Traditional careers in specialization often follow a linear progression within a single field, emphasizing deep expertise and stability. Portfolio careerists combine multiple skills and projects across various areas, fostering adaptability and diverse experiences. This approach enables dynamic growth and broader professional opportunities compared to the more rigid structure of traditional paths.
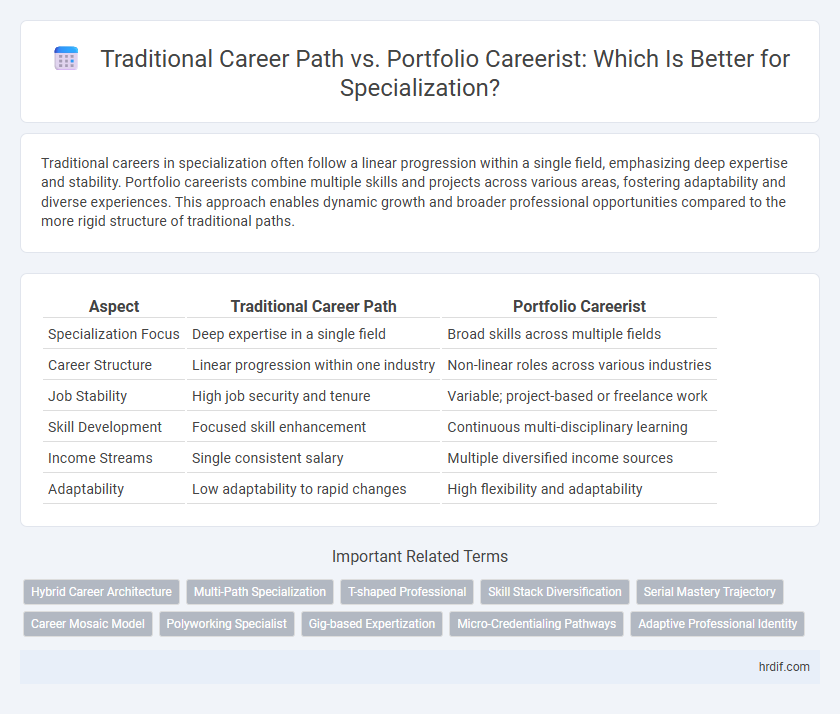
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Career Path | Portfolio Careerist |
|---|---|---|
| Specialization Focus | Deep expertise in a single field | Broad skills across multiple fields |
| Career Structure | Linear progression within one industry | Non-linear roles across various industries |
| Job Stability | High job security and tenure | Variable; project-based or freelance work |
| Skill Development | Focused skill enhancement | Continuous multi-disciplinary learning |
| Income Streams | Single consistent salary | Multiple diversified income sources |
| Adaptability | Low adaptability to rapid changes | High flexibility and adaptability |
Defining Traditional Career Paths and Portfolio Careers
Traditional career paths emphasize linear progression within a single industry or company, focusing on deep specialization and steady advancement through established roles. Portfolio careers involve multiple simultaneous roles or projects across diverse fields, highlighting versatility and skill integration rather than a single specialization. Each approach defines specialization differently: traditional paths prioritize expertise depth, while portfolio careers emphasize breadth and adaptability.
The Nature of Specialization: Deep vs Diverse Skills
Traditional career paths emphasize deep specialization within a single discipline, fostering expertise and long-term advancement in a focused area. Portfolio careerists develop diverse skills across multiple fields, enabling adaptability and a broader professional scope. The nature of specialization varies significantly, with deep skills offering mastery and diverse skills enhancing flexibility in evolving job markets.
Advantages of Specialization in Traditional Careers
Specialization in traditional careers offers deep expertise in a specific field, enhancing job security and professional credibility. It enables individuals to master complex skills, making them indispensable within their industry and often leading to higher salaries and promotions. This focused approach also facilitates clearer career progression and access to well-established professional networks and resources.
Specialization in Portfolio Careers: Is Generalization Inevitable?
Specialization in portfolio careers often demands balancing deep expertise with a broad skill set, making pure generalization inevitable to some extent. Portfolio careerists diversify their roles across multiple domains, requiring adaptable specialization rather than a singular, linear focus typical in traditional career paths. This hybrid approach fosters continuous learning and cross-disciplinary proficiency, challenging the notion that specialization excludes generalization.
Flexibility and Growth: Comparing Career Progression
Traditional career paths offer structured progression within a single field, providing clear benchmarks for advancement but often limiting flexibility. Portfolio careerists embrace diverse roles across multiple industries, fostering adaptability and continuous skill development that enhance growth opportunities. This approach allows for personalized career trajectories and resilience in fluctuating job markets, highlighting the evolving landscape of specialization.
Job Security and Market Demand for Specialists
Specialists following a traditional career path often benefit from higher job security due to their deep expertise aligning with stable, in-demand industries such as healthcare, finance, and engineering. Portfolio careerists leverage diverse skills across multiple roles, enhancing adaptability to shifting market demands but potentially facing less job stability in any single specialization. Market demand for specialists remains strong where technical proficiency and certification are critical, while portfolio careerists thrive in dynamic sectors prioritizing versatility and continuous learning.
