Manager leadership focuses on organizing tasks, directing team members, and maintaining control to achieve goals efficiently. Servant leadership prioritizes the growth and well-being of team members, empowering them to perform at their best through support and collaboration. Choosing servant leadership fosters trust, motivation, and long-term success by valuing people over processes.
Table of Comparison
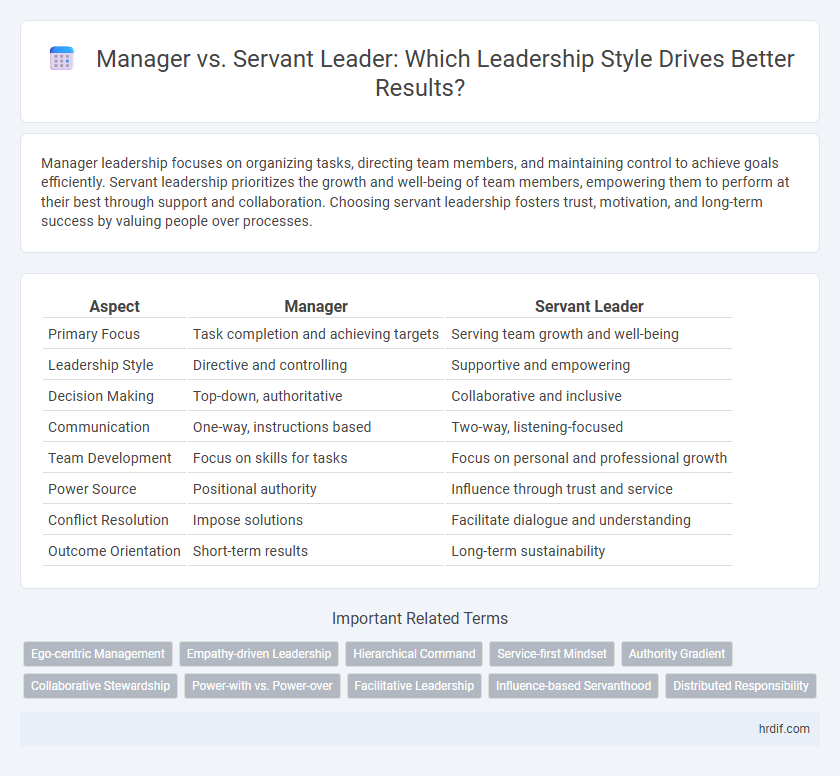
| Aspect | Manager | Servant Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Task completion and achieving targets | Serving team growth and well-being |
| Leadership Style | Directive and controlling | Supportive and empowering |
| Decision Making | Top-down, authoritative | Collaborative and inclusive |
| Communication | One-way, instructions based | Two-way, listening-focused |
| Team Development | Focus on skills for tasks | Focus on personal and professional growth |
| Power Source | Positional authority | Influence through trust and service |
| Conflict Resolution | Impose solutions | Facilitate dialogue and understanding |
| Outcome Orientation | Short-term results | Long-term sustainability |
Defining Managerial Leadership vs. Servant Leadership
Managerial leadership centers on directing teams, making decisions, and ensuring organizational goals are met through structured control and authority. Servant leadership prioritizes serving team members, fostering growth, empowerment, and collaboration by putting others' needs before organizational ambitions. This contrast highlights managerial leadership's focus on hierarchy and tasks versus servant leadership's emphasis on empathy and community.
Core Principles: Authority vs. Service
Managers typically exercise authority by directing tasks, enforcing rules, and maintaining control within organizational hierarchies, emphasizing efficiency and goal achievement. Servant leaders prioritize serving others, fostering collaboration, and empowering team members to unlock their potential, thereby enhancing commitment and trust. The core principle distinguishing these leadership styles lies in wielding power for personal or positional control versus leveraging influence to support and uplift others.
Decision-Making Styles: Directive vs. Collaborative
Managers typically employ a directive decision-making style, focusing on clear, top-down instructions to achieve organizational goals efficiently. Servant leaders embrace a collaborative approach, actively involving team members in problem-solving and valuing diverse perspectives to foster engagement and innovation. This contrast highlights how directive leadership prioritizes control and quick execution, while collaborative leadership enhances team empowerment and shared ownership of decisions.
Impact on Team Motivation and Engagement
Managers often focus on achieving organizational goals through control and task delegation, which can limit team members' intrinsic motivation and engagement. Servant leaders prioritize the growth and well-being of their team, fostering trust and empowerment that significantly enhance motivation and long-term commitment. Research shows teams led by servant leaders experience higher job satisfaction, increased creativity, and stronger collaboration compared to those managed with traditional top-down approaches.
Communication Approaches: Command vs. Empathy
Managers typically use directive communication, emphasizing clear instructions, authority, and control to achieve organizational goals efficiently. Servant leaders prioritize empathetic communication, actively listening and fostering open dialogue to build trust and empower team members. This empathetic approach enhances collaboration, motivation, and overall team well-being.
