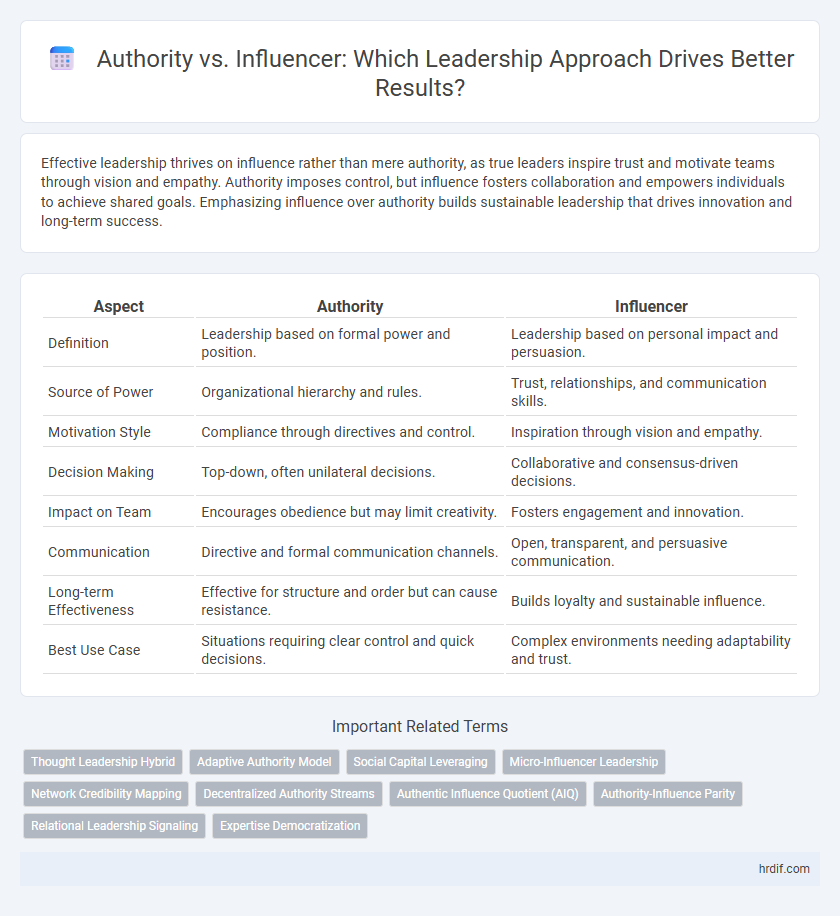
Effective leadership thrives on influence rather than mere authority, as true leaders inspire trust and motivate teams through vision and empathy. Authority imposes control, but influence fosters collaboration and empowers individuals to achieve shared goals. Emphasizing influence over authority builds sustainable leadership that drives innovation and long-term success.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Authority | Influencer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Leadership based on formal power and position. | Leadership based on personal impact and persuasion. |
| Source of Power | Organizational hierarchy and rules. | Trust, relationships, and communication skills. |
| Motivation Style | Compliance through directives and control. | Inspiration through vision and empathy. |
| Decision Making | Top-down, often unilateral decisions. | Collaborative and consensus-driven decisions. |
| Impact on Team | Encourages obedience but may limit creativity. | Fosters engagement and innovation. |
| Communication | Directive and formal communication channels. | Open, transparent, and persuasive communication. |
| Long-term Effectiveness | Effective for structure and order but can cause resistance. | Builds loyalty and sustainable influence. |
| Best Use Case | Situations requiring clear control and quick decisions. | Complex environments needing adaptability and trust. |
Understanding Authority and Influence in Leadership
Leadership effectiveness hinges on the dynamic interplay between authority and influence, where authority is derived from formal position and organizational power, while influence stems from personal credibility, trust, and relationship-building skills. Understanding this distinction enables leaders to leverage their positional power to provide clear direction, yet cultivate influence to inspire, motivate, and drive sustained engagement beyond structural constraints. Mastery of both authority and influence enhances decision-making, fosters team cohesion, and reinforces a leadership approach that balances control with empowerment.
Key Differences Between Authority and Influence
Authority in leadership relies on formal power derived from a position or role, enabling directives and enforcement of rules. Influence stems from the ability to inspire, persuade, and motivate others without relying on official power or hierarchy. Key differences include source of power, with authority grounded in organizational structure, while influence depends on personal relationships and credibility.
Origins of Authority: Formal Power in Leadership
Authority in leadership stems primarily from formal power rooted in organizational hierarchy, granting leaders the legitimate right to make decisions and enforce rules. This formal authority originates from titles, roles, and official positions recognized by the institution, which can command compliance and drive accountability. Unlike influence, which depends on persuasion and relationships, authority relies on established structure and sanctioned control within the leadership framework.
The Nature of Influence: Building Informal Leadership
Influence in leadership stems from the ability to inspire trust and respect rather than relying solely on formal authority or positional power. Informal leadership thrives through authentic relationships, effective communication, and consistent demonstration of expertise and integrity. Developing influence enhances collaboration and drives organizational change by motivating others beyond hierarchical constraints.
