Hierarchical leadership relies on a clear chain of command with defined roles and responsibilities, promoting efficiency and control within an organization. Holacratic leadership distributes authority across self-managing teams, fostering innovation and adaptability by empowering employees to make decisions. Organizations choosing between these structures must weigh the need for stability and uniformity against flexibility and collaborative autonomy.
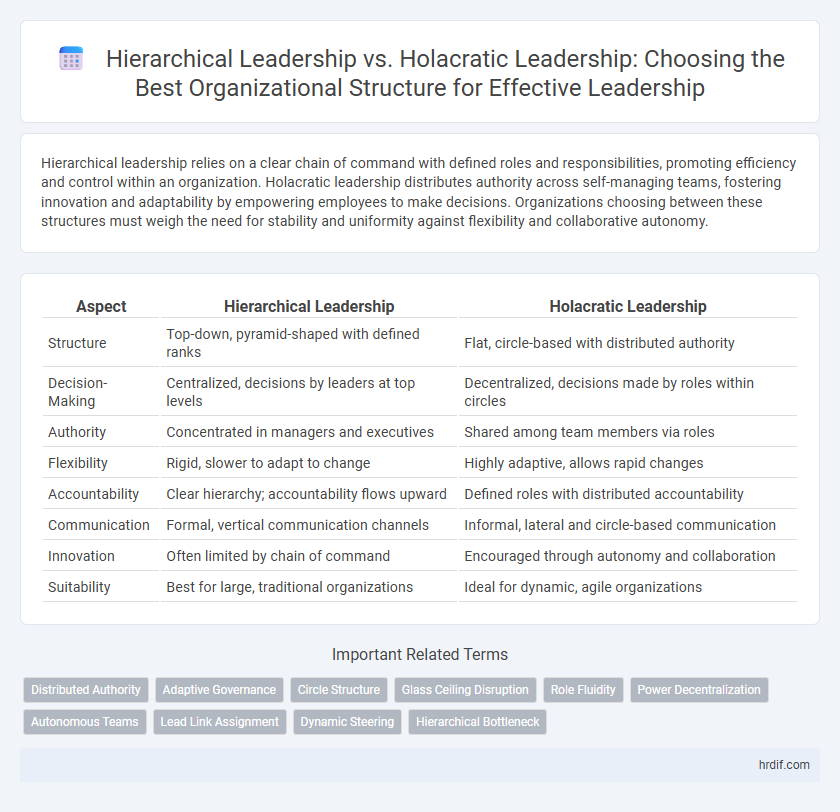
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hierarchical Leadership | Holacratic Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Top-down, pyramid-shaped with defined ranks | Flat, circle-based with distributed authority |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, decisions by leaders at top levels | Decentralized, decisions made by roles within circles |
| Authority | Concentrated in managers and executives | Shared among team members via roles |
| Flexibility | Rigid, slower to adapt to change | Highly adaptive, allows rapid changes |
| Accountability | Clear hierarchy; accountability flows upward | Defined roles with distributed accountability |
| Communication | Formal, vertical communication channels | Informal, lateral and circle-based communication |
| Innovation | Often limited by chain of command | Encouraged through autonomy and collaboration |
| Suitability | Best for large, traditional organizations | Ideal for dynamic, agile organizations |
Understanding Hierarchical Leadership
Hierarchical leadership features a clear chain of command where authority flows from top executives to lower-level employees, ensuring defined roles and responsibilities within the organization. This structure facilitates efficient decision-making and accountability by centralizing power and maintaining control through a formal reporting system. Understanding hierarchical leadership is crucial for organizations prioritizing stability, consistency, and predictability in their operational processes.
Defining Holacratic Leadership
Holacratic leadership is a decentralized organizational structure that distributes authority across self-managing teams rather than relying on a traditional hierarchical chain of command. It empowers employees by defining roles around the work needed, fostering agility, transparency, and collaborative decision-making. This leadership style enhances adaptability and responsiveness in dynamic business environments compared to rigid hierarchical systems.
Core Principles of Hierarchical Structures
Hierarchical leadership structures emphasize clear lines of authority, centralized decision-making, and defined roles, ensuring efficient command and control within organizations. This model relies on a top-down approach where power and responsibility flow from senior management to lower levels, fostering accountability and order. The core principles include formalized hierarchy, standardized procedures, and a well-established chain of command that supports operational consistency.
Key Features of Holacratic Models
Holacratic leadership features decentralized decision-making, distributing authority across self-organizing teams rather than concentrating power at the top. Roles are clearly defined by purpose and accountabilities, dynamically evolving to adapt to organizational needs without traditional managerial hierarchies. This model fosters transparency, agility, and employee empowerment by emphasizing autonomy and collaborative governance through structured processes such as governance and tactical meetings.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making authority at the top levels, enabling clear command and control but often slowing responsiveness and limiting input from lower tiers. Holacratic leadership distributes decision-making across autonomous teams, fostering agility and empowering employees to address issues promptly without relying on traditional managerial approval. This decentralized approach enhances innovation and adaptability by leveraging collective intelligence within the organizational structure.
