Transactional leaders prioritize structure, clear roles, and reward-based systems to maintain stability during change, ensuring tasks are completed efficiently. Agile leaders embrace flexibility, collaboration, and continuous feedback, enabling rapid adaptation to evolving circumstances. Effective change management benefits from integrating transactional clarity with agile responsiveness to balance consistency and innovation.
Table of Comparison
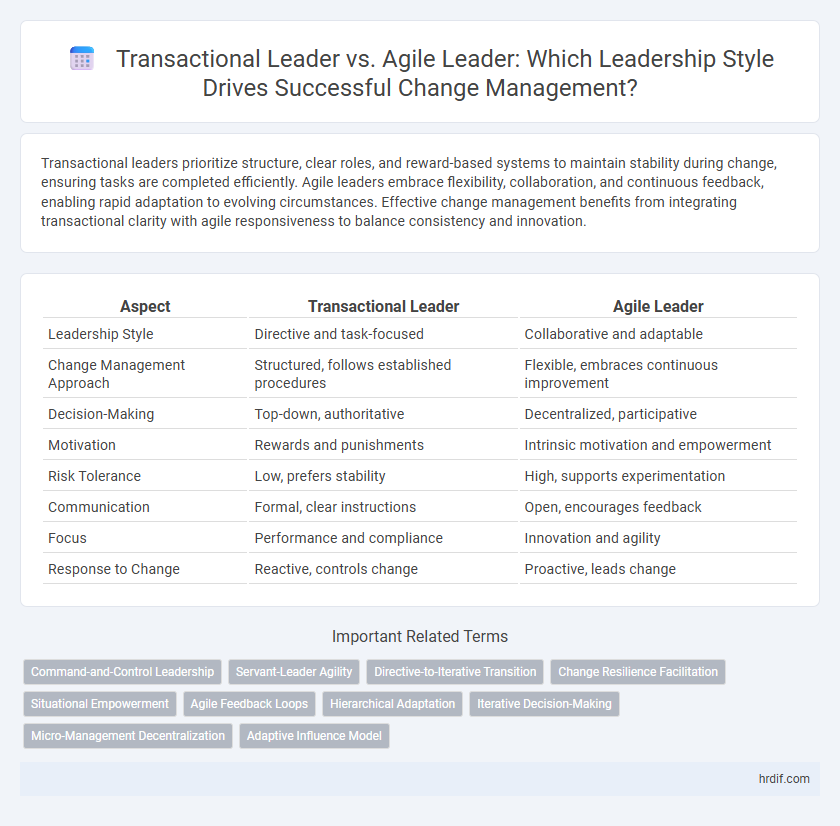
| Aspect | Transactional Leader | Agile Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership Style | Directive and task-focused | Collaborative and adaptable |
| Change Management Approach | Structured, follows established procedures | Flexible, embraces continuous improvement |
| Decision-Making | Top-down, authoritative | Decentralized, participative |
| Motivation | Rewards and punishments | Intrinsic motivation and empowerment |
| Risk Tolerance | Low, prefers stability | High, supports experimentation |
| Communication | Formal, clear instructions | Open, encourages feedback |
| Focus | Performance and compliance | Innovation and agility |
| Response to Change | Reactive, controls change | Proactive, leads change |
Understanding Transactional and Agile Leadership in Change Management
Transactional leaders emphasize structured processes, clear roles, and immediate rewards or penalties to drive change, ensuring stability and consistency during transitions. Agile leaders prioritize adaptability, collaboration, and continuous feedback, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to evolving challenges and foster innovation. Understanding these distinct approaches helps organizations tailor change management strategies that balance control with flexibility for optimal outcomes.
Core Principles: Transactional vs Agile Leadership
Transactional leadership centers on structured hierarchy, clear roles, and reward-based motivation, emphasizing routine and control during change management. Agile leadership values adaptability, collaboration, and continuous feedback, promoting flexibility and innovation to navigate complex organizational transformations. Core principles contrast by prioritizing stability and efficiency in transactional models versus responsiveness and empowerment in agile frameworks.
Decision-Making Approaches in Change Initiatives
Transactional leaders utilize a structured, top-down decision-making approach focused on clear roles and reward-based performance during change initiatives. Agile leaders embrace collaborative, iterative decision-making that encourages adaptability and real-time feedback from diverse stakeholders. This flexibility in agile decision-making enhances responsiveness and innovation in dynamic change environments compared to the more rigid transactional style.
Motivating Teams: Rewards vs Empowerment
Transactional leaders motivate teams through clear rewards and structured incentives, aligning performance directly with specific outcomes. Agile leaders prioritize empowerment by fostering autonomy, encouraging innovation, and enabling team members to take ownership of change processes. This shift from extrinsic rewards to intrinsic motivation enhances adaptability and sustained engagement in dynamic environments.
Flexibility and Adaptability During Change
Transactional leaders emphasize structured processes and clear expectations, which can provide stability but may limit flexibility during change. Agile leaders prioritize adaptability and responsiveness, enabling teams to pivot quickly in dynamic environments and fostering continuous improvement. This flexibility enhances the organization's ability to navigate uncertainty and implement effective change management strategies.
