Entrepreneurs typically launch fully developed business models with established products or services, focusing on market entry and growth. Protopreneurs, on the other hand, experiment with innovative ideas and prototypes, prioritizing learning and adaptation in early-stage ventures. This approach allows protopreneurs to minimize risks while validating their concepts before committing extensive resources.
Table of Comparison
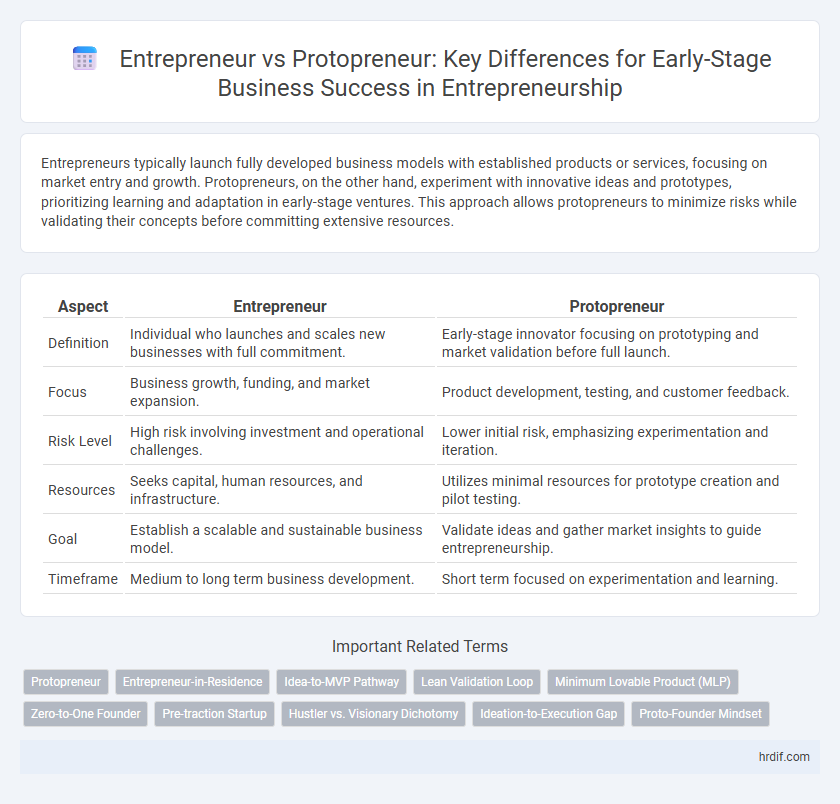
| Aspect | Entrepreneur | Protopreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual who launches and scales new businesses with full commitment. | Early-stage innovator focusing on prototyping and market validation before full launch. |
| Focus | Business growth, funding, and market expansion. | Product development, testing, and customer feedback. |
| Risk Level | High risk involving investment and operational challenges. | Lower initial risk, emphasizing experimentation and iteration. |
| Resources | Seeks capital, human resources, and infrastructure. | Utilizes minimal resources for prototype creation and pilot testing. |
| Goal | Establish a scalable and sustainable business model. | Validate ideas and gather market insights to guide entrepreneurship. |
| Timeframe | Medium to long term business development. | Short term focused on experimentation and learning. |
Defining the Entrepreneur and Protopreneur
Entrepreneurs are individuals who launch and manage early-stage businesses by taking on financial risks to bring innovative ideas to market and achieve sustainable growth. Protopreneurs differ by emphasizing experimental validation and iterative learning, leveraging prototypes to test business concepts rapidly before full-scale launch. This distinction highlights that protopreneurs prioritize quick adaptability and customer feedback integration, crucial for minimizing uncertainty in nascent ventures.
Key Characteristics: Entrepreneur vs Protopreneur
Entrepreneurs are visionaries who identify market opportunities and take calculated risks to build scalable businesses, emphasizing innovation, leadership, and long-term growth. Protopreneurs focus on early-stage experimentation, rapid prototyping, and validating ideas through real-world feedback to minimize failure in uncertain markets. Both roles require adaptability and resilience, but entrepreneurs drive strategic direction while protopreneurs emphasize iterative development and market testing.
Motivation and Mindset Differences
Entrepreneurs are driven by a long-term vision to build scalable, high-impact businesses, often embracing risk and uncertainty as integral to growth and innovation. Protopreneurs prioritize experimentation and adaptability, motivated by learning and rapid iteration to validate ideas before committing significant resources. This mindset fosters a fail-fast approach, emphasizing agile responses to market feedback over immediate business scaling.
Risk Tolerance: Who Takes the Bigger Leap?
Entrepreneurs demonstrate high risk tolerance by investing significant personal resources and committing fully to unproven business ideas, often facing substantial financial and market uncertainties. Protopreneurs exhibit moderate risk tolerance by experimenting with minimal viable products and iterative testing, seeking to validate concepts before making full-scale commitments. Understanding these risk profiles helps early-stage businesses balance innovation with strategic caution for sustainable growth.
Approach to Innovation and Problem-Solving
Entrepreneurs typically pursue well-defined business models, focusing on scaling proven innovations through structured problem-solving methods and market validation. Protopreneurs adopt an experimental approach, embracing rapid iteration and continuous learning to pivot ideas based on real-time feedback and evolving market needs. This agility enables protopreneurs to explore disruptive innovations and adapt solutions dynamically during early-stage development.
