Top-down leadership provides clear authority and streamlined decision-making, enabling quick alignment on team goals and direction. Peer leadership fosters collaboration and shared responsibility, promoting engagement and diverse perspectives within the team. Balancing both approaches can enhance adaptability and drive stronger team performance.
Table of Comparison
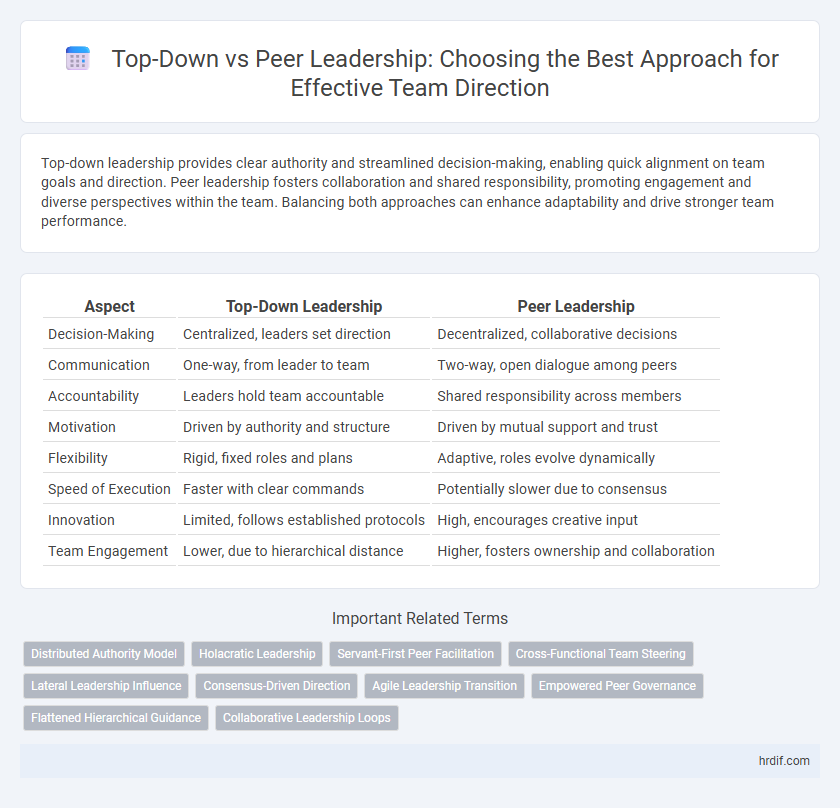
| Aspect | Top-Down Leadership | Peer Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Centralized, leaders set direction | Decentralized, collaborative decisions |
| Communication | One-way, from leader to team | Two-way, open dialogue among peers |
| Accountability | Leaders hold team accountable | Shared responsibility across members |
| Motivation | Driven by authority and structure | Driven by mutual support and trust |
| Flexibility | Rigid, fixed roles and plans | Adaptive, roles evolve dynamically |
| Speed of Execution | Faster with clear commands | Potentially slower due to consensus |
| Innovation | Limited, follows established protocols | High, encourages creative input |
| Team Engagement | Lower, due to hierarchical distance | Higher, fosters ownership and collaboration |
Defining Top-Down and Peer Leadership
Top-down leadership involves a hierarchical approach where decisions and directives flow from senior management to team members, ensuring clear authority and accountability. Peer leadership emphasizes collaboration and shared responsibility among team members, fostering mutual influence and collective decision-making. Understanding these leadership styles helps organizations choose the best approach for effective team direction and performance.
Key Characteristics of Top-Down Leadership
Top-down leadership is characterized by a clearly defined hierarchy where decisions are made by senior leaders and directives flow downward to team members. This approach emphasizes centralized control, clear responsibilities, and fast decision-making, often resulting in consistent guidance and accountability. Leaders typically set goals, monitor progress closely, and enforce policies to maintain order and align team efforts towards organizational objectives.
Essential Traits of Peer Leadership
Peer leadership thrives on collaboration, emotional intelligence, and trust-building, fostering a culture where team members feel empowered and valued. Essential traits include active listening, empathy, and the ability to motivate peers without formal authority, creating an inclusive environment for innovation and productivity. Unlike top-down leadership, peer leadership emphasizes shared responsibility and consensus-based decision-making, enhancing team cohesion and adaptability.
Advantages of Top-Down Leadership
Top-Down Leadership provides clear authority and decision-making efficiency, ensuring swift implementation of strategies aligned with organizational goals. This hierarchical approach enhances accountability, as leaders hold defined responsibility for outcomes, streamlining communication and minimizing confusion within teams. It also fosters consistency in direction, enabling teams to stay focused on priority tasks and achieve measurable results.
Advantages of Peer Leadership
Peer leadership fosters collaboration and enhances team cohesion by leveraging mutual respect and shared responsibility among members. It promotes faster decision-making and adaptability, as team members communicate informally and directly without hierarchical barriers. This approach increases engagement and accountability, leading to higher motivation and improved overall team performance.
