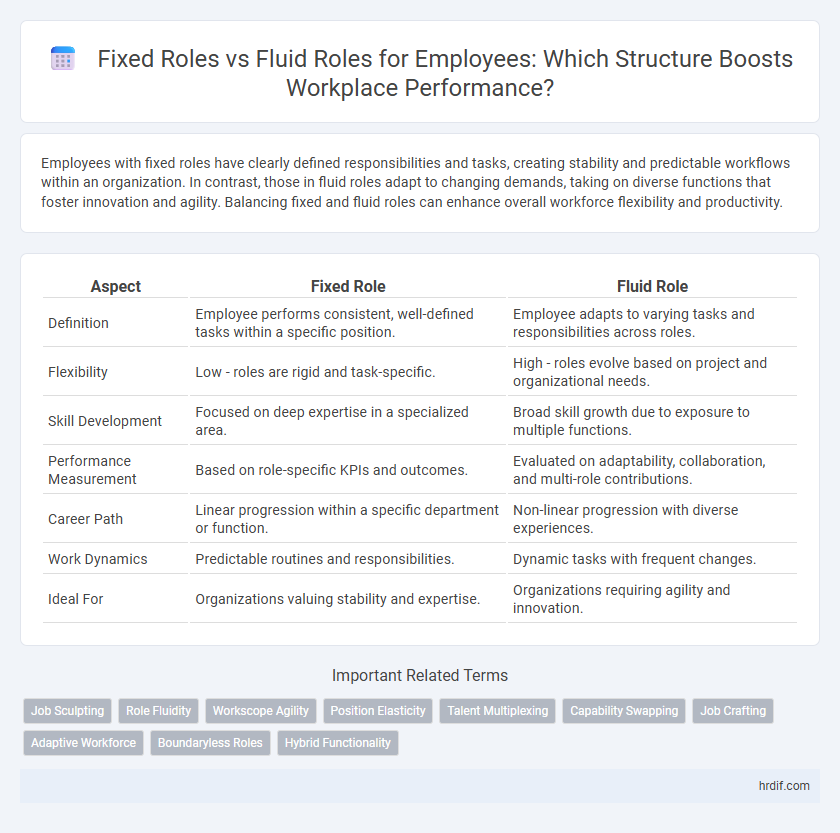
Employees with fixed roles have clearly defined responsibilities and tasks, creating stability and predictable workflows within an organization. In contrast, those in fluid roles adapt to changing demands, taking on diverse functions that foster innovation and agility. Balancing fixed and fluid roles can enhance overall workforce flexibility and productivity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fixed Role | Fluid Role |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee performs consistent, well-defined tasks within a specific position. | Employee adapts to varying tasks and responsibilities across roles. |
| Flexibility | Low - roles are rigid and task-specific. | High - roles evolve based on project and organizational needs. |
| Skill Development | Focused on deep expertise in a specialized area. | Broad skill growth due to exposure to multiple functions. |
| Performance Measurement | Based on role-specific KPIs and outcomes. | Evaluated on adaptability, collaboration, and multi-role contributions. |
| Career Path | Linear progression within a specific department or function. | Non-linear progression with diverse experiences. |
| Work Dynamics | Predictable routines and responsibilities. | Dynamic tasks with frequent changes. |
| Ideal For | Organizations valuing stability and expertise. | Organizations requiring agility and innovation. |
Understanding Fixed and Fluid Roles in the Workplace
Fixed roles in the workplace provide employees with clearly defined responsibilities and consistent tasks, fostering stability and specialization. Fluid roles promote adaptability by allowing employees to take on varying duties and collaborate across functions, driving innovation and responsiveness. Understanding the balance between fixed and fluid roles helps organizations enhance productivity while supporting employee growth and engagement.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Fluid Employee Roles
Fixed employee roles have clearly defined responsibilities, tasks, and hierarchical structures that ensure stability and predictability in job performance. Fluid employee roles emphasize adaptability, cross-functional collaboration, and evolving duties that support innovation and responsiveness to changing business needs. Key differences include role flexibility, scope of responsibilities, and the extent of autonomy, with fixed roles favoring consistency and fluid roles prioritizing dynamic engagement.
Advantages of Fixed Roles for Employees
Fixed roles provide employees with clear expectations and defined responsibilities, enhancing focus and expertise within specific tasks. This stability fosters mastery and efficiency, leading to higher productivity and job satisfaction. Predictable workflows and consistent performance metrics also facilitate better career development and evaluation.
Benefits of Fluid Roles in a Modern Workforce
Fluid roles enhance employee adaptability by allowing individuals to shift responsibilities based on project needs and skill development, fostering continuous learning and innovation. This flexibility leads to higher engagement and job satisfaction, as employees feel empowered to contribute across multiple domains. Organizations benefit from increased agility, enabling faster response to market changes and better utilization of diverse talent pools.
