Hierarchical leaders emphasize clear authority lines and centralized decision-making, which enhances control and accountability within an organization. Horizontal leaders promote collaboration and equal input among team members, fostering innovation and agility. Choosing the right leadership style depends on the organization's goals, culture, and the complexity of tasks involved.
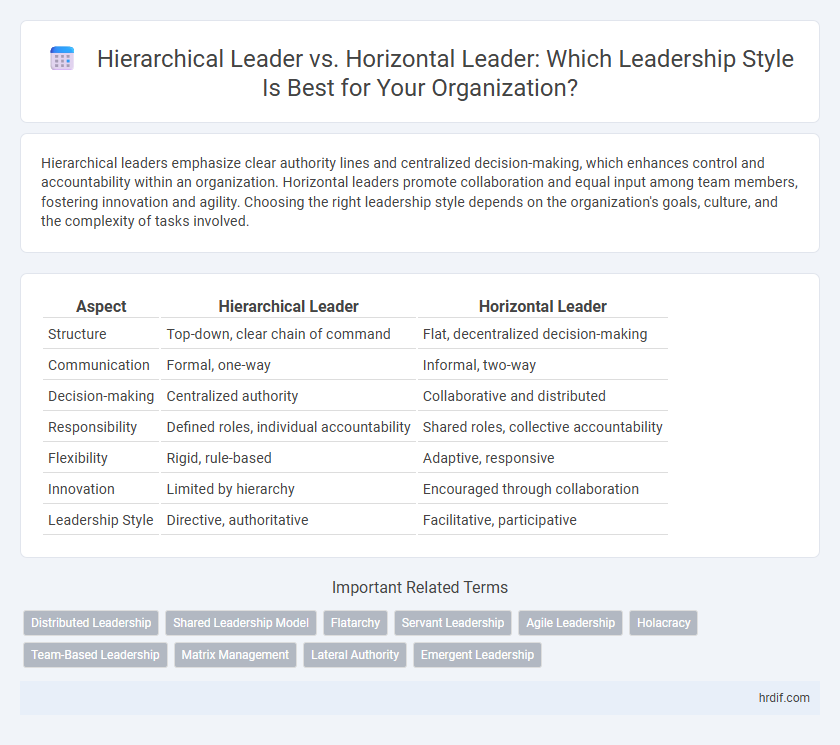
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hierarchical Leader | Horizontal Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Top-down, clear chain of command | Flat, decentralized decision-making |
| Communication | Formal, one-way | Informal, two-way |
| Decision-making | Centralized authority | Collaborative and distributed |
| Responsibility | Defined roles, individual accountability | Shared roles, collective accountability |
| Flexibility | Rigid, rule-based | Adaptive, responsive |
| Innovation | Limited by hierarchy | Encouraged through collaboration |
| Leadership Style | Directive, authoritative | Facilitative, participative |
Defining Hierarchical and Horizontal Leadership
Hierarchical leadership refers to a traditional top-down structure where authority flows from senior leaders to subordinates, emphasizing clear roles and centralized decision-making. Horizontal leadership, in contrast, promotes a collaborative environment with distributed authority, encouraging teamwork and shared responsibility across peers. Both leadership models impact organizational dynamics, communication, and decision processes differently based on their structural design.
Core Principles of Hierarchical Leadership
Hierarchical leadership is grounded in clear authority lines and structured decision-making, emphasizing rank, responsibility, and top-down communication. Core principles include centralized control, accountability at each level, and defined roles that streamline operations and enforce discipline. This leadership style enhances order and efficiency in organizations requiring decisive direction and uniformity.
Fundamental Traits of Horizontal Leadership
Horizontal leadership emphasizes collaboration, shared decision-making, and mutual respect, fostering a culture where diverse perspectives drive innovation. Fundamental traits include strong communication skills, emotional intelligence, and empowering team members to take initiative and share responsibility. This approach minimizes power imbalances and enhances adaptability within organizations, promoting collective ownership of goals and outcomes.
Decision-Making: Top-Down vs Collaborative Approaches
Hierarchical leaders rely on top-down decision-making, where authority is centralized and directives flow from senior management to subordinates, ensuring clear accountability and faster execution. Horizontal leaders emphasize collaborative approaches, promoting shared responsibility and inclusive input across teams to enhance creativity and adaptability. Organizations benefit from aligning leadership styles with their decision-making needs, balancing control with empowerment for optimal performance.
Impact on Organizational Culture and Employee Engagement
Hierarchical leaders typically establish clear authority lines that enhance organizational structure but may suppress open communication, limiting employee engagement and innovation. Horizontal leaders foster collaborative environments that promote trust, inclusivity, and shared decision-making, significantly boosting employee motivation and strengthening organizational culture. Emphasizing empowerment and transparency, horizontal leadership cultivates a more adaptable and resilient workforce compared to the often rigid dynamics of hierarchical leadership.
