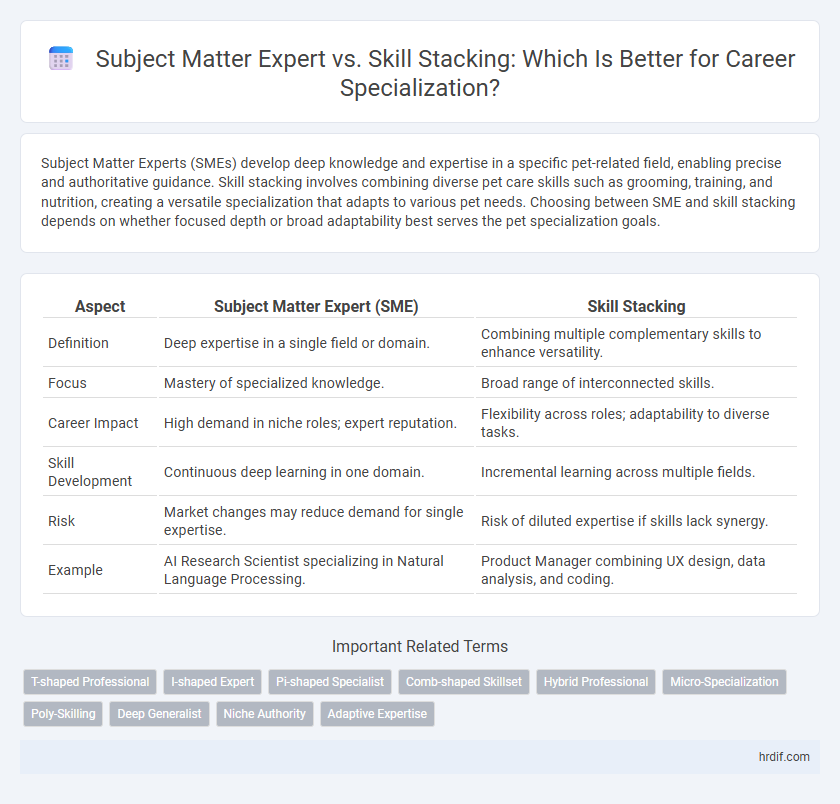
Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) develop deep knowledge and expertise in a specific pet-related field, enabling precise and authoritative guidance. Skill stacking involves combining diverse pet care skills such as grooming, training, and nutrition, creating a versatile specialization that adapts to various pet needs. Choosing between SME and skill stacking depends on whether focused depth or broad adaptability best serves the pet specialization goals.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Subject Matter Expert (SME) | Skill Stacking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deep expertise in a single field or domain. | Combining multiple complementary skills to enhance versatility. |
| Focus | Mastery of specialized knowledge. | Broad range of interconnected skills. |
| Career Impact | High demand in niche roles; expert reputation. | Flexibility across roles; adaptability to diverse tasks. |
| Skill Development | Continuous deep learning in one domain. | Incremental learning across multiple fields. |
| Risk | Market changes may reduce demand for single expertise. | Risk of diluted expertise if skills lack synergy. |
| Example | AI Research Scientist specializing in Natural Language Processing. | Product Manager combining UX design, data analysis, and coding. |
Defining Subject Matter Expertise in Career Development
Subject Matter Expertise (SME) in career development refers to deep, specialized knowledge within a particular field, enabling professionals to provide authoritative insights and solutions. Unlike skill stacking, which involves accumulating diverse competencies across multiple areas, SME emphasizes mastery and credibility in a single domain. This concentrated expertise often leads to increased trust, higher demand, and leadership opportunities within specialized industries.
What is Skill Stacking and How Does it Work?
Skill stacking involves combining multiple complementary skills to create a unique expertise, enhancing versatility and problem-solving ability across various domains. Unlike a Subject Matter Expert, who has deep knowledge in a single area, skill stacking emphasizes breadth and the interconnected application of diverse skills. This approach accelerates specialization by fostering adaptability and innovation through the strategic layering of relevant competencies.
Advantages of Being a Subject Matter Expert
Being a Subject Matter Expert (SME) offers deep proficiency and authoritative knowledge in a specific domain, enabling precise problem-solving and innovation within that field. SMEs are often sought after for critical decision-making, leadership roles, and mentoring due to their comprehensive understanding. This specialization can lead to higher credibility, career advancement, and opportunities to influence industry standards.
Benefits of Adopting a Skill Stacking Approach
Adopting a skill stacking approach enhances specialization by combining diverse competencies that create unique expertise, increasing adaptability in dynamic job markets. This method fosters continuous learning and innovation, allowing professionals to solve complex problems that require interdisciplinary knowledge. Skill stacking leads to higher employability and career growth by differentiating individuals from subject matter experts who possess deep but narrow knowledge.
Potential Drawbacks: Specialization vs. Broad Competencies
Subject Matter Experts often face limitations due to deep but narrow knowledge, which can hinder adaptability in rapidly changing industries. Skill stacking enhances versatility by combining diverse competencies, yet risks diluting expertise critical for mastering complex domains. Balancing specialized depth with broad skill sets is essential to avoid vulnerabilities in professional growth and market relevance.
