Entrepreneur and expatpreneur both refer to individuals who start and run businesses, but expatpreneurs specifically operate in foreign countries, leveraging cross-cultural insights and international networks. Expatpreneurs face unique challenges such as navigating local regulations, cultural differences, and language barriers, which require adaptive strategies for business success. This hybrid approach combines entrepreneurial innovation with global mobility, creating opportunities in diverse markets often overlooked by traditional entrepreneurs.
Table of Comparison
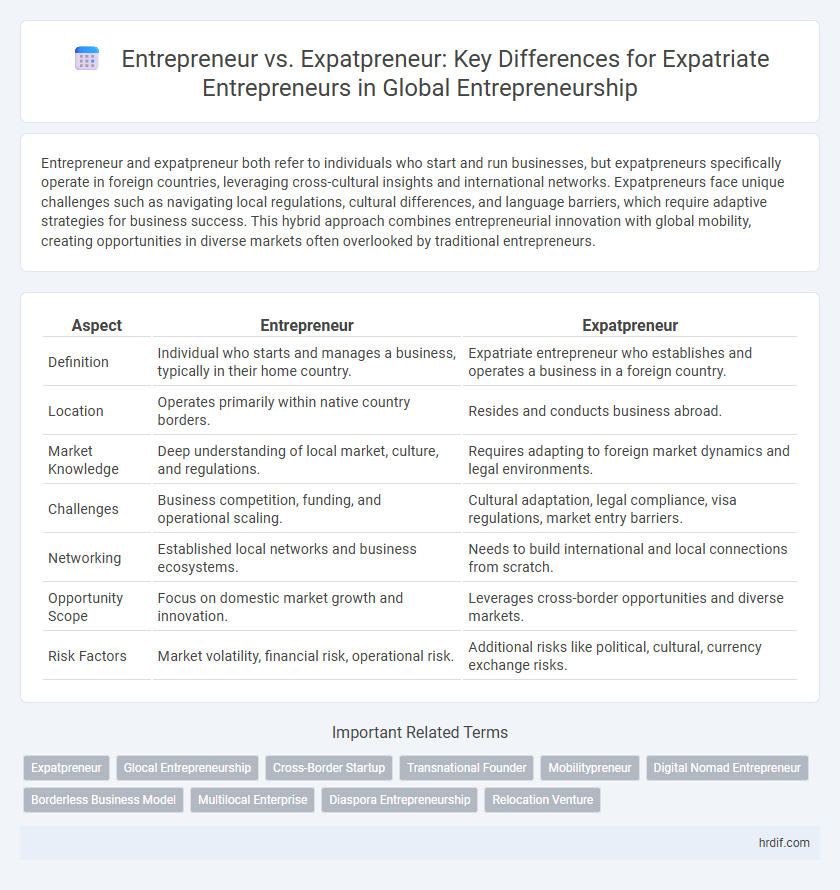
| Aspect | Entrepreneur | Expatpreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual who starts and manages a business, typically in their home country. | Expatriate entrepreneur who establishes and operates a business in a foreign country. |
| Location | Operates primarily within native country borders. | Resides and conducts business abroad. |
| Market Knowledge | Deep understanding of local market, culture, and regulations. | Requires adapting to foreign market dynamics and legal environments. |
| Challenges | Business competition, funding, and operational scaling. | Cultural adaptation, legal compliance, visa regulations, market entry barriers. |
| Networking | Established local networks and business ecosystems. | Needs to build international and local connections from scratch. |
| Opportunity Scope | Focus on domestic market growth and innovation. | Leverages cross-border opportunities and diverse markets. |
| Risk Factors | Market volatility, financial risk, operational risk. | Additional risks like political, cultural, currency exchange risks. |
Defining Entrepreneur vs Expatpreneur
An entrepreneur is an individual who starts and manages a business venture, typically within their home country, by leveraging local networks and market knowledge. An expatpreneur differs by establishing and operating a business while living abroad, navigating diverse cultural, legal, and economic environments unique to their expatriate status. Understanding the challenges and opportunities of expatpreneurship involves recognizing cross-border entrepreneurial strategies, adaptation to foreign markets, and reliance on international networks.
