Hierarchical leaders maintain clear authority lines, enabling efficient decision-making and accountability within a structured chain of command. Flat structure leaders promote collaboration and employee empowerment, fostering innovation and agility by reducing bureaucratic barriers. Selecting between these styles depends on organizational goals, culture, and the need for control versus flexibility in the workplace.
Table of Comparison
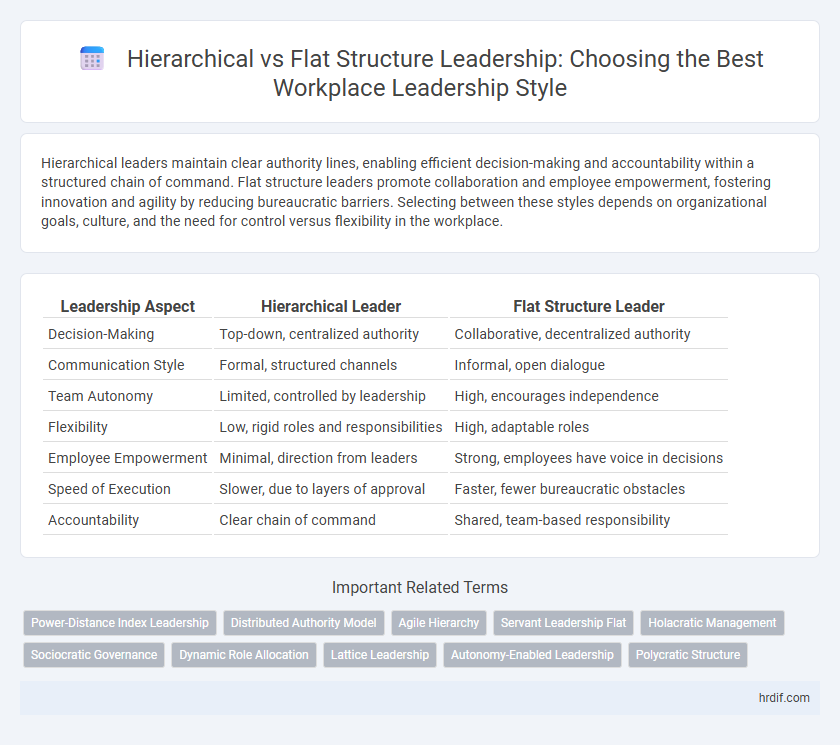
| Leadership Aspect | Hierarchical Leader | Flat Structure Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Top-down, centralized authority | Collaborative, decentralized authority |
| Communication Style | Formal, structured channels | Informal, open dialogue |
| Team Autonomy | Limited, controlled by leadership | High, encourages independence |
| Flexibility | Low, rigid roles and responsibilities | High, adaptable roles |
| Employee Empowerment | Minimal, direction from leaders | Strong, employees have voice in decisions |
| Speed of Execution | Slower, due to layers of approval | Faster, fewer bureaucratic obstacles |
| Accountability | Clear chain of command | Shared, team-based responsibility |
Defining Hierarchical Leadership in the Modern Workplace
Hierarchical leadership in the modern workplace is defined by a clear chain of command where decision-making authority flows from top to bottom, ensuring structured roles and responsibilities. This traditional model emphasizes control, accountability, and specialization, which can streamline processes but may limit flexibility and employee autonomy. Organizations with hierarchical leaders often prioritize stability and consistency, particularly in large, complex environments requiring clear oversight.
Flat Structure Leadership: Principles and Practices
Flat structure leadership emphasizes decentralized decision-making, fostering increased collaboration and innovation among team members. Leaders prioritize transparency, empowerment, and open communication to create an agile and responsive organizational environment. This approach enhances employee engagement and accelerates problem-solving by minimizing bureaucratic barriers.
Key Differences Between Hierarchical and Flat Leadership Styles
Hierarchical leaders emphasize clear authority lines, decision-making power concentrated at the top, and structured communication channels, promoting order and accountability. Flat structure leaders prioritize decentralization, empowering team members with autonomy, fostering collaboration and faster decision-making. Key differences include the level of control, communication flow, and employee involvement in leadership responsibilities.
Decision-Making: Top-Down vs. Collaborative Approaches
Hierarchical leaders typically enforce top-down decision-making, where authority flows from senior management to lower levels, ensuring clear accountability and swift execution of directives. In contrast, flat structure leaders emphasize collaborative decision-making, encouraging input from team members at all levels to foster innovation and shared ownership. Organizations with hierarchical leadership benefit from streamlined processes, while those with flat structures gain agility and enhanced employee engagement.