Communication Styles for Successful Change Management
Transactional leaders emphasize clear, directive communication with structured feedback loops to maintain order during change, ensuring tasks are understood and completed efficiently. Agile leaders prioritize open, collaborative communication, fostering transparency and rapid feedback to adapt quickly to evolving challenges. Effective change management requires blending transactional clarity with agile flexibility to engage teams and drive continuous improvement.
Managing Resistance to Change: Transactional vs Agile Responses
Transactional leaders manage resistance to change by enforcing clear rules, rewards, and penalties, creating a structured environment that minimizes uncertainty. Agile leaders respond with adaptability, encouraging collaboration and continuous feedback to address concerns dynamically and foster collective ownership of change. While transactional approaches prioritize compliance, agile leadership emphasizes flexibility and cultural alignment for sustained transformation.
Performance Measurement and Feedback Loops
Transactional leaders emphasize strict performance measurement through predefined metrics and regular feedback loops to maintain control and ensure task completion. Agile leaders prioritize adaptive feedback cycles and iterative performance evaluations to foster continuous improvement and responsiveness during change management. Effective change management integrates both approaches by balancing quantitative performance data with dynamic, real-time feedback for enhanced organizational agility.
Case Studies: Transactional vs Agile Leaders in Action
Case studies reveal that transactional leaders excel in structured environments by enforcing rules and rewarding compliance during change management initiatives. Agile leaders outperform in dynamic settings by fostering collaboration, adaptability, and continuous feedback to navigate complex change. Organizations embracing agile leadership report higher employee engagement and faster adoption rates compared to those relying solely on transactional methods.
Choosing the Right Leadership Approach for Organizational Change
Transactional leaders emphasize structured processes and clear rewards or penalties, ensuring stability during organizational change. Agile leaders prioritize adaptability and collaboration, fostering innovation and rapid responses in dynamic environments. Selecting the appropriate leadership style depends on the organization's culture, change urgency, and the complexity of the transformation required.
Related Important Terms
Command-and-Control Leadership
Transactional leaders emphasize command-and-control methods, relying on structured tasks, clear directives, and reward-based performance to manage change efficiently. Agile leaders prioritize flexibility, collaboration, and adaptive strategies, encouraging empowerment and rapid response over rigid hierarchical control in dynamic environments.
Servant-Leader Agility
Transactional leaders emphasize structure and clear rewards to maintain order during change, whereas agile leaders, particularly servant-leader agile models, prioritize collaboration, empathy, and adaptability to empower teams and drive sustainable transformation. Servant-leader agility fosters a culture of trust and continuous feedback, enabling organizations to respond swiftly and effectively to evolving challenges in change management.
Directive-to-Iterative Transition
Transactional leaders rely on directive approaches with clear structures and defined tasks, while Agile leaders embrace iterative processes and adaptive strategies to facilitate continuous change management. The transition from transactional to Agile leadership enhances organizational responsiveness and empowers teams through collaborative decision-making and ongoing feedback loops.
Change Resilience Facilitation
Transactional leaders emphasize structured processes and clear rewards to enforce compliance during change, fostering short-term stability but limited adaptability. Agile leaders prioritize flexibility and empowerment, enhancing change resilience by encouraging continuous learning and rapid response to evolving circumstances.
Situational Empowerment
Transactional leaders emphasize clear structures and reward-based systems to ensure compliance during change, while agile leaders prioritize situational empowerment by adapting their approach to foster flexibility and collaboration among team members. This empowerment enables agile leaders to respond swiftly to dynamic environments, enhancing team resilience and driving continuous improvement in change management processes.
Agile Feedback Loops
Transactional leaders emphasize structured feedback through formal evaluations and reward-based systems, limiting adaptability in change management. Agile leaders leverage continuous feedback loops that promote rapid iteration, responsiveness, and collaborative problem-solving to drive effective organizational change.
Hierarchical Adaptation
Transactional leaders emphasize hierarchical adaptation by maintaining clear structures and reward-based compliance during change management, ensuring stability through defined roles and procedures. Agile leaders foster adaptive hierarchies by promoting flexibility, decentralized decision-making, and continuous feedback loops, enabling organizations to respond swiftly and effectively to dynamic change environments.
Iterative Decision-Making
Transactional leaders rely on predefined processes and clear hierarchies to enforce decisions during change management, emphasizing control and compliance. Agile leaders prioritize iterative decision-making by continuously adapting strategies based on real-time feedback and collaborative input, enabling more flexible and responsive change implementation.
Micro-Management Decentralization
Transactional leaders emphasize micro-management by closely monitoring tasks and enforcing strict controls, which can hinder rapid adaptation during change management. Agile leaders promote decentralization by empowering teams with autonomy and fostering collaborative decision-making, enabling more effective and flexible responses to organizational change.
Adaptive Influence Model
Transactional leaders emphasize structured processes and clear rewards to drive change, ensuring compliance through established protocols, while Agile leaders employ the Adaptive Influence Model to foster flexibility, collaboration, and continuous learning, enabling rapid response to dynamic environments. This approach prioritizes situational awareness and emotional intelligence, facilitating effective change management by aligning team behaviors with evolving organizational goals.
Transactional Leader vs Agile Leader for change management. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com