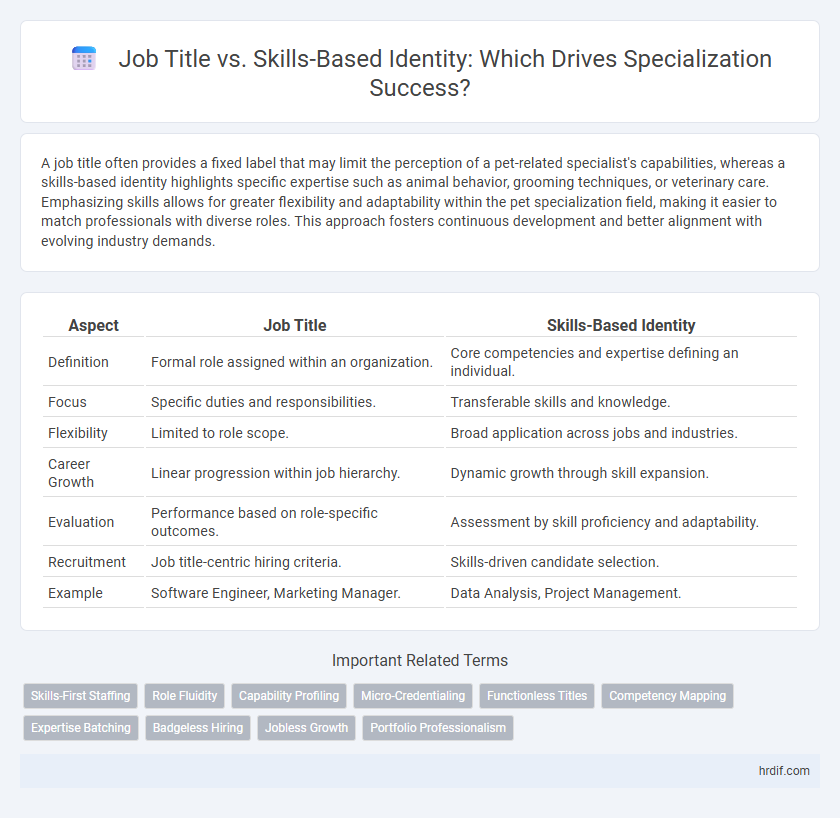
A job title often provides a fixed label that may limit the perception of a pet-related specialist's capabilities, whereas a skills-based identity highlights specific expertise such as animal behavior, grooming techniques, or veterinary care. Emphasizing skills allows for greater flexibility and adaptability within the pet specialization field, making it easier to match professionals with diverse roles. This approach fosters continuous development and better alignment with evolving industry demands.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Job Title | Skills-Based Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal role assigned within an organization. | Core competencies and expertise defining an individual. |
| Focus | Specific duties and responsibilities. | Transferable skills and knowledge. |
| Flexibility | Limited to role scope. | Broad application across jobs and industries. |
| Career Growth | Linear progression within job hierarchy. | Dynamic growth through skill expansion. |
| Evaluation | Performance based on role-specific outcomes. | Assessment by skill proficiency and adaptability. |
| Recruitment | Job title-centric hiring criteria. | Skills-driven candidate selection. |
| Example | Software Engineer, Marketing Manager. | Data Analysis, Project Management. |
Defining Job Titles vs Skills-Based Identity
Defining job titles focuses on specific roles within an organization, creating clear hierarchical or functional distinctions, while skills-based identity emphasizes the competencies and expertise an individual possesses regardless of their position. Job titles can limit specialization by confining professionals to narrow responsibilities, whereas skills-based approaches enable flexible application of diverse talents across various projects and industries. Prioritizing skills over titles enhances adaptability and continuous professional growth in dynamic job markets.
The Evolution of Specialization in Careers
The evolution of specialization in careers reflects a shift from rigid job titles to a skills-based identity that highlights specific competencies and expertise. Modern professionals emphasize adaptable skill sets over traditional roles, enabling greater flexibility and responsiveness to industry changes. This transformation fosters continuous learning and cultivates a dynamic workforce aligned with emerging market demands.
Limitations of Traditional Job Titles
Traditional job titles often fail to accurately reflect the diverse skills and expertise employees bring, limiting opportunities for true specialization and career growth. These rigid labels can obscure an individual's unique capabilities, making it difficult for organizations to align talent with specific project needs. Skills-based identity offers a more dynamic framework, emphasizing competencies over predefined roles to better capture professional specialization.
Advantages of Skills-Based Career Paths
Skills-based career paths offer greater flexibility by allowing professionals to adapt to evolving industry demands without the constraints of rigid job titles. Emphasizing expertise and specific competencies enhances employability and fosters continuous personal development. Organizations benefit from increased innovation and productivity as employees leverage specialized skills to address diverse challenges.
How Skills-Based Identity Enhances Flexibility
Skills-based identity enhances flexibility by allowing professionals to adapt quickly to changing job requirements and industries, as it emphasizes specific competencies rather than fixed job titles. This approach enables seamless transitions across roles and projects, fostering continuous learning and innovation. Emphasizing skills over titles supports personalized career growth and better alignment with market demands.
