long-term scalability.
Time Commitment: Hustle Culture vs. Work-Life Balance
Entrepreneurs often embrace hustle culture, dedicating long hours to rapidly scale their businesses and secure significant market share. Micropreneurs prioritize work-life balance by maintaining manageable business operations that generate steady income without overwhelming time commitments. The choice between these approaches influences stress levels, personal fulfillment, and growth potential within the entrepreneurial journey.
Innovation and Impact: Disruptors Versus Specialists
Entrepreneurs typically drive large-scale innovation and disruption by creating scalable business models that transform markets and industries. Micropreneurs focus on specialized niches, leveraging deep expertise to create meaningful impact within smaller, targeted communities or sectors. Both approaches emphasize innovation, but entrepreneurs prioritize broad market disruption, while micropreneurs excel in tailored, sustainable growth.
Long-Term Vision: Exit Plans and Legacy
Entrepreneurs typically pursue high-growth ventures with clear exit strategies such as acquisitions or IPOs, aiming to maximize financial returns and build a scalable legacy. In contrast, micropreneurs emphasize sustainable, lifestyle-oriented businesses with long-term stability, prioritizing personal fulfillment and community impact over rapid expansion. Both mindsets shape distinct approaches to legacy, where entrepreneurs seek market disruption, while micropreneurs foster enduring, small-scale enterprises.
Choosing the Right Path: Which is Best for You?
Entrepreneurs typically pursue large-scale ventures with significant growth and expansion goals, aiming to secure funding and scale operations rapidly. In contrast, micropreneurs focus on small, sustainable businesses that prioritize work-life balance and localized impact without extensive growth ambitions. Choosing the right path depends on your risk tolerance, financial goals, and desire for control versus scalability in the business model.
Related Important Terms
Solopreneur
Entrepreneurs typically aim to scale their businesses by building teams and expanding operations, whereas micropreneurs prioritize maintaining a small, manageable business size often operating solo to balance work and lifestyle. Solopreneurs exemplify the micropreneur model by leveraging personal skills and digital tools to sustain a one-person enterprise without pursuing significant growth or large-scale ventures.
Indiepreneur
Entrepreneurs typically pursue large-scale business growth with extensive team structures, while micropreneurs prioritize maintaining small, manageable ventures that emphasize personal freedom and lean operations. Indiepreneurs represent a subset of micropreneurs who focus on independent, creative businesses driven by passion and sustainable revenue rather than rapid expansion.
Lifestyle Micropreneur
Lifestyle micropreneurs prioritize personal freedom and work-life balance over rapid business growth, often operating small-scale ventures that align with their passions and values. Unlike traditional entrepreneurs who seek large-scale expansion and significant market impact, lifestyle micropreneurs focus on sustainable income streams while maintaining a flexible lifestyle.
Scalable Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurs focus on scalable business models designed for rapid growth and market expansion, leveraging innovation and investment to build large enterprises. Micropreneurs prioritize sustainable, small-scale operations with steady income and work-life balance, often avoiding the complexities of scaling.
Lean Microbusiness
Entrepreneurs typically seek scalable businesses with significant growth potential, while micropreneurs prioritize lean microbusinesses that emphasize sustainability, manageable risk, and lifestyle alignment. Lean microbusiness strategies leverage minimal resources and agile operations to optimize profitability without extensive capital investment or rapid expansion.
Bootstrapper Model
Entrepreneurs typically pursue scalable business models with high-growth potential, while micropreneurs prioritize sustainable, small-scale ventures emphasizing lifestyle and autonomy. The Bootstrapper Model supports both by encouraging resourceful, self-funded growth, enabling entrepreneurs to maintain control without external investment pressures.
Hybrid-Scale Startup
Entrepreneurs typically pursue large-scale ventures with rapid growth potential, while micropreneurs focus on maintaining small, manageable businesses with stable revenue streams. Hybrid-scale startups blend these approaches by scaling selectively, combining entrepreneurial innovation with micropreneurial agility to optimize growth and sustainability.
Portfolio Micropreneur
Portfolio micropreneurs operate multiple small-scale businesses simultaneously, leveraging diverse income streams to mitigate risk and enhance financial stability compared to traditional entrepreneurs who typically focus on scaling a single venture. This business model emphasizes flexibility, low overhead, and agile management, making it ideal for those seeking sustainable growth without the pressure of rapid expansion.
Gig-Business Operator
Entrepreneurs typically aim to scale their ventures significantly, seeking investment and growth opportunities, while micropreneurs prioritize maintaining a manageable, often solo-operated gig-business with flexible work-life balance. Gig-business operators focus on niche services or freelance work, emphasizing sustainability and autonomy over rapid expansion or large-scale enterprise development.
Minimal Viable Business
Entrepreneurs typically pursue scalable ventures with rapid growth potential, leveraging Minimal Viable Business models to quickly validate market demand and attract investment. Micropreneurs concentrate on sustainable, small-scale operations prioritizing lifestyle balance and direct customer relationships over aggressive expansion.
Entrepreneur vs Micropreneur for business scale. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com