Skill Development: Depth vs Breadth
Traditional career paths emphasize deep specialization, enabling professionals to develop expertise and mastery in a specific domain, often leading to steady advancement within a single industry. Portfolio careerists prioritize breadth of skills across multiple fields, fostering adaptability and cross-disciplinary knowledge that can drive innovation and flexibility in a rapidly changing job market. Skill development in traditional paths tends to focus on depth and refinement, while portfolio careerists seek broad competencies and diverse experience to remain competitive.
Networking and Professional Identity
Traditional career paths emphasize deep specialization within a single industry, fostering strong professional identity and extensive networks built over time in a focused domain. Portfolio careerists cultivate diverse skills across multiple fields, leveraging broad networks and adaptable professional identities to access varied opportunities. Effective networking strategies differ, with traditional specialists prioritizing long-term industry relationships, while portfolio careerists optimize cross-sector connections for versatility and resilience.
Income Stability and Financial Implications
Traditional career paths offer income stability through consistent salaries and structured benefits, which reduce financial uncertainty for specialists. Portfolio careerists experience fluctuating income streams by juggling multiple projects or roles, increasing both financial risk and potential for higher earnings. Specializing within a traditional role often means predictable growth, while portfolio specialization requires agile financial planning to manage variability in cash flow.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider for Specialization
Choosing the right specialization path depends on individual goals, industry demands, and skill adaptability. Traditional career paths emphasize deep expertise within a single domain, providing structured growth and stability, while portfolio careerists leverage diverse skills across multiple fields for flexibility and innovation. Assess factors such as market trends, personal learning style, and long-term career objectives to determine the most suitable specialization strategy.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Career Architecture
Traditional career paths emphasize deep specialization within a single domain, fostering expertise and stability, while portfolio careerists pursue diverse roles across multiple fields, leveraging varied skills and adaptability. Hybrid career architecture combines these approaches, enabling professionals to develop core specialized expertise alongside complementary skills, enhancing career resilience and innovation.
Multi-Path Specialization
Multi-path specialization in career development enables individuals to blend traditional career paths with portfolio careerist approaches, leveraging diverse skills across multiple industries to enhance adaptability and expertise. This strategy facilitates continuous learning and innovation, allowing professionals to maintain depth in core specializations while expanding their marketability through varied roles and projects.
T-shaped Professional
A T-shaped professional exemplifies the balance between deep specialization in a specific domain and broad skills across multiple disciplines, contrasting the traditional career path's narrow expertise with the portfolio careerist's diverse skill set. This specialization model enhances adaptability and innovation by integrating in-depth knowledge with cross-functional collaboration.
Skill Stack Diversification
Traditional career paths emphasize deep specialization within a single domain, leading to mastery and clear hierarchical progression, while portfolio careerists build a diverse skill stack across multiple fields, enhancing adaptability and innovation potential in dynamic job markets. Skill stack diversification enables portfolio professionals to integrate cross-disciplinary expertise, fostering unique value creation beyond conventional specialization limits.
Serial Mastery Trajectory
The Serial Mastery Trajectory emphasizes acquiring deep expertise across multiple disciplines sequentially, contrasting with the Traditional Career Path that prioritizes linear advancement within a single specialization. Portfolio Careerists leverage this approach to cultivate diverse, high-level skills, enhancing adaptability and cross-domain innovation in dynamic industries.
Career Mosaic Model
The Career Mosaic Model emphasizes a dynamic approach to specialization, blending the focused expertise of a Traditional Career Path with the diverse skill sets of a Portfolio Careerist to adapt to evolving industry demands. This hybrid framework enables professionals to cultivate deep domain knowledge while simultaneously developing multiple competencies, enhancing career resilience and marketability.
Polyworking Specialist
Polyworking specialists defy the traditional career path by integrating diverse skills across multiple domains, creating a dynamic portfolio career that emphasizes adaptability and continuous learning. This specialization approach leverages cross-disciplinary expertise to enhance innovation and resilience in rapidly evolving job markets.
Gig-based Expertization
Traditional career paths emphasize deep specialization within a single industry or role, fostering long-term expertise and stable progression. Portfolio careerists leverage gig-based expertization to build diverse, specialized skills across multiple sectors, enhancing adaptability and marketability in dynamic job markets.
Micro-Credentialing Pathways
Traditional career paths emphasize deep specialization through extensive experience in a single field, while portfolio careerists leverage diverse skills across multiple domains, increasingly validated by micro-credentialing pathways. Micro-credentials provide targeted, flexible learning opportunities that enhance specialization by certifying specific competencies, enabling both career models to adapt rapidly to evolving industry demands.
Adaptive Professional Identity
Traditional career paths emphasize deep specialization within a singular industry or role, fostering expertise and long-term stability. Portfolio careerists cultivate an adaptive professional identity by leveraging diverse skills across multiple projects and sectors, enhancing flexibility and resilience in dynamic job markets.
Traditional Career Path vs Portfolio Careerist for specialization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com