Employees with a generalist skill set excel in versatility, adapting to various tasks and roles across departments, which enhances organizational flexibility. T-shaped employees combine broad knowledge with deep expertise in a specific area, driving innovation and collaboration within specialized teams. Balancing generalist adaptability and T-shaped specialization can optimize workforce productivity and foster dynamic problem-solving.
Table of Comparison
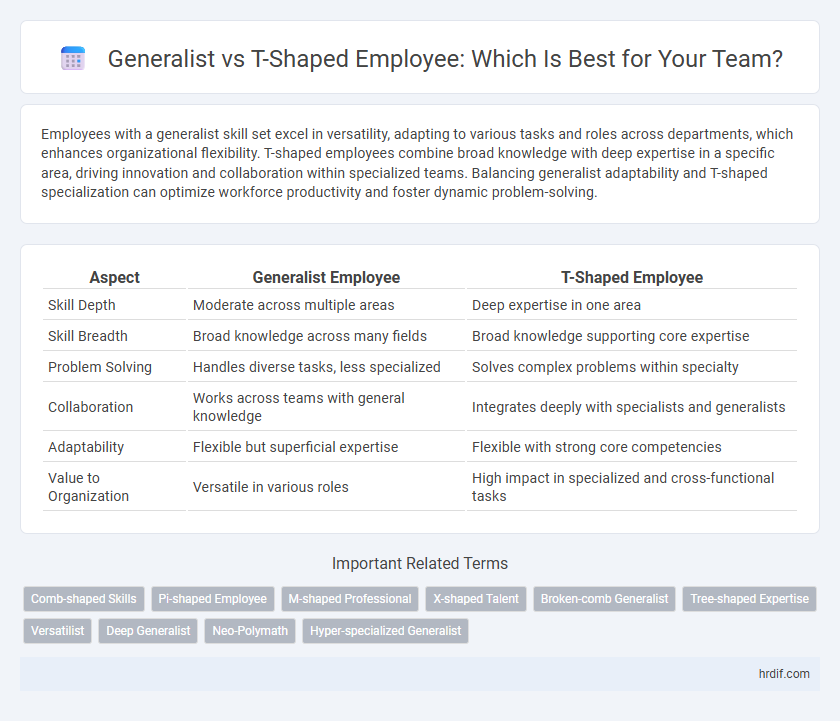
| Aspect | Generalist Employee | T-Shaped Employee |
|---|---|---|
| Skill Depth | Moderate across multiple areas | Deep expertise in one area |
| Skill Breadth | Broad knowledge across many fields | Broad knowledge supporting core expertise |
| Problem Solving | Handles diverse tasks, less specialized | Solves complex problems within specialty |
| Collaboration | Works across teams with general knowledge | Integrates deeply with specialists and generalists |
| Adaptability | Flexible but superficial expertise | Flexible with strong core competencies |
| Value to Organization | Versatile in various roles | High impact in specialized and cross-functional tasks |
Understanding Generalist and T-Shaped Employee Models
Generalist employees possess broad skills across multiple domains, enabling flexibility and adaptability in various tasks and projects. T-Shaped employees complement this by having deep expertise in one specialized area while maintaining a working knowledge in related fields, fostering both specialization and collaboration. Understanding these models helps organizations optimize team composition for innovation, agility, and skill diversity.
Key Differences Between Generalists and T-Shaped Professionals
Generalists possess broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, enabling flexibility and adaptability in various roles, while T-shaped professionals combine broad understanding with deep expertise in one or two areas, optimizing both versatility and specialization. Generalists excel in coordination and problem-solving across domains, whereas T-shaped employees drive innovation and contribute significant value in their core specialties. The key difference lies in the depth of expertise: generalists maintain a wide skill set, whereas T-shaped professionals cultivate mastery in specific fields alongside general competencies.
Advantages of Being a Generalist in the Workplace
A generalist in the workplace offers versatility by possessing a broad skill set applicable to multiple roles, enabling seamless adaptation to diverse tasks and challenges. This flexibility supports cross-functional collaboration and problem-solving, which enhances overall team productivity. Generalists often drive innovation by integrating insights from different domains, making them valuable assets in dynamic business environments.
Benefits of T-Shaped Skills for Employees
T-shaped skills enhance employee adaptability by combining deep expertise in one area with broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, enabling seamless collaboration across teams. This versatility increases innovation potential and problem-solving capabilities, driving higher productivity and career growth opportunities. Employers value T-shaped employees for their ability to bridge gaps between specialized departments and contribute to overall business agility.
When to Choose a Generalist vs T-Shaped Approach
Choosing a generalist employee is ideal for roles requiring versatility and broad skill sets across multiple functions, especially in startups or dynamic environments where adaptability is crucial. T-shaped employees, possessing deep expertise in one area alongside a broad understanding of related fields, excel in collaborative settings and teams aiming for innovation and cross-functional solutions. Organizations should prefer generalists for flexible task management and T-shaped professionals when depth of knowledge combined with interdisciplinary collaboration drives competitive advantage.
Industry Preferences: Generalist or T-Shaped Employees?