Advantages of Authority-Driven Leadership
Authority-driven leadership ensures clear decision-making and swift execution by establishing formal power structures within an organization. Leaders with authoritative roles can enforce rules consistently and maintain order, facilitating predictable and stable environments ideal for crisis management or highly regulated industries. This approach bolsters accountability, as authority delineates responsibility, enabling effective performance evaluation and organizational control.
Benefits of Influencer-Based Leadership Styles
Influencer-based leadership enhances team motivation by fostering trust and collaboration, leading to higher engagement and productivity. This approach leverages emotional intelligence and effective communication to inspire innovation and adaptability within diverse teams. Unlike authority-driven methods, influencer leadership cultivates a positive organizational culture that supports long-term growth and employee development.
Potential Pitfalls: Authority vs Influencer Approaches
Authority-based leadership risks fostering dependency and resistance by prioritizing control and compliance, which can stifle creativity and reduce team morale. Influencer-based leadership, while promoting engagement and collaboration, may encounter challenges in maintaining consistency and decisiveness when authority is unclear. Balancing authority with influence requires awareness of power dynamics to avoid pitfalls such as over-reliance on hierarchy or weakened accountability.
Situational Leadership: Choosing Authority or Influence
Situational Leadership emphasizes adapting between authority and influence based on team dynamics and task complexity. Leaders exercising authority set clear expectations and control, ideal for crisis or high-pressure scenarios requiring swift decisions. Influence fosters collaboration and motivation, effective in developmental stages where employee autonomy and creativity drive results.
Developing Leadership Presence Through Influence
Leadership presence is most effectively developed through influence rather than authority, as influence inspires trust and fosters genuine connections within teams. Utilizing emotional intelligence and active listening enhances a leader's ability to motivate and empower others, cultivating a collaborative work environment. Research indicates leaders who prioritize influence over formal authority achieve higher employee engagement and long-term organizational success.
Balancing Authority and Influence for Effective Leadership
Balancing authority and influence in leadership enhances team motivation and decision-making effectiveness. Authority establishes clear roles and accountability, while influence fosters trust, collaboration, and innovation. Effective leaders integrate both by using positional power to set direction and personal influence to inspire commitment and drive performance.
Related Important Terms
Thought Leadership Hybrid
A Thought Leadership Hybrid in leadership seamlessly blends authority's decisive command with influencer-driven inspiration, fostering an environment where expertise guides strategic decisions while empathy and persuasion engage teams. This approach enhances organizational agility, driving innovation and trust by aligning authoritative knowledge with authentic relationship-building.
Adaptive Authority Model
The Adaptive Authority Model redefines leadership by balancing formal authority with influence, emphasizing flexibility in decision-making and team engagement. This approach prioritizes situational awareness and emotional intelligence to adapt leadership style, fostering collaboration and driving organizational success.
Social Capital Leveraging
Effective leaders leverage social capital by prioritizing influence over authority, fostering trust and collaboration within their networks. This approach enhances organizational resilience and drives sustainable success through relational power rather than positional control.
Micro-Influencer Leadership
Micro-influencer leadership harnesses personalized authority by leveraging trust and authentic connections within small, focused groups, driving engagement and motivation more effectively than traditional hierarchical authority. This approach emphasizes relational influence over positional power, fostering a collaborative environment where leadership emerges from credibility and consistent value delivery.
Network Credibility Mapping
Network Credibility Mapping highlights that leaders relying solely on formal authority often face limited influence, whereas those leveraging influencer tactics build trust and expand their impact across diverse connections. Effective leadership integrates authority with strategic relationship-building to enhance network credibility and facilitate collaborative success.
Decentralized Authority Streams
Decentralized authority streams empower leaders to distribute decision-making power across multiple levels, enhancing agility and responsiveness in dynamic environments. Emphasizing influence over formal authority cultivates trust, collaboration, and innovation, driving sustainable organizational success.
Authentic Influence Quotient (AIQ)
Authentic Influence Quotient (AIQ) measures a leader's ability to inspire and motivate through genuine connections rather than relying solely on formal authority or positional power. High AIQ correlates with increased team engagement, trust, and long-term organizational success by fostering authentic relationships and empowering others.
Authority-Influence Parity
Effective leadership balances authority and influence, recognizing that true power emerges when formal authority aligns with the ability to inspire and impact others. Authority-Influence Parity fosters trust and collaboration, enhancing decision-making and driving organizational success.
Relational Leadership Signaling
Relational leadership signaling emphasizes building trust and connection, where authority relies on positional power while influencers leverage social cues and emotional intelligence to inspire collaboration and commitment. Effective leaders balance authority with influence to foster authentic relationships that drive team engagement and performance.
Expertise Democratization
Authority-based leadership relies on formal power and hierarchical control, while influencer-driven leadership prioritizes expertise democratization, empowering team members through shared knowledge and collaborative decision-making. This approach enhances organizational agility and fosters innovation by leveraging diverse insights rather than centralized command.
Authority vs Influencer for leadership approach. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com