White-collar employees typically work in office settings performing managerial, administrative, or professional tasks that require specialized knowledge or education. Green-collar employees focus on environmentally sustainable jobs such as renewable energy, conservation, and waste management, often blending technical skills with a commitment to ecological responsibility. Both roles play crucial parts in the modern workforce, addressing different industry needs and career aspirations.
Table of Comparison
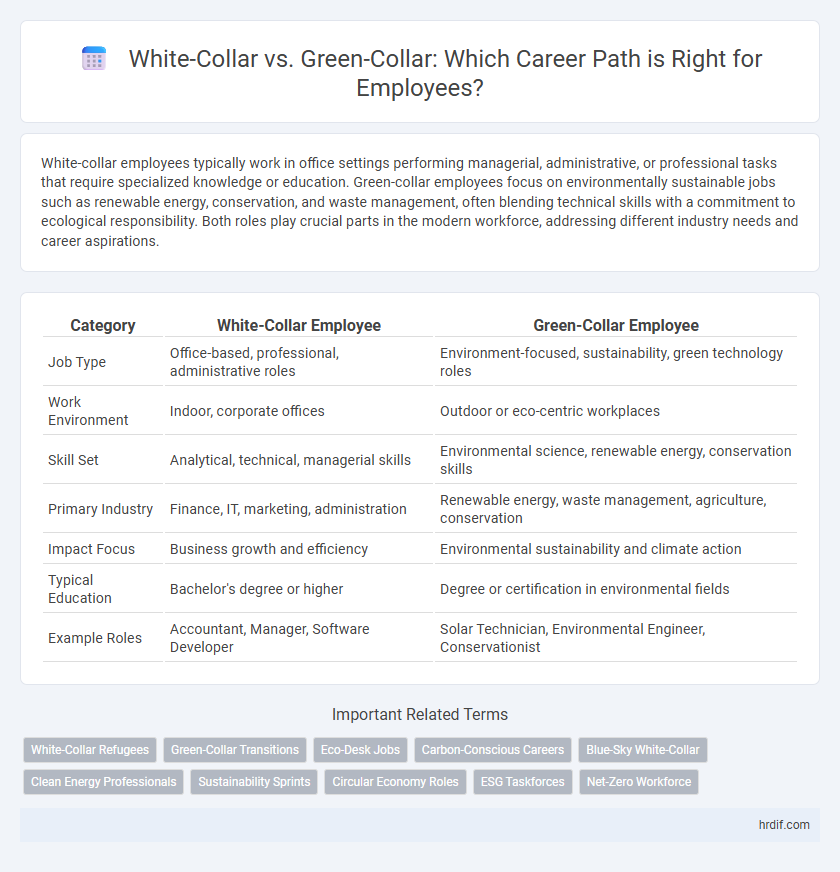
| Category | White-Collar Employee | Green-Collar Employee |
|---|---|---|
| Job Type | Office-based, professional, administrative roles | Environment-focused, sustainability, green technology roles |
| Work Environment | Indoor, corporate offices | Outdoor or eco-centric workplaces |
| Skill Set | Analytical, technical, managerial skills | Environmental science, renewable energy, conservation skills |
| Primary Industry | Finance, IT, marketing, administration | Renewable energy, waste management, agriculture, conservation |
| Impact Focus | Business growth and efficiency | Environmental sustainability and climate action |
| Typical Education | Bachelor's degree or higher | Degree or certification in environmental fields |
| Example Roles | Accountant, Manager, Software Developer | Solar Technician, Environmental Engineer, Conservationist |
Understanding White-Collar and Green Collar Roles
White-collar employees typically work in office settings, engaging in administrative, managerial, or professional tasks that require specialized knowledge and formal education. Green-collar workers focus on environmentally sustainable jobs such as renewable energy, conservation, and sustainable agriculture, emphasizing skills that contribute to ecological preservation and green technology innovations. Understanding the distinct roles helps businesses align workforce strategies with economic and environmental goals.
Key Differences: White-Collar vs Green Collar Jobs
White-collar jobs typically involve professional, managerial, or administrative work performed in office environments, emphasizing mental tasks and specialized skills. Green-collar jobs focus on environmentally sustainable industries, including renewable energy, conservation, and eco-friendly manufacturing, often requiring technical or trade skills. Key differences lie in the nature of work, workplace settings, and the impact on environmental sustainability priorities.
Skills Required for White-Collar and Green Collar Employees
White-collar employees typically require advanced analytical, communication, and technical skills, often gained through higher education and professional training, to perform tasks in offices, management, and knowledge-based roles. Green-collar employees need specialized skills related to environmental sustainability, renewable energy, and conservation practices, combining manual labor with technical know-how to support eco-friendly industries. Both sectors emphasize problem-solving and adaptability, but green-collar roles often demand hands-on expertise in green technologies and regulatory compliance.
Salary and Job Security: A Comparative Analysis
White-collar employees typically earn higher salaries ranging from $60,000 to over $100,000 annually, benefiting from greater job security due to corporate structures and union protections. Green-collar workers, often in renewable energy or environmental sectors, earn between $40,000 and $70,000, with job security growing as demand for sustainability rises. Salary trends indicate white-collar roles maintain steady growth, while green-collar positions experience increasing employment opportunities driven by governmental policies and global climate initiatives.
Work Environment: Office vs Field
White-collar employees typically work in office settings characterized by desk jobs, digital tools, and controlled environments, emphasizing cognitive tasks and administrative responsibilities. Green-collar employees operate primarily in outdoor or field environments, engaging in sustainable practices such as environmental conservation, renewable energy projects, and agricultural work. The contrasting work environments influence daily routines, physical demands, and interaction with technology for each employee category.