Industries such as consulting, startups, and creative sectors often prefer T-shaped employees for their ability to combine deep expertise with broad skills across multiple domains, enhancing innovation and adaptability. In contrast, traditional industries like manufacturing, finance, and government tend to favor generalist employees who can manage a wide range of tasks and responsibilities efficiently. Companies increasingly value T-shaped professionals in technology and R&D fields where specialized knowledge must integrate with cross-functional collaboration.
Career Growth Potential: Generalist vs T-Shaped Employees
Generalist employees possess broad skills across multiple domains, enabling flexibility and adaptability in diverse roles, which supports steady career growth through varied experiences. T-shaped employees combine deep expertise in one area with a broad understanding of related fields, accelerating advancement opportunities by driving innovation and cross-functional collaboration. Organizations value T-shaped professionals for their ability to solve complex problems and lead interdisciplinary teams, often resulting in faster promotions and leadership roles.
Building a T-Shaped Skill Set as an Employee
Building a T-shaped skill set as an employee involves developing deep expertise in a core area while acquiring broad knowledge across related fields to enhance collaboration and adaptability. This approach fosters innovation and problem-solving by enabling employees to contribute specialized skills and understand diverse perspectives within a team. Organizations benefit from T-shaped employees through improved cross-functional workflows and greater agility in dynamic work environments.
Challenges Faced by Generalists and T-Shaped Professionals
Generalists often face challenges in achieving deep expertise, which can limit their ability to solve complex, specialized problems and reduce their competitiveness in niche areas. T-shaped professionals struggle to balance the breadth and depth of skills, sometimes leading to overextension or gaps in knowledge within rapidly evolving fields. Both types encounter difficulties in career progression, with generalists needing to prove value beyond versatility and T-shaped professionals needing to continuously update their specialized expertise.
Future Workplace Trends: Demand for Generalist vs T-Shaped Employees
Future workplace trends reveal a rising demand for T-shaped employees who combine deep expertise in a specific area with broad skills across multiple disciplines, enabling agile collaboration and innovation. Employers increasingly value generalists for their versatility and problem-solving abilities, particularly in dynamic, cross-functional roles requiring adaptability. The evolving business landscape favors a balanced workforce blending T-shaped specialists with generalists to drive growth and competitive advantage.
Related Important Terms
Comb-shaped Skills
Employees with comb-shaped skills possess deep expertise in multiple areas combined with broad knowledge across various disciplines, enhancing versatility and adaptability in dynamic work environments. Unlike generalists who have broad but shallow knowledge or T-shaped professionals with depth in one domain plus breadth, comb-shaped employees maximize problem-solving capabilities through multifaceted skill sets.
Pi-shaped Employee
Pi-shaped employees combine deep expertise in two distinct areas with broad generalist skills, enabling versatile problem-solving and cross-functional collaboration. Their dual-specialized knowledge enhances innovation and adaptability, outperforming traditional generalists and T-shaped professionals in dynamic, multidisciplinary work environments.
M-shaped Professional
An M-shaped professional combines deep expertise in multiple core areas with broad cross-functional skills, enabling versatility beyond traditional generalist or T-shaped employees. This hybrid skill set supports innovation and adaptability, driving organizational growth through multidisciplinary collaboration.
X-shaped Talent
X-shaped talent combines the broad skill set of a generalist with deep expertise in multiple areas, enhancing cross-functional collaboration and innovation within organizations. This multifaceted competency enables employees to adapt rapidly, solve complex problems, and drive strategic initiatives more effectively than traditional generalist or T-shaped profiles.
Broken-comb Generalist
Broken-comb Generalists possess a diverse skill set across multiple domains with deep expertise in several key areas, blending the breadth of knowledge typical of generalists with the depth seen in T-Shaped employees. This versatility enables Broken-comb Generalists to adapt quickly to complex tasks and innovate by connecting insights from various disciplines.
Tree-shaped Expertise
Tree-shaped expertise in employees combines broad generalist knowledge with deep, interconnected skills spanning multiple disciplines, enabling adaptive problem-solving and innovation. This approach surpasses traditional T-shaped skills by fostering a multi-branched proficiency model that supports complex project collaboration and strategic versatility.
Versatilist
A versatilist employee combines broad generalist skills with deep expertise in key areas, enabling adaptability across various functions while maintaining specialized knowledge. This unique blend enhances organizational agility by fostering innovative problem-solving and cross-disciplinary collaboration.
Deep Generalist
A Deep Generalist employee combines broad interdisciplinary skills with specialized expertise in multiple areas, enabling flexible problem-solving and adaptive innovation across diverse projects. Unlike T-Shaped professionals who emphasize depth in a single domain alongside broad knowledge, Deep Generalists maintain substantial proficiency across several fields, fostering cross-functional collaboration and strategic insights.
Neo-Polymath
A Neo-Polymath employee combines deep expertise across multiple disciplines with broad generalist skills, surpassing traditional T-Shaped models by constantly evolving and integrating knowledge from diverse fields to drive innovation and adaptability. This approach enhances problem-solving capabilities, making Neo-Polymaths valuable assets for organizations seeking dynamic and interdisciplinary talent in rapidly changing markets.
Hyper-specialized Generalist
A hyper-specialized generalist employee combines broad industry knowledge with deep expertise in a specific domain, enhancing adaptability and problem-solving across multiple functions. This blend fosters innovation and agility, enabling organizations to swiftly respond to complex challenges while leveraging specialized skills.
Generalist vs T-Shaped for employee. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com