Specialist talent excels in deep, focused expertise that drives innovation and mastery within a specific pet specialization. Multidisciplinary professionals offer versatility by integrating diverse skills, enhancing problem-solving across various pet care fields. Balancing specialization with multidisciplinary abilities optimizes performance and adaptability in the evolving pet industry.
Table of Comparison
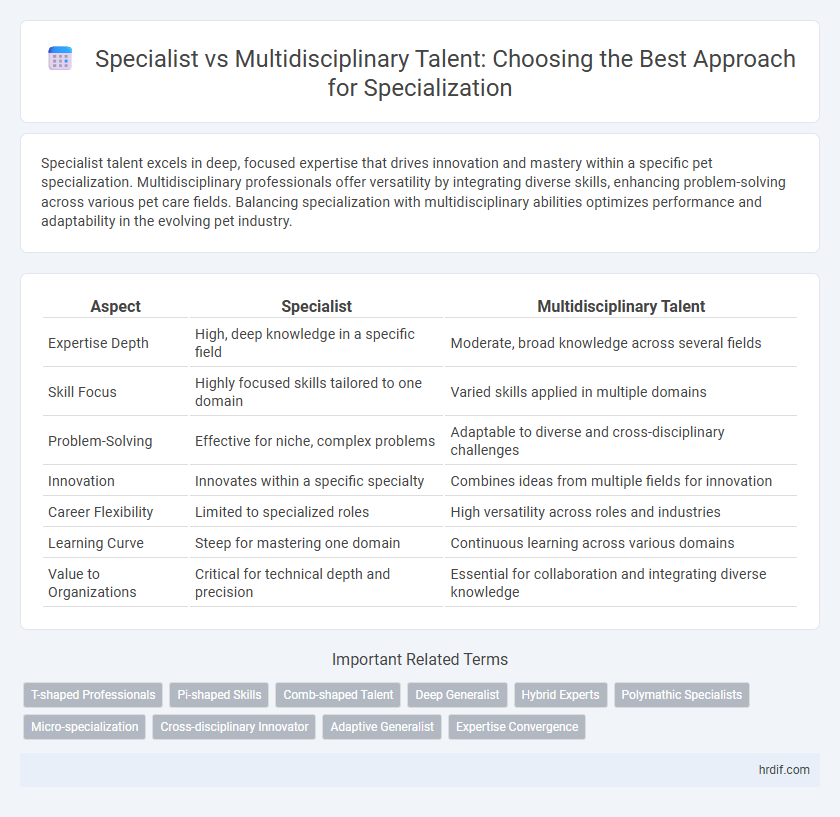
| Aspect | Specialist | Multidisciplinary Talent |
|---|---|---|
| Expertise Depth | High, deep knowledge in a specific field | Moderate, broad knowledge across several fields |
| Skill Focus | Highly focused skills tailored to one domain | Varied skills applied in multiple domains |
| Problem-Solving | Effective for niche, complex problems | Adaptable to diverse and cross-disciplinary challenges |
| Innovation | Innovates within a specific specialty | Combines ideas from multiple fields for innovation |
| Career Flexibility | Limited to specialized roles | High versatility across roles and industries |
| Learning Curve | Steep for mastering one domain | Continuous learning across various domains |
| Value to Organizations | Critical for technical depth and precision | Essential for collaboration and integrating diverse knowledge |
Defining Specialist and Multidisciplinary Talent
A specialist possesses deep expertise and advanced skills in a specific field, enabling them to solve complex problems with precision and authority. Multidisciplinary talent integrates knowledge across various domains, fostering innovative approaches and versatile problem-solving capabilities. Specialization emphasizes depth, while multidisciplinary talent values breadth, each playing a unique role in driving professional excellence.
The Benefits of Specialization in the Workplace
Specialization in the workplace enhances efficiency by allowing professionals to develop deep expertise in a specific domain, leading to higher quality outcomes and innovative solutions. Specialists bring precise, advanced knowledge that accelerates problem-solving and drives competitive advantage within industries. Organizations benefit from specialization through increased productivity, reduced training time, and improved consistency in task execution.
Advantages of Multidisciplinary Skills for Career Growth
Multidisciplinary skills enhance career growth by fostering adaptability and innovation across various fields, enabling professionals to solve complex problems with diverse perspectives. Employers value talents who integrate knowledge from multiple disciplines, leading to increased opportunities for leadership roles and cross-functional projects. This versatility drives long-term career resilience and accelerates professional development in dynamic job markets.
Specialist vs Multidisciplinary: Impact on Job Opportunities
Specialists possess deep expertise in a specific field, making them highly sought after for roles requiring advanced technical skills or niche knowledge, often resulting in higher demand and salary potential within specialized industries. Multidisciplinary talents, with their broad skill sets across various domains, offer versatility and adaptability, increasing employability in dynamic environments that value cross-functional collaboration and innovation. Job opportunities for specialists typically align with focused career paths, whereas multidisciplinary professionals thrive in roles demanding integrated problem-solving and strategic thinking across multiple sectors.
Adaptability and Innovation: Who Performs Better?