Unique Challenges Faced by Expatpreneurs
Expatpreneurs encounter unique challenges distinct from traditional entrepreneurs, such as navigating complex legal and visa requirements in foreign countries while adapting business models to diverse cultural and economic environments. Language barriers and unfamiliar market dynamics require strategic localization and robust cross-cultural communication skills. Managing remote teams across time zones and building local networks often add layers of complexity to establishing a sustainable enterprise abroad.
Advantages of Entrepreneurship Abroad
Entrepreneurship abroad offers expatriate entrepreneurs unique advantages such as access to diverse markets, enabling innovation through cross-cultural insights and expanding business networks internationally. Expatpreneurs benefit from favorable regulatory environments and potential tax incentives in host countries, which can reduce operational costs and increase profitability. Establishing a business overseas fosters adaptability and global competitiveness, key drivers for sustainable growth in today's interconnected economy.
Legal and Regulatory Differences
Entrepreneur and expatpreneur face distinct legal and regulatory challenges, with expatpreneurs often navigating complex visa requirements, work permits, and local business registration laws in foreign jurisdictions. Expatpreneurs must comply with host country tax regulations, which may differ significantly from their home country's policies, affecting income reporting and business deductions. Understanding local labor laws and intellectual property rights is crucial for expatpreneurs to establish compliant and sustainable ventures abroad.
Cultural Adaptation in Foreign Markets
Cultural adaptation plays a crucial role in the success of both entrepreneurs and expatpreneurs operating in foreign markets. While traditional entrepreneurs may rely on generic business strategies, expatpreneurs must navigate complex cultural nuances to build trust and establish local networks effectively. Mastery of language, customs, and consumer behavior significantly enhances market entry and long-term sustainability for expatriate entrepreneurs.
Networking and Support Systems
Entrepreneur expatriates who adopt the expatpreneur model benefit from targeted networking opportunities that blend local insights with global connections, enhancing their business growth and cultural adaptation. Unlike traditional entrepreneurs, expatpreneurs leverage specialized support systems such as expatriate business clubs, international trade organizations, and multicultural mentorship programs that address the unique challenges of operating in foreign markets. This integration of global and local resources fosters resilient business networks essential for overcoming legal, financial, and social barriers encountered by expatriate entrepreneurs.
Funding Opportunities for Expatpreneurs
Expatpreneurs benefit from unique funding opportunities such as international venture capital firms, global angel investors, and expatriate-focused grant programs that specifically support cross-border business initiatives. Access to home country funding networks combined with local startup ecosystems enhances capital availability and fosters diversified investment sources. Leveraging these channels increases the chances of acquiring tailored financial resources crucial for scaling expatriate-led ventures globally.
Navigating Local Business Practices
Expatpreneurs excel at navigating local business practices by leveraging their deep understanding of cultural nuances and legal regulations in foreign markets. Unlike traditional entrepreneurs who often rely on familiar domestic frameworks, expatpreneurs adapt strategies to align with local customer behaviors and regulatory environments. Mastery of local business customs and proactive networking are critical for expatpreneurs seeking successful market entry and sustainable growth abroad.
Case Studies: Entrepreneur vs Expatpreneur Success Stories
Case studies reveal that while traditional entrepreneurs excel by leveraging local market insights, expatpreneurs thrive by combining cross-cultural expertise with global networks to innovate in foreign markets. Success stories highlight expatpreneurs' ability to adapt business models to diverse cultural contexts, often resulting in accelerated growth and competitive advantage. These examples demonstrate the unique resilience and resourcefulness required to succeed as an expatpreneur compared to conventional entrepreneurship.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Entrepreneurship for expatriates involves deciding between traditional entrepreneurship and expatpreneurship, each offering distinct advantages based on market access, cultural integration, and local regulatory environments. Key factors include understanding host country business laws, leveraging cross-cultural networks, and assessing personal adaptability to foreign markets. Selecting the right path maximizes growth potential by aligning business strategies with expatriate lifestyle and local economic conditions.