Challenges Faced in Fixed Role Environments
Employees in fixed role environments often encounter challenges such as limited skill development opportunities and reduced adaptability to changing business demands. The rigidity of predefined responsibilities can hinder innovation and constrain employee motivation, leading to decreased job satisfaction. This inflexibility may result in higher turnover rates and difficulty in responding to dynamic market conditions.
Potential Drawbacks of Adopting Fluid Roles
Adopting fluid roles in the workplace can lead to ambiguity in responsibilities, causing confusion and decreasing overall productivity among employees. The lack of clear role definition may result in inconsistent performance evaluations and hinder career development pathways. Moreover, employees might experience increased stress due to constantly shifting expectations and unclear priorities.
Impact of Role Structure on Employee Development
A fixed role provides employees with clear expectations and specialized skill development, leading to deep expertise and stability in their career paths. Fluid roles encourage adaptability and cross-functional learning, promoting innovation and broader competency growth. The structure of roles significantly influences employee motivation, skill diversification, and long-term professional development outcomes.
Fixed vs Fluid Roles: Effects on Job Satisfaction
Employees in fixed roles often experience higher job security and clearer expectations, leading to increased job satisfaction. Conversely, fluid roles can enhance engagement by offering variety and opportunities for skill development but may also cause uncertainty and stress. Balancing role stability with flexibility is crucial for optimizing employee well-being and performance.
Matching Employee Skills to Role Types
Matching employee skills to fixed roles ensures specialization and deep expertise, optimizing performance in clearly defined job functions. Fluid roles require versatile skills and adaptability, allowing employees to dynamically shift responsibilities based on organizational needs. Effective role assignment enhances productivity by aligning individual competencies with either stable or evolving job demands.
Choosing the Right Role Structure for Career Growth
Selecting the right role structure influences an employee's career trajectory by balancing specialization and adaptability. Fixed roles provide deep expertise and clear responsibilities, enhancing stability and mastery in a specific domain. Fluid roles offer flexibility and diverse experiences, fostering innovation and broader skill development essential for dynamic career growth.
Related Important Terms
Job Sculpting
Job sculpting allows employees to transition from fixed roles to fluid roles by customizing tasks that align with their strengths and career goals, enhancing engagement and productivity. This adaptive approach promotes skill development and organizational agility by redefining job responsibilities based on evolving employee capabilities and business needs.
Role Fluidity
Role fluidity enhances employee adaptability by allowing individuals to shift responsibilities and skills across projects, fostering innovation and continuous learning. This dynamic approach contrasts with fixed roles by promoting flexibility, collaboration, and responsiveness to evolving business needs.
Workscope Agility
Employees with fixed roles benefit from clear responsibilities and specialized expertise, enabling consistency and efficiency within defined tasks. In contrast, fluid roles enhance workscope agility by allowing employees to adapt to changing demands, foster cross-functional collaboration, and support dynamic business environments.
Position Elasticity
Position elasticity allows employees with fluid roles to adapt responsibilities based on organizational needs, enhancing agility and innovation. In contrast, fixed roles offer stability but limit flexibility, potentially hindering responsiveness to changing business demands.
Talent Multiplexing
Talent multiplexing enhances workforce agility by enabling employees to switch seamlessly between fixed and fluid roles, optimizing skill utilization across projects. This dynamic allocation fosters innovation and responsiveness, allowing organizations to leverage diverse talents for complex problem-solving and strategic growth.
Capability Swapping
Fixed roles define specific job responsibilities and skills, limiting capability swapping among employees, while fluid roles encourage adaptability by allowing employees to exchange skills and tasks dynamically. This capability swapping enhances workforce flexibility, promotes continuous learning, and improves overall organizational resilience.
Job Crafting
Fixed roles in employee job crafting offer stability with well-defined responsibilities, enhancing efficiency and predictability in task execution. Fluid roles encourage adaptability and innovation, allowing employees to reshape job boundaries and responsibilities dynamically to better align with evolving skills and organizational needs.
Adaptive Workforce
Fixed roles provide employees with clear responsibilities and stability, whereas fluid roles promote versatility and continuous skill development, enabling a more adaptive workforce that can swiftly respond to evolving business needs and market demands. Emphasizing fluid roles supports organizational agility by encouraging cross-functional collaboration and leveraging diverse talents to drive innovation and resilience.
Boundaryless Roles
Boundaryless roles empower employees by dissolving traditional fixed role limitations, promoting agility and cross-functional collaboration that enhance innovation and adaptability in dynamic work environments. Emphasizing fluid role structures allows organizations to leverage diverse skill sets and respond swiftly to changing business demands, driving sustained employee growth and organizational success.
Hybrid Functionality
Fixed roles in hybrid work environments provide employees with clear, consistent responsibilities that enhance specialization and accountability, while fluid roles enable adaptability and cross-functional collaboration to respond effectively to dynamic business needs. Balancing fixed and fluid roles optimizes hybrid functionality by leveraging employee expertise and fostering innovation through flexible task allocation.
Fixed Role vs Fluid Role for employee. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com