Industries Favoring Subject Matter Experts
Industries such as healthcare, law, and finance heavily favor Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) due to the critical need for deep, specialized knowledge and regulatory compliance. SMEs provide unparalleled expertise that drives innovation, risk management, and informed decision-making in complex, high-stakes environments. In contrast, skill stacking, which combines multiple complementary skills, tends to be more valued in dynamic sectors like tech startups or creative industries where versatility enhances adaptability.
Job Markets Where Skill Stackers Thrive
Job markets such as tech startups, digital marketing, and freelance consulting favor skill stackers who combine diverse competencies like coding, design, and communication to drive innovation and flexibility. Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) excel in highly specialized industries like pharmaceuticals, law, or engineering, where deep expertise and precision are critical for compliance and complex problem-solving. Skill stacking enhances adaptability in rapidly changing environments, while SMEs provide authoritative knowledge essential for niche roles requiring advanced technical proficiency.
Navigating Career Growth: Deep Expertise or Versatile Skills?
Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) provide deep, focused knowledge essential for technical roles and industry leadership, driving innovation through specialized insight. Skill stacking combines diverse competencies, enabling adaptability and cross-functional problem-solving crucial for dynamic career environments. Balancing niche expertise with versatile skills supports strategic career growth by aligning depth with breadth in professional development.
Personal Branding: SME vs. Skill Stack Differentiation
Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) build personal branding through deep expertise in a specific domain, showcasing authoritative knowledge and credibility that attracts industry recognition. Skill stacking enhances personal branding by combining diverse yet complementary skills, creating a unique value proposition that appeals to a broader range of opportunities. Emphasizing SME versus skill stack differentiation allows professionals to strategically position themselves in competitive markets by either highlighting focused mastery or versatile adaptability.
Deciding Your Path: Factors to Consider for Specialization
Choosing between Subject Matter Expert (SME) and Skill Stacking involves evaluating industry demands, personal strengths, and long-term career goals. SMEs excel by developing deep knowledge in a specific area, which is highly valued in specialized fields like cybersecurity or legal advisory. Skill stacking combines complementary skills, enhancing versatility and innovation, particularly in dynamic roles such as digital marketing or product management.
Related Important Terms
T-shaped Professional
A Subject Matter Expert (SME) possesses deep knowledge in a specific domain, providing authoritative insights and solutions, while skill stacking involves combining diverse competencies to build a versatile profile. T-shaped professionals blend both approaches by developing deep expertise in one area complemented by broad skills across multiple disciplines, enhancing adaptability and innovation in specialized roles.
I-shaped Expert
An I-shaped expert possesses deep, specialized knowledge in a single domain, contrasting with skill stacking, which combines diverse competencies to create a broader skill set. Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) excel in focused expertise, driving innovation and mastery within their specialization, while skill stacking emphasizes versatility across multiple fields.
Pi-shaped Specialist
A Pi-shaped specialist combines deep expertise in a core domain with complementary skills, enhancing adaptability and innovation beyond the traditional Subject Matter Expert's narrow focus. This approach leverages skill stacking by integrating cross-disciplinary proficiencies, fostering a versatile specialization that meets complex, evolving industry demands.
Comb-shaped Skillset
A comb-shaped skillset combines deep expertise as a Subject Matter Expert (SME) with a broad range of complementary skills, enabling specialization that adapts to dynamic industries and complex problems. Unlike narrow SME focus, comb-shaped professionals leverage skill stacking to integrate diverse capabilities, enhancing innovation and cross-functional collaboration.
Hybrid Professional
Hybrid professionals maximize their specialization by combining deep Subject Matter Expert (SME) knowledge with diverse complementary skills through skill stacking, resulting in enhanced problem-solving abilities and adaptability across industries. This blend of expertise and multifaceted skills creates a unique value proposition, driving innovation and competitive advantage in complex, dynamic markets.
Micro-Specialization
Micro-specialization leverages subject matter experts' deep knowledge in narrow fields, creating high-value expertise within specific niches. Skill stacking combines diverse but complementary skills, enabling professionals to solve complex problems and adapt quickly in micro-specialized roles.
Poly-Skilling
Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) provide deep, specialized knowledge critical for niche problems, while skill stacking enhances specialization by combining diverse competencies to create unique value and adaptability. Poly-skilling leverages multiple interconnected skills, fostering innovation and versatility beyond traditional singular expertise.
Deep Generalist
A Deep Generalist leverages skill stacking by integrating diverse yet complementary competencies to solve complex problems, whereas a Subject Matter Expert offers highly specialized knowledge within a narrowly defined domain. This hybrid approach enhances adaptability and innovation, enabling professionals to bridge gaps between disciplines while maintaining depth in critical areas.
Niche Authority
Subject Matter Experts build deep, focused knowledge within a specialized niche, establishing strong authority through expertise in a singular domain. In contrast, Skill Stacking combines complementary skills across multiple areas, enhancing adaptability and creating unique value propositions that also contribute to niche authority by bridging interdisciplinary gaps.
Adaptive Expertise
Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) develop deep knowledge in a specific domain, enabling precise problem-solving and expert judgment, while Skill Stacking combines multiple complementary skills to create versatile problem-solvers. Adaptive Expertise emerges when individuals integrate SME depth with broad skill stacks, enhancing their ability to innovate and adjust strategies in dynamic environments.
Subject Matter Expert vs Skill Stacking for specialization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com