Communication Flows: Command Chains vs Open Networks
Hierarchical leaders rely on command chains that ensure clear, top-down communication and decision-making, essential for maintaining order in structured organizations. Horizontal leaders foster open communication networks that encourage collaboration, information sharing, and collective problem-solving across all levels. Effective leadership balances these communication flows to enhance organizational agility and employee engagement.
Adaptability and Innovation in Leadership Structures
Hierarchical leaders maintain clear chains of command that enhance decision-making efficiency but often limit adaptability and slow innovation due to rigid structures. Horizontal leaders promote collaboration across teams, fostering a flexible environment where rapid innovation and responsiveness to change thrive. Organizations aiming to enhance adaptability and drive innovation benefit from adopting horizontal leadership models that empower diverse input and dynamic problem-solving.
Performance Management and Accountability Methods
Hierarchical leaders emphasize structured performance management through clear chains of command, formal evaluations, and top-down accountability, which ensures consistent adherence to organizational goals. Horizontal leaders prioritize collaborative performance tracking using peer reviews, shared responsibility, and collective accountability to foster innovation and agility. These distinct methods influence transparency, motivation, and efficiency within leadership organizations.
Suitability Across Different Industries and Teams
Hierarchical leadership structures excel in industries requiring clear authority and quick decision-making, such as manufacturing, military, and construction, ensuring efficiency and accountability. Horizontal leadership proves more suitable for creative, tech, and startup environments, fostering collaboration, innovation, and adaptability within diverse teams. Selecting the appropriate leadership style based on industry demands and team dynamics enhances organizational performance and employee engagement.
Navigating the Transition: Shifting Leadership Models
Navigating the transition from hierarchical leadership to horizontal leadership requires reconfiguring organizational structures to prioritize collaboration and decentralized decision-making. Emphasizing transparent communication channels and empowering team members at all levels fosters innovation and agility in adapting to change. This shift challenges traditional authority dynamics, promoting shared ownership and collective accountability to drive performance and engagement.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Leadership
Hierarchical leaders centralize decision-making authority within structured levels of power, which can slow communication and limit innovation, while horizontal leaders promote distributed leadership by empowering teams to share responsibility and collaborate across functions. Emphasizing distributed leadership enhances organizational agility and fosters a culture of accountability and collective problem-solving.
Shared Leadership Model
Hierarchical leadership centralizes authority with clear top-down decision-making, while horizontal leadership promotes shared responsibility and collaborative influence across team members. Emphasizing the Shared Leadership Model enhances organizational agility and innovation by distributing leadership roles and fostering mutual accountability within teams.
Flatarchy
Flatarchy combines hierarchical and horizontal leadership by integrating clear authority with collaborative decision-making, promoting agility and innovation in organizational structures. This hybrid model accelerates communication flow and empowers teams, making it ideal for dynamic environments where adaptability and speed are critical.
Servant Leadership
Hierarchical leaders emphasize structured authority and top-down decision-making, while horizontal leaders prioritize collaboration and shared responsibility, aligning closely with the principles of servant leadership that focus on empowering and serving team members. Servant leadership fosters a culture of trust and support by promoting empathy, active listening, and the growth of individuals within a horizontal organizational framework.
Agile Leadership
Hierarchical leaders emphasize top-down decision-making and clear authority lines, which can slow responsiveness in Agile environments focused on collaboration and adaptability. Horizontal leaders foster empowered teams and decentralized control, enhancing innovation and rapid problem-solving essential for effective Agile Leadership.
Holacracy
Hierarchical leaders rely on top-down decision-making with clearly defined roles and authority, whereas horizontal leaders promote distributed power and collaborative governance, as epitomized by Holacracy's self-management system where roles are dynamic and accountability is shared. Holacracy enhances organizational agility by replacing traditional hierarchy with circles that encourage transparent communication and rapid adaptation.
Team-Based Leadership
Hierarchical leaders emphasize top-down command structures that clearly define authority and roles, fostering efficiency in decision-making within rigid frameworks. Horizontal leaders promote collaborative, team-based environments where shared responsibility and open communication enhance innovation and adaptability.
Matrix Management
Hierarchical leaders emphasize clear chain-of-command structures essential for matrix management, enabling accountability and streamlined decision-making across multiple reporting lines. Horizontal leaders foster collaboration and cross-functional communication, driving innovation and agility by empowering teams to work beyond traditional vertical silos.
Lateral Authority
Hierarchical leaders exercise vertical authority with clear top-down decision-making, while horizontal leaders emphasize lateral authority, promoting collaboration and shared responsibility across teams. Lateral authority in horizontal leadership enhances agility, innovation, and employee engagement by flattening organizational structures and empowering cross-functional communication.
Emergent Leadership
Hierarchical leaders maintain structured authority with clear top-down directives, while horizontal leaders promote collaborative decision-making and shared responsibility, fostering emergent leadership that arises naturally through team interactions and expertise. In organizations prioritizing innovation and adaptability, emergent leadership within horizontal frameworks enhances responsiveness and employee engagement by leveraging diverse perspectives and decentralized influence.
Hierarchical Leader vs Horizontal Leader for leadership organization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com