Startup founders typically build companies with scalable business models, aiming to grow teams and attract external investment, while solopreneurs often operate independently, focusing on personal expertise and maintaining full control over their business. Founders prioritize market disruption and rapid growth, leveraging resources and partnerships to expand, whereas solopreneurs emphasize flexibility, direct client relationships, and sustainable, manageable workloads. Choosing between the two paths depends on the entrepreneur's vision, risk tolerance, and preferred operational structure in the pet industry.
Table of Comparison
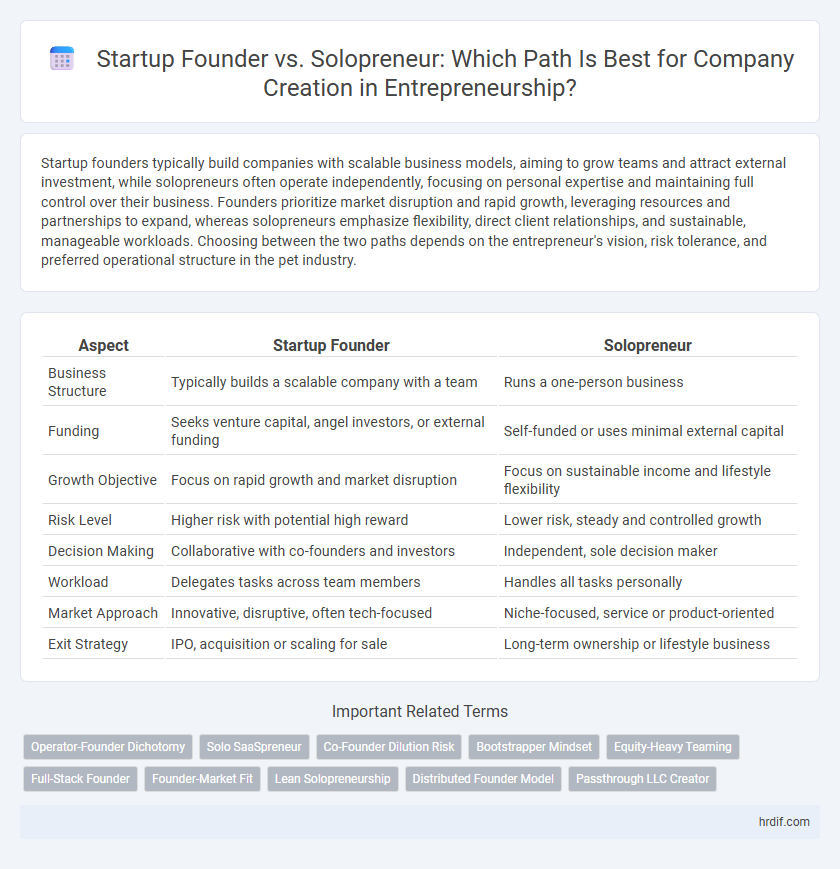
| Aspect | Startup Founder | Solopreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Business Structure | Typically builds a scalable company with a team | Runs a one-person business |
| Funding | Seeks venture capital, angel investors, or external funding | Self-funded or uses minimal external capital |
| Growth Objective | Focus on rapid growth and market disruption | Focus on sustainable income and lifestyle flexibility |
| Risk Level | Higher risk with potential high reward | Lower risk, steady and controlled growth |
| Decision Making | Collaborative with co-founders and investors | Independent, sole decision maker |
| Workload | Delegates tasks across team members | Handles all tasks personally |
| Market Approach | Innovative, disruptive, often tech-focused | Niche-focused, service or product-oriented |
| Exit Strategy | IPO, acquisition or scaling for sale | Long-term ownership or lifestyle business |
Defining Startup Founder and Solopreneur
A startup founder is an individual who initiates and leads a high-growth company, often seeking external funding and building a scalable business model with a team. A solopreneur operates a business independently, managing all aspects alone without intending rapid scale or external investment. The distinction lies in the founder's emphasis on innovation and growth potential versus the solopreneur's focus on self-managed, steady operations.
Key Differences in Business Models
Startup founders typically build scalable businesses designed for rapid growth and external investment, often leveraging teams and venture capital to accelerate development. Solopreneurs operate lean, prioritizing autonomy and control by managing all aspects of the business independently, usually focusing on sustainable, steady revenue. The core business model distinction lies in scalability and funding approach, with startups aiming for exponential expansion while solopreneurs emphasize self-sufficiency and direct client relationships.
Funding Strategies: Venture Capital vs. Bootstrapping
Startup founders often pursue venture capital funding to accelerate growth, leveraging investor networks and substantial capital to scale rapidly. Solopreneurs typically rely on bootstrapping, utilizing personal savings and organic revenue to maintain control and minimize financial risk. The choice between venture capital and bootstrapping significantly impacts ownership structure, operational flexibility, and long-term business strategy.
Team Dynamics: Building a Team vs. Working Solo
Startup founders often prioritize assembling a diverse team with complementary skills to foster innovation, scale operations, and attract investment, creating a collaborative environment crucial for company growth. Solopreneurs, however, maintain full control by working independently, relying on personal expertise and agility but facing challenges in handling multiple roles and limited scalability. Effective team dynamics in startups enhance problem-solving and resource sharing, whereas solopreneurs benefit from streamlined decision-making and flexibility.
Risk and Reward Profiles
Startup founders typically face high risks involving substantial financial investment and team management challenges, but they also stand to gain significant rewards through equity growth and large-scale business success. Solopreneurs assume lower financial risks as they often self-fund and operate independently, yet their reward potential is limited to personal income and small-scale business growth. Risk tolerance and desired reward magnitude strongly influence the choice between pursuing a startup founder role or solopreneurship.