Related Important Terms
Expatpreneur
Expatpreneurs leverage their unique cultural insights and global networks to innovate and expand businesses beyond traditional domestic markets, often overcoming cross-border regulatory challenges and adapting to diverse consumer behaviors. This strategic advantage distinguishes expatpreneurs from typical entrepreneurs by enabling them to create value in multicultural environments and tap into international opportunities more effectively.
Glocal Entrepreneurship
Expatpreneurs blend global insights with local market understanding, leveraging glocal entrepreneurship to create innovative businesses that adapt to diverse cultural and economic environments. This approach enhances cross-border opportunities and drives sustainable growth by merging expatriate experiences with entrepreneurial agility.
Cross-Border Startup
Expatpreneurs leverage unique cultural insights and local market knowledge to navigate cross-border startup challenges more effectively than traditional entrepreneurs, facilitating innovation and expanding global business networks. Their ability to blend diverse entrepreneurial ecosystems accelerates scalable solutions and optimizes resource allocation across international borders.
Transnational Founder
Transnational founders transcend traditional entrepreneurship by leveraging cross-border networks, cultural insights, and global market opportunities to build scalable ventures beyond their home country. Unlike typical entrepreneurs, expatpreneurs integrate diverse regulatory environments and international resources, enabling innovation and competitive advantage in multiple regions.
Mobilitypreneur
Expatpreneurs combine entrepreneurship with international mobility, leveraging global networks and cross-cultural insights to establish businesses abroad. Unlike traditional entrepreneurs, Mobilitypreneurs excel in navigating diverse markets and regulatory environments while continuously relocating to optimize business opportunities.
Digital Nomad Entrepreneur
Entrepreneurial success for digital nomad entrepreneurs hinges on balancing local market insights with global digital strategies, differentiating expatpreneurs from traditional entrepreneurs by their mobility and adaptability across borders. Leveraging online platforms and remote work tools optimizes business scalability while navigating varying legal and cultural landscapes inherent to expatriate entrepreneurship.
Borderless Business Model
Expatpreneurs leverage the borderless business model by seamlessly operating across multiple countries, utilizing digital platforms and global networks to overcome traditional geographic limitations faced by entrepreneurs. This approach enables expatriate entrepreneurs to capitalize on diverse markets, optimize resource allocation, and foster innovation without being tethered to a single location.
Multilocal Enterprise
Expatpreneurs leverage their unique position as expatriate entrepreneurs to build multilocal enterprises that operate across diverse geographic markets, combining local insights with global strategies. This approach enables the creation of adaptive business models that optimize resources and opportunities in multiple international locations, differentiating them from traditional entrepreneurs focused solely on a single domestic market.
Diaspora Entrepreneurship
Diaspora entrepreneurship blends traditional entrepreneurial skills with unique expatriate experiences, enabling expatpreneurs to leverage transnational networks and cultural insights for market innovation. Unlike conventional entrepreneurs, expatpreneurs navigate dual economic environments, fostering cross-border business opportunities and enhancing diaspora-led economic development.
Relocation Venture
Expatpreneurs leverage their entrepreneurial skills to start ventures in foreign markets, combining deep cultural insights with global business strategies to overcome relocation challenges and capitalize on local opportunities. Unlike traditional entrepreneurs, expatpreneurs navigate complex legal frameworks, cultural adaptations, and network-building in foreign ecosystems, driving innovation and economic growth in host countries through their cross-border ventures.
Entrepreneur vs Expatpreneur for expatriate entrepreneurs. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com