Job Market Demands: Titles or Skills?
Job market demands increasingly prioritize skills-based identities over traditional job titles, as employers seek specific competencies that adapt to evolving industry needs. Skills such as data analysis, coding, and project management offer more flexibility and relevance than static job titles. This shift encourages professionals to build specialized skill sets aligned with current market trends to enhance employability and career growth.
Shaping Your Professional Brand Beyond Job Titles
Shaping your professional brand beyond job titles involves emphasizing a skills-based identity that highlights your unique expertise and capabilities. This approach allows professionals to stand out by showcasing specific competencies and value they bring, rather than being confined to traditional job titles. Embracing a skills-based identity fosters greater adaptability and alignment with evolving industry demands, positioning individuals as specialists in their fields.
Navigating Job Searches: Title-Driven vs Skills-Driven Approaches
Job title-driven approaches streamline job searches by targeting specific roles like "Data Analyst" or "Marketing Manager," making application processes straightforward but potentially limiting flexibility. Skills-based identity emphasizes core competencies such as data analysis, project management, and digital marketing, offering adaptability across multiple job titles and industries. Navigating job searches effectively requires balancing title recognition with a robust skills portfolio to align specialization with evolving market demands.
Organizational Shifts Toward Skills-Based Specialization
Organizations are increasingly prioritizing skills-based identity over traditional job titles to foster specialization and agility in talent management. This shift enables precise alignment of employee capabilities with evolving project demands, enhancing productivity and innovation. Emphasizing competencies rather than hierarchical roles supports dynamic workforce development and adaptive organizational structures.
Future Trends: Skills as the New Specialization Standard
Future specialization trends emphasize skills-based identity over traditional job titles, reflecting a shift toward adaptable expertise in dynamic industries. Organizations prioritize proficiency in critical skills like data analysis, cybersecurity, and AI integration, enabling workforce agility and innovation. This evolution encourages continuous learning and skill validation as the core of professional identity, redefining specialization standards.
Related Important Terms
Skills-First Staffing
Skills-based identity emphasizes specific competencies and expertise over traditional job titles, enabling more precise alignment with project requirements and organizational needs. Skills-First Staffing leverages this approach by identifying and deploying talent based on verified capabilities, improving workforce agility and productivity.
Role Fluidity
Role fluidity highlights the shift from rigid job titles to skills-based identity, emphasizing adaptability and continuous learning as core components of specialization. Embracing a skills-focused approach enables professionals to navigate dynamic career landscapes and respond effectively to evolving industry demands.
Capability Profiling
Capability profiling emphasizes skills-based identity over traditional job titles to foster specialization by mapping competencies directly to performance outcomes. This approach enables organizations to identify talent gaps, tailor training, and align workforce capabilities with strategic objectives for enhanced agility and innovation.
Micro-Credentialing
Micro-credentialing enhances specialization by prioritizing skills-based identity over traditional job titles, enabling professionals to showcase specific competencies verified through targeted certifications. This approach fosters a more dynamic and accurate representation of expertise, aligning workforce capabilities with evolving industry demands.
Functionless Titles
Functionless titles often obscure true specialization by emphasizing generic job labels over specific skills, reducing clarity in professional identity and hindering accurate assessments of expertise. Emphasizing skills-based identity enables precise competency mapping, improving role alignment and enhancing talent development within specialized fields.
Competency Mapping
Competency mapping enables organizations to identify and develop skills-based identities that transcend traditional job titles, fostering specialization through precise skill alignment. Emphasizing skills over job titles enhances workforce agility, allowing employees to adapt to evolving roles and industry demands with targeted expertise.
Expertise Batching
Expertise batching enhances specialization by grouping related skills rather than relying solely on traditional job titles, enabling professionals to showcase specific competencies aligned with industry demands. This approach promotes a skills-based identity, improving adaptability and precision in matching talent with specialized roles in dynamic job markets.
Badgeless Hiring
Job title-based specialization often limits candidate evaluation by rigid labels, whereas skills-based identity emphasizes specific competencies and proficiencies critical for role success, aligning seamlessly with Badgeless Hiring practices that prioritize verified skillsets over formal titles. This approach enhances workforce agility and diversity by focusing on measurable abilities, facilitating better job matches and reducing bias inherent in traditional title-centric recruitment.
Jobless Growth
Jobless growth highlights the limitations of relying solely on traditional job titles for specialization, as many emerging roles require dynamic, skills-based identities that better capture candidate capabilities. Emphasizing skills over fixed job titles enables organizations to adapt to evolving labor market demands and address unemployment despite economic expansion.
Portfolio Professionalism
A skills-based identity emphasizes specialized competencies and practical expertise that enhance portfolio professionalism, allowing professionals to demonstrate versatility and adaptability beyond a static job title. This approach prioritizes continuous skill development and tangible accomplishments, making specialization more dynamic and market-relevant.
Job title vs Skills-based identity for specialization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com