Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new ventures and taking full ownership of risks and rewards, fostering groundbreaking ideas from conception to market launch. Intrapreneurs, operating within established organizations, leverage company resources to innovate and improve processes while navigating corporate structures. Both roles are essential for sustained innovation, with entrepreneurs focusing on external disruption and intrapreneurs enhancing internal growth.
Table of Comparison
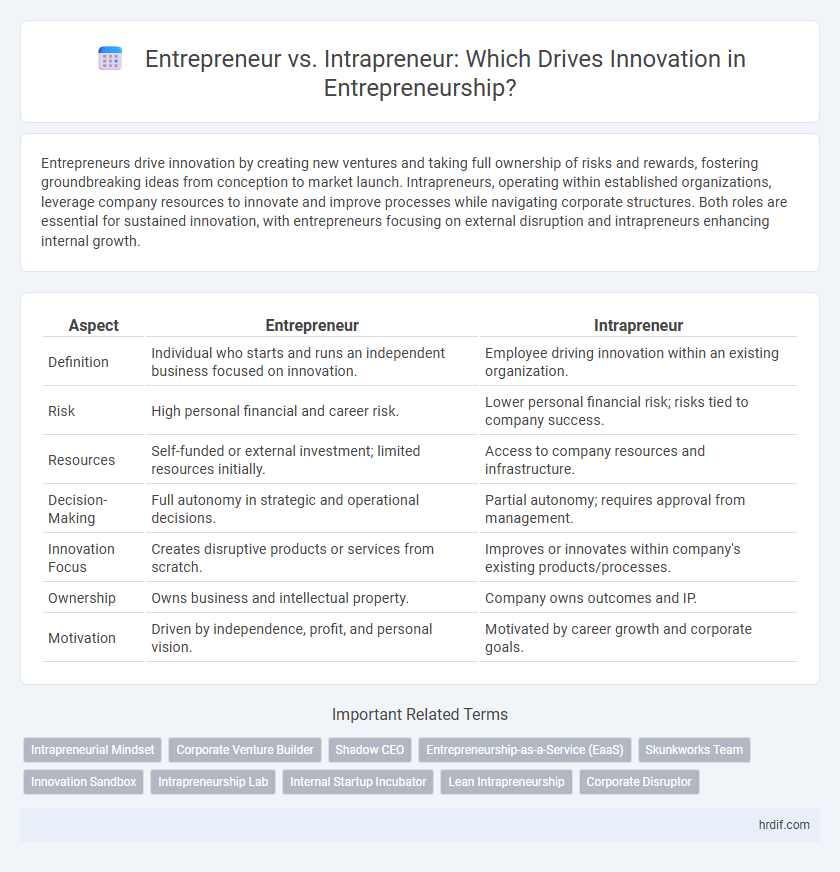
| Aspect | Entrepreneur | Intrapreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual who starts and runs an independent business focused on innovation. | Employee driving innovation within an existing organization. |
| Risk | High personal financial and career risk. | Lower personal financial risk; risks tied to company success. |
| Resources | Self-funded or external investment; limited resources initially. | Access to company resources and infrastructure. |
| Decision-Making | Full autonomy in strategic and operational decisions. | Partial autonomy; requires approval from management. |
| Innovation Focus | Creates disruptive products or services from scratch. | Improves or innovates within company's existing products/processes. |
| Ownership | Owns business and intellectual property. | Company owns outcomes and IP. |
| Motivation | Driven by independence, profit, and personal vision. | Motivated by career growth and corporate goals. |
Defining Entrepreneurs and Intrapreneurs
Entrepreneurs are individuals who create and manage new businesses, assuming financial risks to innovate and bring original products or services to market. Intrapreneurs operate within established organizations, leveraging existing resources to drive innovation and improve processes without bearing personal financial risk. Both roles are crucial for fostering innovation but differ in risk ownership, resource control, and organizational context.
Core Differences in Innovation Approach
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new ventures, leveraging risk-taking and autonomy to disrupt markets and develop original products or services. Intrapreneurs foster innovation within existing organizations by utilizing available resources and navigating corporate structures to improve processes and generate incremental advancements. The core difference lies in entrepreneurs operating independently with ownership stakes, while intrapreneurs innovate internally, balancing creativity with organizational constraints.
Risk-Taking: Entrepreneurship vs Intrapreneurship
Entrepreneurs embrace high-risk environments to launch new ventures, leveraging personal capital and market uncertainty to drive breakthrough innovations. Intrapreneurs operate within established organizations, managing moderate risks by utilizing existing resources while navigating corporate constraints to implement innovative projects. The contrast in risk-taking underscores entrepreneurs' willingness to face financial and market volatility, whereas intrapreneurs balance innovation with organizational stability.
Resource Access and Constraints
Entrepreneurs often face significant resource constraints, relying on limited capital and external funding to drive innovation independently. Intrapreneurs benefit from easier access to organizational resources such as established networks, technology, and expert teams, enabling faster innovation within company boundaries. Resource flexibility and risk tolerance directly influence how entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs capitalize on innovation opportunities.
Organizational Support and Autonomy
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by leveraging high levels of autonomy and seeking external organizational support to launch and scale ventures. Intrapreneurs foster innovation within existing companies by using company resources and structures while maintaining freedom to experiment and implement new ideas. Strong organizational support enables intrapreneurs to navigate internal barriers, whereas entrepreneurs rely more on external networks and self-directed decision-making to achieve innovation.
