Employees who are salaried benefit from consistent monthly income and job security, while gig workers enjoy flexibility and autonomy but face income variability. Salaried roles often include benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, which gig positions typically lack. Choosing between salaried and gig work depends on personal priorities like stability versus freedom and the need for structured benefits.
Table of Comparison
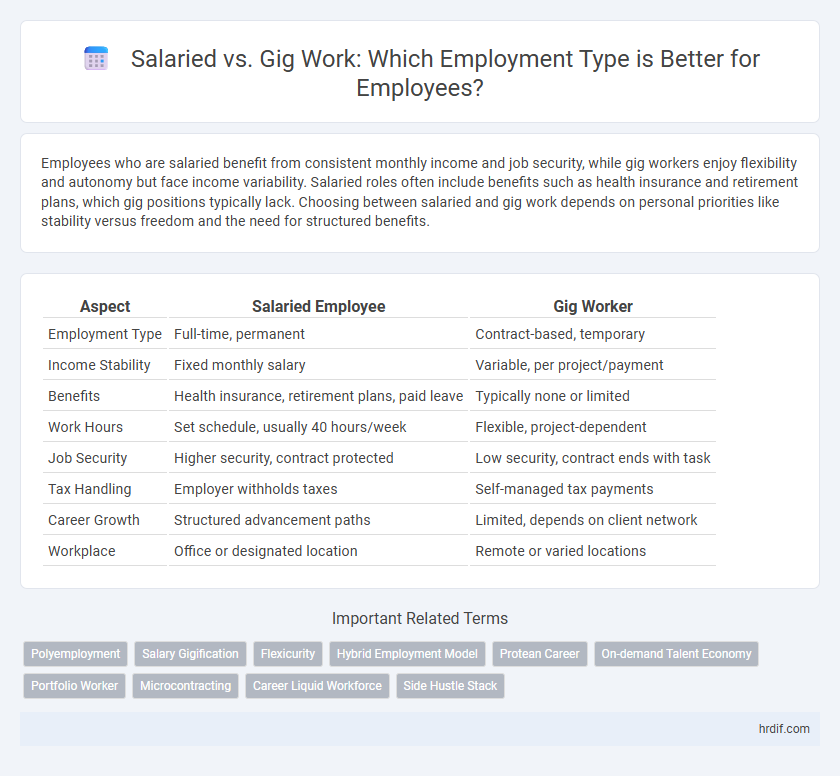
| Aspect | Salaried Employee | Gig Worker |
|---|---|---|
| Employment Type | Full-time, permanent | Contract-based, temporary |
| Income Stability | Fixed monthly salary | Variable, per project/payment |
| Benefits | Health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave | Typically none or limited |
| Work Hours | Set schedule, usually 40 hours/week | Flexible, project-dependent |
| Job Security | Higher security, contract protected | Low security, contract ends with task |
| Tax Handling | Employer withholds taxes | Self-managed tax payments |
| Career Growth | Structured advancement paths | Limited, depends on client network |
| Workplace | Office or designated location | Remote or varied locations |
Understanding Salaried Employment
Salaried employment offers employees a fixed annual income, providing financial stability and predictable benefits such as healthcare, retirement plans, and paid time off. This employment type often requires adherence to set schedules and job duties defined by the employer, promoting a structured work environment. Understanding the trade-offs between consistent earnings and flexibility is essential when comparing salaried roles to gig work arrangements.
What is Gig Work?
Gig work refers to short-term, flexible jobs typically performed by independent contractors or freelancers rather than salaried employees. This type of employment emphasizes project-based tasks, offering workers autonomy over their schedules but often lacks traditional benefits like health insurance or retirement plans. Platforms such as Uber, Upwork, and Fiverr are common marketplaces where gig workers connect with clients seeking specific services.
Job Security: Salaried vs Gig Roles
Salaried employees enjoy enhanced job security with consistent income, benefits, and legal protections, reducing financial uncertainty. Gig roles offer flexibility but often lack steady pay and social benefits, leading to potential income instability. Understanding these distinctions helps employees balance security needs with work autonomy preferences.
Income Stability and Predictability
Salaried employees benefit from consistent monthly income and predictable paychecks, making financial planning straightforward. Gig workers often face variable earnings due to fluctuating demand and project availability, resulting in income instability. Stable income from salaried positions supports long-term financial commitments, while gig income requires flexible budgeting strategies.
Work-Life Balance Considerations
Salaried employees often benefit from predictable income and structured work hours, which can enhance work-life balance by providing stability and routine. Gig workers experience greater flexibility in scheduling but may face income variability and inconsistent workloads, potentially increasing stress and impacting personal time. Evaluating work-life balance preferences is essential when choosing between salaried positions and gig opportunities.
