Top-down leaders maintain clear authority and decision-making control, driving direction through a centralized approach that ensures consistency and swift execution. Distributed leaders empower team members by sharing responsibilities and fostering collaboration, promoting innovation and adaptability within the team. Choosing between these styles depends on organizational needs, as top-down leadership suits structured environments while distributed leadership thrives in dynamic, creative settings.
Table of Comparison
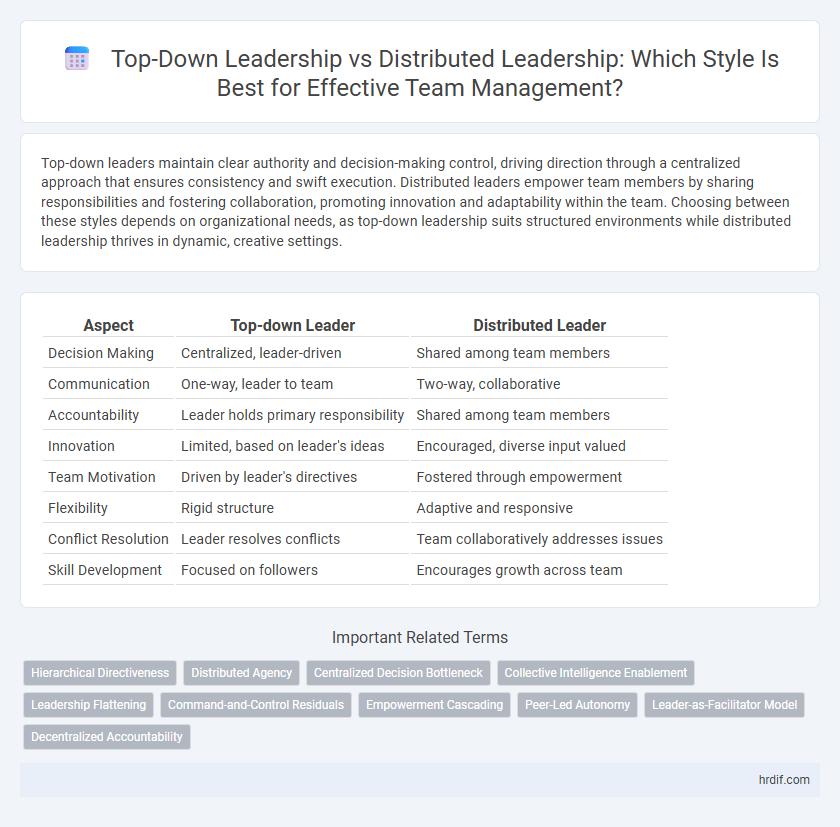
| Aspect | Top-down Leader | Distributed Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Making | Centralized, leader-driven | Shared among team members |
| Communication | One-way, leader to team | Two-way, collaborative |
| Accountability | Leader holds primary responsibility | Shared among team members |
| Innovation | Limited, based on leader's ideas | Encouraged, diverse input valued |
| Team Motivation | Driven by leader's directives | Fostered through empowerment |
| Flexibility | Rigid structure | Adaptive and responsive |
| Conflict Resolution | Leader resolves conflicts | Team collaboratively addresses issues |
| Skill Development | Focused on followers | Encourages growth across team |
Understanding Top-down vs Distributed Leadership
Top-down leadership centralizes decision-making power in a single leader, ensuring clear directives and streamlined control, which can accelerate decision processes but may limit team autonomy. Distributed leadership disperses authority across team members, fostering collaboration, innovation, and shared responsibility, which enhances adaptability and collective problem-solving. Understanding the balance between these models is essential for optimizing team dynamics and achieving organizational goals.
Core Principles of Top-down Leadership
Top-down leadership centers on a clear hierarchy where decision-making authority rests primarily with senior leaders, ensuring streamlined communication and control. This approach emphasizes accountability through defined roles and structured command, facilitating quick execution and consistency across the team. Core principles include centralized decision-making, clear direction from leaders, and adherence to established protocols for efficient management.
Core Principles of Distributed Leadership
Distributed leadership centers on shared responsibility, fostering collaboration among team members to leverage diverse skills and perspectives. It emphasizes empowerment, encouraging individuals at all levels to take initiative and make decisions aligned with common goals. This approach enhances adaptability and innovation by distributing authority rather than consolidating power in a single leader.
Leadership Styles: Key Differences
Top-down leaders centralize decision-making authority, providing clear direction and maintaining control through hierarchical structures, which can streamline accountability but may limit team autonomy and innovation. Distributed leaders share leadership roles across team members, fostering collaboration, empowerment, and diverse input, enhancing adaptability and collective problem-solving. This contrast in leadership styles impacts communication flow, team engagement, and overall organizational agility.