Leadership Style and Team Building
Entrepreneurs often exhibit a visionary leadership style, making decisive choices that steer early-stage businesses toward growth, while protopreneurs emphasize collaborative leadership, fostering team cohesion and adaptive problem-solving. Protopreneurs prioritize building diverse, cross-functional teams to navigate uncertainty, leveraging collective expertise to iterate rapidly. This distinction in leadership and team-building approaches significantly impacts innovation, resilience, and scalability during the critical early phases of business development.
Funding Strategies: Diverging Paths
Entrepreneurs typically pursue traditional funding strategies such as venture capital, angel investors, and crowdfunding, focusing on scaling their early-stage business rapidly. Protopreneurs often rely on more flexible and experimental funding approaches, including bootstrapping, micro-investments, and pre-sales, emphasizing validation and market fit before seeking large-scale investment. These diverging paths reflect distinct priorities and risk tolerances inherent to each approach in early-stage business development.
Common Challenges in Early-Stage Ventures
Entrepreneurs and protopreneurs both face common challenges in early-stage ventures, including limited access to capital, market uncertainty, and the need for rapid product validation. While entrepreneurs often focus on launching fully developed business models, protopreneurs emphasize experimenting with prototypes and iterative testing to minimize risk. Navigating these challenges requires strong adaptability, resource management, and a clear understanding of customer feedback to pivot effectively.
Success Metrics and Growth Perspectives
Entrepreneurs measure success through scalable revenue growth, market share expansion, and securing investment rounds, reflecting long-term business viability. Protopreneurs prioritize rapid prototyping, customer feedback integration, and agile iteration as key metrics to validate concepts and pivot quickly. Growth perspectives differ as entrepreneurs aim for steady scaling, while protopreneurs focus on early-stage experimentation to identify viable business models before full market entry.
Choosing the Right Path: Entrepreneur or Protopreneur?
Choosing the right path between entrepreneur and protopreneur hinges on the business stage and risk tolerance: entrepreneurs typically launch fully developed ventures seeking significant market impact, while protopreneurs focus on iterative testing and validation of ideas with limited resources. Early-stage businesses benefit from the protopreneur approach, emphasizing lean methodologies, rapid prototyping, and customer feedback to refine their product-market fit. Understanding these distinctions enables founders to align their strategies with growth objectives and capital efficiency, optimizing success potential.
Related Important Terms
Protopreneur
Protopreneurs embody the experimental mindset essential for early-stage businesses, rapidly testing and iterating ideas to find viable market solutions. Unlike traditional entrepreneurs who plan extensively, protopreneurs prioritize agility and learning through customer feedback to minimize risk and accelerate growth.
Entrepreneur-in-Residence
Entrepreneur-in-Residence (EIR) roles bridge the gap between traditional entrepreneurs and protopreneurs by providing early-stage ventures with experienced guidance and strategic insights during critical development phases. EIRs leverage their hands-on entrepreneurial expertise to validate market opportunities and accelerate scalable business models, enhancing the likelihood of startup success in uncertain environments.
Idea-to-MVP Pathway
Entrepreneurs focus on validating scalable business models through structured MVP development, emphasizing market fit and customer feedback loops. Protopreneurs prioritize rapid prototyping and experimentation, leveraging iterative design to refine core ideas before full market entry.
Lean Validation Loop
Entrepreneurs focus on launching and scaling startups with validated business models, while protopreneurs emphasize iterative experimentation within the Lean Validation Loop to rapidly test assumptions and pivot early-stage ideas. The Lean Validation Loop accelerates product-market fit by continuously gathering customer feedback, minimizing risk, and optimizing resource allocation during the prototyping phase.
Minimum Lovable Product (MLP)
Entrepreneurs prioritize launching a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to test market fit, while Protopreneurs emphasize the Minimum Lovable Product (MLP) to create early emotional engagement and customer loyalty. The MLP strategy accelerates user feedback and fosters brand advocates, enhancing growth potential in early-stage businesses.
Zero-to-One Founder
Zero-to-One founders distinguish themselves by pioneering entirely new markets or innovative products, embodying the essence of entrepreneurship through creating unique value from scratch. Protopreneurs, meanwhile, validate early-stage ideas by testing assumptions and iterating prototypes, serving as crucial catalysts in transforming nascent concepts into scalable ventures.
Pre-traction Startup
Entrepreneurs typically focus on launching and scaling businesses with validated market demand, while protopreneurs emphasize early-stage experimentation, rapid prototyping, and customer discovery in pre-traction startups. In the pre-traction phase, protopreneurs leverage iterative learning and agile development to identify product-market fit before committing significant resources to scaling.
Hustler vs. Visionary Dichotomy
Entrepreneurs often embody the hustler mindset, aggressively driving early-stage business growth through hands-on execution and rapid problem-solving; protopreneurs, by contrast, lean toward visionary thinking, strategically anticipating market shifts and innovating future-oriented solutions. This hustler versus visionary dichotomy highlights the essential balance between immediate operational grit and long-term conceptual foresight in launching successful startups.
Ideation-to-Execution Gap
Entrepreneurs often face challenges bridging the ideation-to-execution gap, as they typically focus on developing a comprehensive business model and scaling operations. Protopreneurs, in contrast, emphasize rapid prototyping and iterative testing to validate ideas quickly, minimizing risks during early-stage business development.
Proto-Founder Mindset
The Proto-Founder mindset emphasizes agile experimentation and rapid iteration, distinguishing Protopreneurs from traditional Entrepreneurs by prioritizing validating business hypotheses before scaling. Embracing uncertainty, Protopreneurs leverage lean startup principles to pivot efficiently, fostering innovation in early-stage ventures.
Entrepreneur vs Protopreneur for early-stage business. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com