Innovation Speed and Scalability
Entrepreneurs drive innovation with rapid decision-making and bold risk-taking, enabling faster market entry and scalability through flexible business models. Intrapreneurs accelerate innovation within established organizations by leveraging existing resources and infrastructure, often achieving scalability with lower risk but slower speed due to corporate processes. Both roles are crucial for innovation ecosystems, with entrepreneurs excelling in disruptive breakthroughs and intrapreneurs optimizing incremental innovation at scale.
Impact on Company Culture
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by pioneering new ventures, often fostering a culture of risk-taking and agility within startups. In contrast, intrapreneurs innovate from within established companies, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration while leveraging existing resources. Both roles significantly shape company culture by embedding innovation values tailored to the organization's growth stage and strategic goals.
Career Growth and Learning Opportunities
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating and scaling new ventures, offering unparalleled career growth through complete ownership and risk management, while intrapreneurs innovate within established organizations, benefiting from structured learning opportunities and access to resources without the burden of startup uncertainties. Intrapreneurs leverage corporate networks to accelerate skill development in strategic innovation, whereas entrepreneurs cultivate diverse skill sets by navigating market challenges independently. Both roles foster distinct career trajectories, with entrepreneurs gaining expansive autonomy and intrapreneurs advancing through organizational support and collaboration.
Compensation and Recognition Structures
Entrepreneurs often receive equity stakes and profit-sharing opportunities that align compensation with business success, fostering high-risk innovation initiatives. Intrapreneurs typically benefit from structured salaries, performance bonuses, and formal recognition programs within established organizations, providing stable rewards linked to project impact. Organizations aiming to drive innovation must balance risk-sharing incentives for entrepreneurs with clear advancement pathways and acknowledgment frameworks for intrapreneurs.
Choosing Your Path: Entrepreneur or Intrapreneur?
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by founding startups, assuming full ownership and risk to bring disruptive ideas to market, while intrapreneurs innovate within established companies, leveraging existing resources to develop new products or processes. Choosing your path depends on your risk tolerance, desire for autonomy, and access to capital, as entrepreneurs face uncertainty but gain complete control, whereas intrapreneurs benefit from organizational support but have limited decision-making power. Both roles are crucial for technological advancement and economic growth, offering distinct opportunities to impact innovation ecosystems.
Related Important Terms
Intrapreneurial Mindset
The intrapreneurial mindset drives innovation within established organizations by fostering risk-taking, proactive problem-solving, and ownership of projects, enabling employees to act like entrepreneurs without the financial risks. Unlike entrepreneurs who build ventures from scratch, intrapreneurs leverage company resources and navigate corporate structures to accelerate product development and market adaptation.
Corporate Venture Builder
Corporate Venture Builders leverage intrapreneurs who innovate within established companies by driving startup-like projects, contrasting with entrepreneurs who launch independent ventures; this internal innovation accelerates market-ready solutions while mitigating external risks. By fostering intrapreneurial mindset, Corporate Venture Builders harness organizational resources to scale disruptive ideas faster than traditional entrepreneurship, optimizing innovation pipelines and generating competitive advantage.
Shadow CEO
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by taking full ownership of ventures, acting as Shadow CEOs who steer strategy and risk independently, while intrapreneurs foster innovation within established corporations by leveraging internal resources and navigating organizational constraints. This Shadow CEO mindset enables entrepreneurs to challenge market boundaries, whereas intrapreneurs innovate by aligning with corporate goals and culture.
Entrepreneurship-as-a-Service (EaaS)
Entrepreneurship-as-a-Service (EaaS) leverages intrapreneurs within organizations to drive innovation by applying entrepreneurial skills and risk-taking mindsets while utilizing existing company resources and infrastructure. Unlike traditional entrepreneurs, intrapreneurs accelerate product development and market disruption through structured corporate support, enabling scalable innovation without external venture risks.
Skunkworks Team
Skunkworks teams, often found within established companies, empower intrapreneurs to drive breakthrough innovation by operating with startup-like agility and autonomy. Entrepreneurs typically launch ventures independently, but intrapreneurs in skunkworks environments leverage corporate resources to rapidly develop disruptive products while mitigating organizational risks.
Innovation Sandbox
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new market opportunities and launching startups, while intrapreneurs innovate within existing companies by leveraging corporate resources and navigating organizational structures. The Innovation Sandbox serves as a collaborative environment encouraging both entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs to experiment with disruptive ideas, accelerating product development and enhancing competitive advantage.
Intrapreneurship Lab
Intrapreneurship Labs empower employees to innovate within established companies by providing resources, autonomy, and a startup-like environment that drives internal growth and competitive advantage. Unlike entrepreneurs who launch independent ventures, intrapreneurs leverage corporate support systems to accelerate innovation while mitigating risks associated with external entrepreneurship.
Internal Startup Incubator
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by launching external startups that bring disruptive products to market, while intrapreneurs foster innovation within existing organizations by leveraging Internal Startup Incubators to develop and scale new business ideas. Internal Startup Incubators empower intrapreneurs to access company resources, reduce risk, and accelerate innovation cycles without leaving the corporate environment.
Lean Intrapreneurship
Lean Intrapreneurship fosters innovation within established organizations by empowering employees to apply entrepreneurial principles such as rapid experimentation and customer-centric development without the risks faced by external entrepreneurs. This approach accelerates product innovation cycles and drives organizational agility by leveraging internal resources and market insights more efficiently than traditional entrepreneurship.
Corporate Disruptor
Corporate disruptors leverage intrapreneurship to drive innovation within established companies by fostering risk-taking and agile problem-solving, unlike entrepreneurs who build ventures independently. Intrapreneurs accelerate digital transformation and competitive advantage by applying startup mindset and disruptive strategies inside corporate structures.
Entrepreneur vs Intrapreneur for innovation role. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com