Impact on Team Collaboration
Top-down leadership centralizes decision-making, often limiting team members' input and reducing collaborative innovation, which can hinder overall team engagement. Distributed leadership promotes shared responsibility and empowers individuals to contribute ideas, fostering a culture of trust and enhanced collaboration. Teams managed with distributed leadership typically experience higher creativity, improved problem-solving, and stronger interpersonal connections.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Top-down leaders centralize decision-making authority, enabling quick, unilateral decisions aligned with organizational goals but often limiting team input and creativity. Distributed leaders share decision-making across team members, fostering collaboration and diverse perspectives, which can enhance innovation and adaptability but may slow the process. Balancing control with empowerment optimizes team responsiveness and engagement in dynamic environments.
Motivating and Empowering Teams
Top-down leaders maintain control by setting clear directives, which can streamline decision-making but may limit team motivation and empowerment. Distributed leaders foster an environment where team members share responsibility, increasing motivation through autonomy and collaborative engagement. Research shows distributed leadership enhances creative problem-solving and job satisfaction by promoting trust and individual accountability.
Accountability and Responsibility Distribution
Top-down leaders centralize accountability, assigning clear responsibilities to specific individuals, which streamlines decision-making but may limit team autonomy. Distributed leadership spreads responsibility across team members, fostering shared ownership and enhancing collective accountability. This approach encourages collaboration and empowers individuals to take initiative, improving adaptability and overall team performance.
Success Stories: Real-World Examples
Top-down leadership proved effective in companies like Apple, where Steve Jobs' decisive vision drove innovation and market dominance. Distributed leadership succeeded at Google, leveraging collaborative decision-making to foster creativity and responsiveness across teams. These real-world examples highlight how leadership styles align with organizational goals to achieve exceptional performance.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Team
Top-down leadership centralizes decision-making authority, enabling quick direction and clear accountability, which suits teams requiring strong guidance and efficiency. Distributed leadership fosters collaboration and shared responsibility, encouraging innovation and engagement in teams that benefit from diverse input and collective problem-solving. Evaluating your team's size, complexity, and goals helps determine whether centralized control or empowered autonomy best drives performance and morale.
Related Important Terms
Hierarchical Directiveness
Top-down leadership emphasizes hierarchical directiveness, where decisions flow from senior leaders down to team members, ensuring clear authority and control in project execution. Distributed leadership spreads decision-making across team members, fostering collaboration and shared responsibility, but may reduce clarity in hierarchical command structures.
Distributed Agency
Distributed leadership fosters greater team autonomy by empowering members to make decisions, leveraging diverse expertise to enhance collaboration and innovation. This decentralized approach increases accountability and adaptability, driving more resilient and effective organizational performance compared to traditional top-down management.
Centralized Decision Bottleneck
Top-down leadership often creates a centralized decision bottleneck, slowing down team responsiveness and innovation by funneling all decisions through a single leader. Distributed leadership empowers team members to make decisions independently, reducing delays and increasing adaptability in dynamic environments.
Collective Intelligence Enablement
Top-down leadership centralizes decision-making authority, often limiting a team's ability to leverage diverse perspectives, whereas distributed leadership fosters Collective Intelligence Enablement by empowering team members to contribute insights and make decisions collaboratively. This approach enhances problem-solving efficiency and innovation through shared accountability and distributed expertise across the organization.
Leadership Flattening
Top-down leadership centralizes decision-making authority, often slowing responsiveness and reducing employee empowerment, while distributed leadership flattens organizational hierarchy by sharing responsibilities across team members, enhancing collaboration and innovation. Leadership flattening fosters a more agile environment where diverse skills and perspectives drive collective problem-solving and accountability.
Command-and-Control Residuals
Top-down leadership often retains command-and-control residuals that limit team autonomy and slow decision-making, whereas distributed leadership promotes shared responsibility and empowers team members to act independently. This shift reduces hierarchical bottlenecks, enhances collaboration, and fosters a more adaptive and resilient organizational culture.
Empowerment Cascading
Top-down leadership centralizes decision-making, often limiting team autonomy, while distributed leadership promotes empowerment cascading by delegating authority and encouraging collaborative problem-solving across all levels. This approach enhances innovation, accountability, and engagement by enabling team members to take ownership and contribute to organizational success.
Peer-Led Autonomy
Peer-led autonomy in distributed leadership empowers team members to make decisions independently, fostering innovation and engagement by leveraging collective expertise. Unlike top-down leadership, distributed leaders cultivate a collaborative environment where responsibility and accountability are shared, resulting in enhanced agility and resilience within teams.
Leader-as-Facilitator Model
The Leader-as-Facilitator model in team management emphasizes empowering team members by distributing decision-making authority rather than relying on a top-down leadership approach, fostering collaboration and innovation. This distributed leadership style enhances accountability and adaptability, enabling teams to respond effectively to complex challenges and achieve collective goals.
Decentralized Accountability
Distributed leadership fosters decentralized accountability by empowering team members to make decisions and take ownership of their roles, enhancing adaptability and innovation. In contrast, top-down leadership centralizes authority, often limiting responsiveness and reducing individual accountability within the team.
Top-down Leader vs Distributed Leader for team management. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com