Growth Opportunities in White-Collar and Green Collar Careers
White-collar careers often provide extensive growth opportunities through advanced education, professional certifications, and leadership roles in sectors like finance, technology, and management. Green-collar careers emphasize growth in sustainable industries such as renewable energy, environmental conservation, and urban farming, with increasing demand for specialized skills and innovation. Both paths offer upward mobility, but white-collar growth focuses on corporate hierarchy, while green-collar growth centers on sustainability-driven expertise and environmental impact.
Impact of Technology on White-Collar and Green Collar Jobs
Technology has significantly transformed white-collar jobs by automating routine tasks, enhancing data analysis capabilities, and enabling remote work, which increases productivity but also demands continuous skill upgrading. In green-collar jobs, technology drives innovation in sustainable practices, such as renewable energy systems and environmental monitoring tools, improving efficiency while creating new roles focused on eco-friendly solutions. The evolving tech landscape necessitates employees in both sectors to adapt rapidly to maintain job relevance and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact in Career Choices
White-collar employees increasingly prioritize sustainability by choosing careers in industries focused on reducing environmental impact, such as renewable energy, environmental consulting, and sustainable finance. Green-collar jobs directly contribute to environmental preservation through roles in clean energy installation, conservation, and eco-friendly technology development. The growing demand for sustainable practices influences career paths, promoting a shift toward green-collar employment with measurable benefits for ecological health and corporate social responsibility.
Educational Paths for White-Collar and Green Collar Positions
White-collar employees typically pursue higher education such as bachelor's or advanced degrees in fields like business, law, or technology, emphasizing theoretical knowledge and professional certifications. Green-collar positions often require specialized vocational training, certifications in environmental technologies, or associate degrees focused on sustainability and renewable energy practices. Emphasizing practical skills and hands-on experience, green-collar education paths align with industries like environmental management, conservation, and clean energy sectors.
Choosing the Right Path: White-Collar or Green Collar for Your Future
Choosing between white-collar and green-collar careers hinges on individual skills, industry growth, and personal values. White-collar jobs typically involve office-based, professional roles in sectors such as finance, technology, or law, offering stability and higher earning potential. Green-collar careers focus on environmental sustainability, renewable energy, and conservation efforts, appealing to employees passionate about combating climate change and fostering eco-friendly innovation.
Related Important Terms
White-Collar Refugees
White-collar refugees, typically professionals displaced due to economic shifts or technological advancements, face unique challenges in transitioning to green-collar roles which emphasize environmental sustainability and manual skilled labor. Understanding the skill gaps and retraining needs of white-collar refugees is critical for integrating them into the growing green-collar workforce focused on renewable energy, conservation, and sustainable infrastructure.
Green-Collar Transitions
Green-collar employees specialize in environmentally sustainable roles such as renewable energy, conservation, and eco-friendly construction, driving the shift towards a low-carbon economy. Transitioning from traditional white-collar jobs to green-collar positions involves acquiring skills in clean technology, environmental policy, and sustainable resource management to meet the growing demand for eco-conscious expertise.
Eco-Desk Jobs
White-collar employees typically work in office environments involving managerial, administrative, or professional tasks, whereas green-collar employees are engaged in environmentally focused roles promoting sustainability and eco-friendly practices. Eco-desk jobs combine elements of both, requiring white-collar skills to develop, manage, and implement green initiatives within corporate or organizational settings.
Carbon-Conscious Careers
White-collar employees in carbon-conscious careers often engage in environmental policy, sustainability consulting, and green technology development, driving corporate responsibility towards reducing carbon footprints. Green-collar employees focus on hands-on roles such as renewable energy installation, environmental restoration, and sustainable agriculture, directly contributing to ecological resilience and carbon reduction efforts.
Blue-Sky White-Collar
Blue-Sky white-collar employees, often engaged in innovative, strategic, and forward-thinking roles, contrast sharply with traditional white-collar professionals focused on administrative or routine office tasks. These employees drive sustainable development and creative problem-solving, aligning corporate goals with environmental and social responsibility, thereby bridging white-collar expertise with green-collar values.
Clean Energy Professionals
Clean energy professionals, often categorized as green-collar employees, specialize in roles supporting renewable energy, energy efficiency, and environmental sustainability, contrasting with white-collar workers who typically engage in office-based or administrative tasks. Green-collar jobs are critical in driving the transition to a low-carbon economy, encompassing positions such as solar panel installers, wind turbine technicians, and energy auditors.
Sustainability Sprints
White-collar employees typically engage in strategic planning and innovation during Sustainability Sprints, leveraging their expertise to develop eco-friendly business solutions and policies. Green-collar workers focus on implementing these sustainability initiatives through hands-on roles in renewable energy, conservation projects, and environmental maintenance, driving practical change on the ground.
Circular Economy Roles
White-collar employees in circular economy roles typically focus on designing sustainable products, managing supply chains, and developing policies that promote resource efficiency. Green-collar workers are often engaged in hands-on activities such as recycling, renewable energy installation, and waste management to support the implementation of circular economy principles.
ESG Taskforces
White-collar employees typically lead ESG taskforces by developing sustainability strategies, implementing corporate governance policies, and overseeing social responsibility initiatives, ensuring alignment with environmental, social, and governance criteria. Green-collar employees execute these strategies on the ground through roles in renewable energy, conservation, and sustainable operations, directly contributing to an organization's environmental impact and compliance goals.
Net-Zero Workforce
White-collar employees primarily drive strategic decisions and innovation essential for achieving a net-zero workforce, while green-collar workers implement sustainable practices and manage environmental technologies on the ground. Combining the expertise of both white-collar professionals and green-collar laborers is crucial for organizations aiming to meet net-zero carbon emission targets and foster long-term green job growth.
White-collar vs Green Collar for Employee Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com