Communication Flow in Each Structure
Hierarchical leadership structures feature top-down communication flows where directives and feedback move vertically between management levels, often resulting in slower decision-making and limited lateral collaboration. Holacratic leadership promotes decentralized, multi-directional communication through self-managed teams and roles, enhancing transparency and real-time information exchange across the organization. Studies show holacracy improves adaptive communication by encouraging open dialogues and reducing bottlenecks inherent in rigid hierarchical chains.
Adaptability and Innovation Potential
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making authority, which can slow adaptability and limit innovation due to rigid structures and slower communication flows. Holacratic leadership distributes power across self-managing teams, enhancing organizational flexibility and accelerating innovation through empowered employees and rapid iteration. Organizations adopting holacracy often experience increased responsiveness to market changes and more dynamic innovation pipelines compared to traditional hierarchies.
Impact on Employee Engagement
Hierarchical leadership often limits employee engagement due to rigid authority lines and restricted decision-making power, which can stifle creativity and motivation. In contrast, holacratic leadership distributes authority through self-managed teams, fostering greater autonomy, collaboration, and a sense of ownership among employees. Studies indicate organizations implementing holacracy experience higher levels of employee satisfaction and innovative contribution, boosting overall productivity and retention.
Challenges Facing Both Approaches
Hierarchical leadership often encounters challenges such as rigid communication flows, slow decision-making, and reduced employee autonomy, which can hinder innovation and adaptability. Holacratic leadership struggles with difficulties in role clarity, potential conflicts from decentralized authority, and the need for cultural shifts toward self-management. Both models require organizations to address resistance to change and invest in leadership development to optimize effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Organization
Hierarchical leadership features clear chains of command and centralized decision-making, optimizing efficiency in large, complex organizations with defined roles. Holacratic leadership disperses authority through self-managed teams, fostering agility and innovation ideal for dynamic, fast-evolving environments. Choosing the right structure depends on factors such as organizational size, industry, culture, and strategic goals to balance control with flexibility.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Authority
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making power at the top levels, resulting in clear authority but slower adaptability, while holacratic leadership distributes authority across self-managing teams, enhancing agility and employee empowerment. Organizations adopting holacracy benefit from increased innovation and responsiveness by decentralizing control, fostering a dynamic structure that contrasts with the rigid, top-down approach of hierarchical models.
Adaptive Governance
Hierarchical leadership relies on a clear chain of command and centralized decision-making, enabling swift execution but often limiting flexibility in dynamic environments. Holacratic leadership promotes distributed authority and self-governing teams, fostering adaptive governance that enhances organizational responsiveness and innovation in complex, rapidly changing markets.
Circle Structure
Holacratic leadership replaces traditional hierarchical leadership by distributing authority through interconnected circles, each responsible for specific roles and accountabilities, enhancing agility and employee autonomy. The circle structure promotes transparent decision-making and dynamic role evolution, fostering innovation and responsiveness within organizations.
Glass Ceiling Disruption
Hierarchical leadership often reinforces glass ceilings by centralizing decision-making power within a fixed chain of command, limiting upward mobility for marginalized groups. Holacratic leadership disrupts these barriers by distributing authority across self-managing teams, fostering inclusivity and equal opportunity for advancement.
Role Fluidity
Hierarchical leadership relies on fixed roles and clear lines of authority, limiting role fluidity and adaptability within organizations. Holacratic leadership enhances role fluidity by distributing decision-making power across self-organizing teams, allowing employees to assume multiple roles based on skills and situational needs.
Power Decentralization
Hierarchical leadership centralizes power within a top-down structure, concentrating decision-making authority among senior executives, which can limit flexibility and slow innovation. Holacratic leadership decentralizes power by distributing decision-making across self-organizing teams, enhancing agility and employee empowerment within the organizational structure.
Autonomous Teams
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making authority, often limiting team autonomy and slowing responsiveness, whereas holacratic leadership distributes power across autonomous teams that self-organize and make decisions independently, enhancing agility and innovation. Organizations adopting holacracy experience increased employee engagement and faster adaptation to market changes by empowering teams with clarity in roles and dynamic governance.
Lead Link Assignment
Hierarchical leadership assigns a Lead Link to a specific managerial role, centralizing decision-making authority and clarifying accountability within a defined chain of command. In contrast, holacratic leadership distributes Lead Link roles across self-managed teams, promoting autonomy and dynamic role assignments that align with evolving organizational priorities.
Dynamic Steering
Hierarchical leadership relies on a top-down approach with clear authority lines, enabling decisive dynamic steering through centralized decision-making and structured command chains. Holacratic leadership fosters adaptive dynamic steering by distributing authority across self-organizing teams, promoting agility and rapid response to organizational changes.
Hierarchical Bottleneck
Hierarchical leadership often creates bottlenecks as decision-making is centralized at the top levels, slowing down communication and innovation within the organizational structure. In contrast, holacratic leadership distributes authority across self-managing teams, reducing delays and increasing agility by empowering employees at all levels.
Hierarchical Leadership vs Holacratic Leadership for organizational structure. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com