Time Commitment and Work-Life Balance
Startup founders often face intense time commitments, dedicating long hours to scaling and managing teams, which can challenge work-life balance. Solopreneurs typically have more control over their schedules, enabling flexible work hours but may experience higher workloads due to handling all business aspects alone. Balancing time demands is crucial for both paths, yet startup founders prioritize growth and investor relations, while solopreneurs focus on sustainable, self-managed operations.
Growth Potential and Scalability
Startup founders typically focus on high-growth potential ventures aiming for rapid scalability through team expansion and external funding, making their companies suitable for significant market disruption. Solopreneurs prioritize control and flexibility, often operating smaller-scale businesses with limited scalability due to solo management and resource constraints. While startup founders pursue exponential growth and market capture, solopreneurs leverage niche expertise to maintain sustainable, steady income streams.
Skill Sets and Competencies Required
Startup founders require strong leadership, team-building abilities, and strategic vision to guide rapid growth and manage diverse stakeholders effectively. Solopreneurs prioritize multi-disciplinary skills, including marketing, sales, and operational management, enabling them to independently handle all business functions. Both roles demand resilience and adaptability, but founders typically focus more on delegation and scaling, while solopreneurs emphasize hands-on execution and self-reliance.
Success Metrics: How Each Measures Success
Startup founders typically measure success through rapid growth indicators such as user acquisition rates, funding milestones, and market share expansion, reflecting scalability and investor appeal. In contrast, solopreneurs prioritize personal metrics like consistent revenue generation, work-life balance, and customer satisfaction, emphasizing sustainable, independent business operations. Both definitions of success shape strategy, resource allocation, and long-term vision in company creation.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Entrepreneurial Journey
Startup founders often seek scalable growth by building teams and securing external funding to accelerate company expansion, while solopreneurs prioritize independence and direct control over their business operations, often relying on personal resources. Selecting the right path depends on your risk tolerance, desired growth trajectory, and operational preferences, where founders embrace collaboration and investors, and solopreneurs focus on self-sufficiency and nimble decision-making. Understanding these distinctions helps entrepreneurs align their goals with the appropriate structure, maximizing potential for long-term success.
Related Important Terms
Operator-Founder Dichotomy
Startup founders typically build scalable companies by assembling teams and securing venture capital, focusing on rapid growth and market disruption, whereas solopreneurs operate independently, managing all aspects of their business to maintain full control and flexibility. This operator-founder dichotomy highlights that founders prioritize organizational expansion and delegation, while solopreneurs emphasize autonomy and hands-on management in company creation.
Solo SaaSpreneur
A Solo SaaSpreneur leverages specialized software-as-a-service expertise to create scalable, automated business models without the need for a traditional startup team. Unlike startup founders who seek external funding and build larger companies, Solo SaaSpreneurs prioritize efficiency, lean operations, and direct customer engagement to rapidly iterate and grow their ventures independently.
Co-Founder Dilution Risk
Startup founders face co-founder dilution risk as equity is divided among multiple partners, potentially reducing individual control and financial upside. Solopreneurs retain full ownership and decision-making power, avoiding dilution but shouldering all responsibilities and risks alone.
Bootstrapper Mindset
A startup founder often builds a scalable company with a team and external funding, while a solopreneur operates independently, relying heavily on the bootstrapper mindset to minimize costs and maximize resourcefulness. Embracing lean strategies and iterative product development enables both roles to innovate effectively despite limited initial capital.
Equity-Heavy Teaming
Startup founders typically build equity-heavy teams by distributing ownership stakes among co-founders, investors, and key employees to drive scalable growth and embed long-term commitment. Solopreneurs, however, retain full equity control, focusing on autonomous decision-making and agile execution without diluting ownership or relying on external equity partners.
Full-Stack Founder
A Full-Stack Founder combines technical, marketing, and operational skills, enabling rapid product development and agile decision-making in startup creation. Unlike solopreneurs who manage solo ventures with limited scalability, Full-Stack Founders drive scalable startups by leading cross-functional teams and securing venture capital.
Founder-Market Fit
Founder-market fit is crucial for both startup founders and solopreneurs, as it aligns their skills, experiences, and passions with the market needs, increasing the likelihood of successful company creation. While startup founders often seek complementary team members to scale rapidly, solopreneurs rely on their unique expertise and direct market engagement to drive business growth independently.
Lean Solopreneurship
Lean solopreneurship emphasizes streamlining business creation with minimal resources, allowing solo founders to rapidly test and iterate ideas without the overhead of a traditional startup team. Unlike startup founders who often seek venture capital and scale quickly, lean solopreneurs prioritize agile development, bootstrapping, and direct customer feedback to maintain control and reduce risk in early company formation.
Distributed Founder Model
Distributed Founder Model enhances company creation by allowing Startup Founders to leverage diverse expertise across geographies, unlike Solopreneurs who single-handedly manage all roles. This model accelerates innovation and scalability by fostering collaborative decision-making and resource sharing among co-founders situated in different locations.
Passthrough LLC Creator
A Passthrough LLC creator operating as a solopreneur maintains full control and benefits from simplified tax filings by reporting business income directly on personal returns, unlike a startup founder who often seeks external funding and scalability through complex equity structures. This streamlined approach favors individual entrepreneurs prioritizing flexibility and direct financial flow without the administrative burdens typical of multi-member startups.
Startup Founder vs Solopreneur for company creation. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com