Challenges and Limitations of Top-Down Leadership
Top-down leadership often faces challenges such as limited employee engagement and reduced innovation due to its hierarchical structure, which can stifle open communication and creative problem-solving. Decision-making concentration in upper management leads to slower response times and decreased adaptability in dynamic business environments. This leadership style may also create dependency and lower morale, as team members feel less empowered to contribute ideas or take initiative.
Challenges and Limitations of Peer Leadership
Peer leadership often encounters challenges such as lack of clear authority, which can lead to decision-making delays and conflicts within the team. Without formal hierarchical support, peers may struggle to enforce accountability and maintain consistent direction, resulting in diminished team cohesion. The egalitarian nature of peer leadership can also limit strategic alignment and complicate the resolution of competing priorities among team members.
Situations Where Top-Down Leadership Works Best
Top-down leadership excels in crisis situations requiring swift, decisive action, such as emergency responses and organizational restructuring, where clear authority accelerates decision-making. This approach is effective in highly regulated industries like healthcare and finance, where adherence to strict protocols ensures compliance and mitigates risks. Top-down leadership also benefits teams lacking experience or clarity in roles, offering structured guidance and reducing ambiguity to achieve targeted outcomes efficiently.
Situations Where Peer Leadership Excels
Peer leadership excels in collaborative environments where team members possess diverse expertise and require mutual influence to foster innovation and agility. This approach enhances decision-making by leveraging collective insights, promoting shared accountability, and increasing motivation through equal participation. It thrives in dynamic projects where flexibility and rapid adaptation are critical for success.
Choosing the Right Leadership Model for Your Team
Top-down leadership provides clear authority and decision-making efficiency, ideal for teams needing structure and quick guidance. Peer leadership fosters collaboration and shared responsibility, enhancing creativity and engagement in teams with experienced members. Selecting the right model depends on team size, project complexity, and organizational culture to balance control and autonomy effectively.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Authority Model
Top-down leadership centralizes decision-making with clear directives from executives, ensuring consistent alignment but potentially limiting team creativity and autonomy. Peer leadership within a distributed authority model empowers team members to share responsibilities, fostering collaboration, faster innovation, and adaptable problem-solving across organizational layers.
Holacratic Leadership
Holacratic leadership emphasizes distributed authority by enabling self-organizing teams to set direction through peer collaboration rather than relying on traditional top-down commands. This approach fosters agility, empowerment, and innovation by integrating transparent roles and circles that replace hierarchical decision-making structures.
Servant-First Peer Facilitation
Top-down leadership often centralizes decision-making authority, which can streamline direction but risks limiting team autonomy and innovation. Servant-first peer facilitation empowers team members by fostering collaboration, mutual support, and shared accountability, enhancing engagement and collective problem-solving.
Cross-Functional Team Steering
Top-down leadership provides clear, centralized direction essential for aligning cross-functional teams towards unified goals, ensuring streamlined decision-making and accountability. Peer leadership fosters collaborative dynamics that enhance innovation and adaptability within diverse team structures by leveraging shared expertise and mutual influence.
Lateral Leadership Influence
Top-down leadership relies on hierarchical authority to set team direction, often limiting lateral influence among peers. In contrast, peer leadership emphasizes lateral leadership influence, fostering collaboration, shared responsibility, and enhanced innovation within teams.
Consensus-Driven Direction
Top-down leadership centralizes decision-making power, enabling swift, authoritative direction but potentially limiting team input and buy-in. Peer leadership fosters consensus-driven direction by encouraging collaboration and shared responsibility, enhancing team engagement and collective commitment to goals.
Agile Leadership Transition
Top-down leadership centralizes decision-making within senior management, enabling swift direction but often limiting team autonomy and innovation, whereas peer leadership fosters collaborative decision-making, enhancing agility and responsiveness crucial for Agile leadership transitions. Agile teams thrive under peer leadership by promoting shared responsibility and continuous feedback, which accelerates adaptability and empowers team members in a dynamic environment.
Empowered Peer Governance
Empowered peer governance fosters collaborative decision-making within teams, enhancing innovation and accountability by distributing leadership roles equitably among members. Contrasting with top-down leadership, this approach leverages collective expertise and autonomy to drive team direction and performance.
Flattened Hierarchical Guidance
Flattened hierarchical guidance enhances team autonomy by distributing decision-making authority more evenly than traditional top-down leadership, fostering collaboration and faster problem-solving among peers. Peer leadership increases accountability and engagement, driving innovation through collective expertise rather than relying solely on directives from higher management.
Collaborative Leadership Loops
Top-down leadership establishes clear authority and decision-making paths, ensuring swift execution of strategic goals, while peer leadership fosters mutual accountability and agility through equal participation. Collaborative leadership loops enhance team direction by integrating continuous feedback and shared responsibility, driving innovation and adaptive problem-solving.
Top-Down vs Peer Leadership for team direction. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com