Benefits and Perks Comparison
Salaried employees typically receive comprehensive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and job security, which gig workers often lack. Gig workers enjoy flexible schedules and the ability to diversify income streams but usually must manage their own taxes, health insurance, and retirement savings. Understanding these differences helps employees weigh the value of stability and perks against flexibility and autonomy in their work arrangements.
Career Growth Opportunities
Salaried employees typically benefit from structured career growth opportunities, including promotions, professional development programs, and consistent performance reviews that support long-term advancement. Gig workers often experience limited upward mobility due to the project-based nature of assignments and lack of formal organizational support. Investing in skill-building and networking remains crucial for gig workers to enhance their career prospects despite fewer traditional growth pathways.
Flexibility in Work Arrangements
Salaried employees typically experience structured work hours with limited flexibility, whereas gig workers enjoy the freedom to choose their schedules and projects, enhancing work-life balance. Gig arrangements allow individuals to tailor their workloads based on personal preferences and availability, promoting autonomy. Flexibility in gig work can lead to increased job satisfaction and adaptability, contrasting with the predictability and stability found in salaried positions.
Legal Rights and Protections
Salaried employees benefit from stronger legal rights and protections, including guaranteed minimum wage, overtime pay, unemployment benefits, and workplace safety regulations under laws like the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) and Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA). Gig workers, classified often as independent contractors, typically lack these protections and are excluded from many labor laws that safeguard salaried employees, limiting their access to benefits like workers' compensation and collective bargaining rights. The classification impacts eligibility for unemployment benefits and antidiscrimination protections under Title VII, highlighting significant legal disparities between salaried employees and gig workers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Career
Choosing between salaried and gig work depends on your career goals, financial stability, and desired flexibility. Salaried positions offer consistent income, benefits, and job security, while gig work provides autonomy and varied experiences but with income fluctuations and limited benefits. Assessing personal priorities and market trends can guide employees in making the right choice for long-term career growth.
Related Important Terms
Polyemployment
Polyemployment reflects a growing trend where employees engage simultaneously in salaried jobs and gig work, combining steady income with flexible, project-based earnings. This hybrid employment model enhances financial resilience and diversifies skillsets, enabling workers to adapt to dynamic job markets while maximizing overall compensation.
Salary Gigification
Salary gigification transforms traditional salaried roles into flexible, project-based engagements, enabling employees to diversify income sources and enhance skill adaptability. This shift fosters dynamic workforce participation, appealing to professionals seeking autonomy while maintaining financial stability through hybrid compensation models.
Flexicurity
Salaried employees benefit from financial stability and access to social security, while gig workers enjoy greater work flexibility but often face limited labor protections; flexicurity aims to balance these by combining flexible job opportunities with robust social safety nets. Implementing flexicurity policies enhances workforce adaptability and mitigates the risks associated with non-standard employment contracts in the evolving labor market.
Hybrid Employment Model
The hybrid employment model combines features of salaried and gig work, allowing employees to enjoy stable income alongside flexible project-based assignments, enhancing workforce adaptability and job satisfaction. Organizations leverage this model to optimize talent utilization, balancing predictable payroll costs with the dynamic demands of gig economy tasks.
Protean Career
Salaried employees typically experience structured career paths with predictable income, whereas gig workers navigate protean careers characterized by self-directed, flexible, and adaptive job roles. Embracing a protean career allows employees to prioritize personal values and continuous skill development over traditional employment stability.
On-demand Talent Economy
Salaried employees benefit from stable income and comprehensive benefits, while gig workers in the on-demand talent economy enjoy flexibility and autonomy with varied project opportunities. The rise of digital platforms has accelerated gig work, highlighting the need for businesses to balance workforce agility with talent retention strategies.
Portfolio Worker
Portfolio workers blend salaried stability with gig flexibility by managing multiple incomes through diverse projects and freelance roles, enhancing career resilience and skill development. This hybrid employment model leverages the security of a regular salary while capitalizing on the entrepreneurial opportunities of gig work for optimized professional growth.
Microcontracting
Microcontracting offers employees flexible, short-term engagements compared to traditional salaried positions, enabling access to diverse projects without long-term commitment. This model leverages digital platforms to match skills with specific tasks, enhancing autonomy while challenging benefits and job security typical of salaried employment.
Career Liquid Workforce
Salaried employees benefit from stability, structured career growth, and consistent income, while gig workers in a liquid workforce experience flexibility, project-based opportunities, and diverse skill development. The rise of the liquid workforce emphasizes adaptability, with employees balancing traditional roles and gig assignments to enhance career resilience and marketability.
Side Hustle Stack
Salaried employees benefit from steady income and job security, while gig workers enjoy flexible schedules and diverse income streams, making the Side Hustle Stack a strategic approach to combine both for financial resilience. Integrating multiple gig roles alongside a salaried position enhances earning potential and skill diversification without sacrificing stability.
Salaried vs Gig for Employee Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com