Specialists demonstrate deep expertise enabling precise problem-solving in complex scenarios, while multidisciplinary talents excel in adaptability by integrating diverse perspectives for innovative solutions. Adaptability often favors multidisciplinary professionals who can pivot and apply cross-domain knowledge in dynamic environments. Innovation thrives when varied skills converge, making multidisciplinary talent more effective in fostering creative breakthroughs.
Industry Trends: Demand for Specialists vs Generalists
Industry trends reveal increasing demand for specialists equipped with deep expertise in niche fields such as artificial intelligence and cybersecurity, as companies seek precision and innovation in complex problem-solving. However, multidisciplinary talent remains valuable in roles requiring adaptability and cross-functional collaboration, especially in startups and agile environments. Businesses prioritize specialists for tasks requiring technical depth, while generalists fill gaps where versatile skill sets drive growth and integration across departments.
Career Progression Paths: Specialist and Multidisciplinary Approaches
Career progression for specialists often follows a deepening expertise trajectory within a focused domain, leading to senior expert or niche consultant roles. Multidisciplinary talent advances through broadening skill sets across multiple fields, enabling leadership in cross-functional projects or strategic innovation roles. Organizations value specialists for solving complex, domain-specific problems and multidisciplinary professionals for integrating diverse perspectives to drive adaptable business solutions.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Talent Type
Specialist talent often faces challenges such as limited adaptability and risk of skill obsolescence due to their narrow expertise. Multidisciplinary talent encounters difficulties in achieving deep knowledge in any single domain, which can hinder their ability to solve complex problems requiring expert-level insights. Balancing depth with breadth remains a critical limitation for organizations leveraging either specialization approach.
How Employers Value Specialization vs Broad Skillsets
Employers often prioritize specialists for roles requiring deep expertise to drive innovation and solve complex problems efficiently. However, multidisciplinary talent is increasingly valued for adaptability and collaboration across diverse projects, enhancing organizational agility. Balancing specialization with broad skillsets enables companies to optimize team performance and address evolving market demands effectively.
Choosing the Right Path: Self-Assessment for Career Specialization
Evaluating personal strengths and industry demands guides the choice between specialist and multidisciplinary talent for career specialization. Specialists deepen expertise in a focused domain, enhancing skill precision and market value within niche sectors. Multidisciplinary talent leverages diverse skills, driving innovation and adaptability across interconnected fields.
Related Important Terms
T-shaped Professionals
T-shaped professionals combine deep expertise in one domain with broad skills across multiple disciplines, enabling effective collaboration and innovation within specialized teams. This balance between specialist knowledge and multidisciplinary capabilities drives adaptability and comprehensive problem-solving in complex projects.
Pi-shaped Skills
Specialist talent demonstrates deep expertise in a specific domain, enabling advanced problem-solving and innovation, while multidisciplinary talent integrates knowledge across various fields to adapt and collaborate effectively. Pi-shaped skills combine vertical specialization with horizontal breadth, empowering professionals to excel deeply in one area while applying complementary skills across disciplines for increased versatility.
Comb-shaped Talent
Comb-shaped talent combines deep expertise in a specialized field with broad skills across multiple disciplines, enabling innovative problem-solving and adaptability in complex environments. Unlike pure specialists who excel exclusively in one area, comb-shaped professionals leverage interdisciplinary knowledge to drive collaboration and create comprehensive solutions.
Deep Generalist
Deep Generalists combine the extensive knowledge of multidisciplinary talent with the profound expertise of specialists, enabling innovative problem-solving across complex domains. This hybrid specialization fosters adaptability and depth, making deep generalists uniquely valuable in dynamic industries requiring both breadth and focused mastery.
Hybrid Experts
Hybrid experts combine deep specialization with broad multidisciplinary knowledge, enabling innovative problem-solving across complex domains. Their unique ability to integrate insights from multiple fields enhances adaptability and drives competitive advantage in rapidly evolving industries.
Polymathic Specialists
Polymathic specialists combine deep expertise in a single domain with broad knowledge across multiple fields, enabling innovative problem-solving and adaptable skill application. This unique blend enhances specialization by fostering interdisciplinary insights while maintaining authoritative competence in a core area.
Micro-specialization
Micro-specialization hones expertise within a highly focused niche, enabling specialists to deliver unparalleled depth and innovative solutions in their domain. Multidisciplinary talent offers broader perspectives, but micro-specialization drives mastery and precision critical for cutting-edge advancements and competitive advantage.
Cross-disciplinary Innovator
Cross-disciplinary innovators combine deep specialization with broad multidisciplinary skills, enabling them to integrate diverse knowledge areas and drive groundbreaking solutions. Their unique ability to navigate and synthesize multiple domains fosters innovation that pure specialists or generalists may not achieve.
Adaptive Generalist
Adaptive generalists blend deep specialization with broad multidisciplinary skills, enabling them to innovate by connecting insights across diverse fields. Their versatile expertise fosters problem-solving agility, making them valuable in complex, evolving industries where pure specialists may lack flexibility.
Expertise Convergence
Specialist talent offers deep expertise in a specific domain, enabling precision and mastery, while multidisciplinary talent integrates knowledge across various fields, fostering innovation through expertise convergence. Organizations leveraging expertise convergence from multidisciplinary teams achieve synergistic solutions that address complex challenges more effectively than isolated specialist efforts.
Specialist vs Multidisciplinary talent for specialization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com