Performance Outcomes: Short-Term vs. Long-Term Success
Managers typically emphasize short-term performance outcomes by focusing on meeting immediate targets and efficiency metrics, often driven by deadlines and resource allocation. Servant leaders prioritize long-term success through empowering team members, fostering collaboration, and nurturing professional growth, which leads to sustainable organizational performance. Studies show organizations led by servant leaders experience higher employee engagement and retention, directly influencing consistent long-term results.
Employee Development: Control vs. Empowerment
Managers emphasize control by directing tasks and closely monitoring employee performance, which can limit creative problem-solving and growth. Servant leaders prioritize empowerment, fostering an environment where employees are encouraged to take initiative and develop their skills through support and trust. This approach leads to higher engagement, innovation, and long-term professional development.
Organizational Culture: Hierarchy vs. Inclusivity
Managers often enforce hierarchical structures that prioritize command and control, leading to rigid organizational cultures where decision-making is centralized. Servant leaders cultivate inclusivity by empowering employees, fostering openness, collaboration, and shared responsibility throughout the organization. This shift from hierarchy to inclusivity enhances morale, innovation, and long-term adaptability within teams.
Adaptability and Change Management Styles
Managers typically rely on structured approaches and hierarchical authority to enforce change, while servant leaders emphasize adaptability by prioritizing team needs and fostering collaboration. Servant leadership enhances change management through empathy and active listening, enabling responsiveness to evolving circumstances and employee feedback. This flexible style cultivates resilience and innovation, contrasting with the more rigid, top-down methods often employed by traditional managers.
Choosing the Right Leadership Style for Your Career
Selecting the right leadership style hinges on understanding your team's needs and objectives; managers prioritize task completion and organizational goals, while servant leaders focus on empowering and serving their team members. Research shows servant leadership enhances employee engagement, trust, and long-term performance, making it ideal for careers centered on collaboration and innovation. Analyzing workplace dynamics and your personal values guides whether a directive managerial approach or a supportive servant leadership style aligns best with your career growth.
Related Important Terms
Ego-centric Management
Ego-centric management often defines traditional managers who prioritize authority and control, leading to decision-making driven by personal gain rather than team success. In contrast, servant leaders emphasize empathy and support, fostering collaboration and empowering others by putting team needs above their own ego.
Empathy-driven Leadership
Empathy-driven leadership differentiates servant leaders, who prioritize understanding and meeting their team's emotional and professional needs, from traditional managers who often focus on task completion and authority. Servant leaders foster trust and collaboration by actively listening and supporting individual growth, resulting in higher employee engagement and organizational resilience.
Hierarchical Command
Manager leadership relies on hierarchical command structures that emphasize control, authority, and top-down decision-making to achieve organizational goals efficiently. Servant leadership prioritizes empowering team members, fostering collaboration, and facilitating growth, which contrasts with the rigid command chains typical of managerial roles.
Service-first Mindset
Servant leaders prioritize the growth and well-being of their teams, fostering a service-first mindset that empowers employees and enhances collaboration. Managers often focus on task completion and authority, whereas servant leadership drives sustainable success through empathy, active listening, and putting others' needs above organizational goals.
Authority Gradient
Manager leadership relies on hierarchical authority and top-down decision-making, creating a steep authority gradient that may hinder open communication and innovation. Servant leaders flatten the authority gradient by prioritizing team empowerment and active listening, fostering collaboration and trust within the organization.
Collaborative Stewardship
Servant leaders prioritize collaborative stewardship by fostering trust, empowering team members, and facilitating shared decision-making, which drives sustainable organizational growth and employee engagement. In contrast, traditional managers often rely on authority and control, limiting innovation and reducing team cohesion within leadership dynamics.
Power-with vs. Power-over
Servant leaders embody power-with by fostering collaboration, empathy, and shared decision-making, which cultivates trust and empowerment among team members. In contrast, traditional managers exercise power-over through hierarchical control and authority, often leading to compliance rather than genuine engagement and innovation.
Facilitative Leadership
Facilitative leadership thrives under servant leaders who prioritize team empowerment, active listening, and removing obstacles, fostering collaboration and innovation. Unlike traditional managers who direct and control, servant leaders enable shared decision-making and nurture growth, leading to higher engagement and sustainable success.
Influence-based Servanthood
Influence-based servanthood prioritizes empowering team members by fostering collaboration, active listening, and servant leadership rather than directing through authority or control. This approach enhances organizational trust and motivation by placing the leader's focus on serving others to achieve collective goals instead of merely managing tasks or people.
Distributed Responsibility
Distributed responsibility in leadership emphasizes empowering team members to take ownership and make decisions, which servant leaders prioritize by fostering collaboration and support. Managers often focus on centralized control and task delegation, whereas servant leaders cultivate shared accountability to enhance team autonomy and collective success.
Manager vs Servant Leader for Leadership. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com