Communication Flow: Structured Chains vs. Open Networks
Hierarchical leaders maintain communication through structured chains, ensuring clear authority and accountability but often slowing information flow and innovation. Flat structure leaders promote open networks, fostering faster communication, collaborative problem-solving, and increased employee empowerment. The choice between these models impacts organizational agility, with hierarchical systems prioritizing order and flat structures enhancing flexibility.
Employee Empowerment in Hierarchical vs. Flat Organizations
Hierarchical leaders typically exert control through defined chains of command, limiting employee empowerment by constraining decision-making authority to higher levels. In contrast, flat structure leaders encourage autonomy and collaboration, fostering a culture where employees actively participate in problem-solving and innovation. Empowerment in flat organizations correlates with increased job satisfaction, creativity, and faster response times to workplace challenges.
Scalability and Growth: Which Structure Performs Better?
Hierarchical leaders excel in scalability due to clear authority lines and defined roles, enabling large organizations to maintain control and streamline decision-making processes. Flat structure leaders foster faster innovation and adaptability by minimizing layers, which supports agile growth in dynamic markets. Scalability in hierarchical models suits stable environments, while flat structures drive growth in rapidly changing industries through collaborative leadership.
Impact on Innovation and Agility
Hierarchical leaders often enforce strict chains of command that can slow decision-making and stifle innovation by limiting open communication and employee autonomy. Flat structure leaders promote a collaborative environment where quick feedback and decentralized decision-making enhance agility and foster a culture of continuous innovation. Organizations with flat leadership structures typically experience faster adaptation to market changes and higher employee engagement driving creative problem-solving.
Case Studies: Success Stories from Both Leadership Models
Case studies reveal that hierarchical leaders excel in large corporations by ensuring clear authority and streamlined decision-making, which boosts operational efficiency and accountability. In contrast, flat structure leaders thrive in innovative startups where collaborative environments foster creativity and rapid problem-solving. Companies like Toyota demonstrate hierarchical success through consistent quality control, whereas Valve Corporation showcases flat leadership benefits by empowering employee autonomy and agile project development.
Choosing the Right Leadership Structure for Your Organization
Hierarchical leaders excel in organizations requiring clear authority and well-defined roles, promoting accountability through structured chains of command. Flat structure leaders thrive in dynamic environments, fostering collaboration and rapid decision-making by minimizing managerial layers. Selecting the right leadership structure depends on organizational size, industry complexity, and the desired balance between control and flexibility.
Related Important Terms
Power-Distance Index Leadership
Hierarchical leaders emphasize clear authority and centralized decision-making, reflecting high Power-Distance Index cultures where subordinates accept unequal power distribution; flat structure leaders promote collaboration and egalitarian relationships consistent with low Power-Distance Index environments, fostering employee empowerment and open communication. Organizations aligned with the Power-Distance Index of their leadership style experience improved efficiency and workplace satisfaction by matching authority distribution to cultural expectations.
Distributed Authority Model
Hierarchical leaders operate within a centralized authority model, where decision-making is top-down and roles are clearly defined, while flat structure leaders embrace a distributed authority model that decentralizes decision-making, empowering employees and fostering collaboration. The distributed authority model enhances agility and innovation by promoting accountability at all levels and reducing bureaucratic delays inherent in hierarchical systems.
Agile Hierarchy
Agile hierarchy balances the decisiveness of hierarchical leadership with the flexibility of flat structure leaders by promoting adaptive decision-making and empowering teams at all levels. This approach enhances workplace responsiveness and collaboration while maintaining clear accountability within evolving organizational goals.
Servant Leadership Flat
A Servant Leadership approach thrives in flat organizational structures by emphasizing employee empowerment, collaboration, and open communication, fostering a supportive and inclusive workplace culture. Unlike hierarchical leaders who prioritize authority and control, servant leaders focus on meeting the needs of their team to enhance innovation, engagement, and long-term performance.
Holacratic Management
Holacratic management eliminates traditional hierarchical leadership by distributing decision-making authority across self-organizing teams, fostering agility and employee empowerment. This flat structure leader model contrasts with hierarchical leaders who centralize control, often resulting in slower decision processes and reduced innovation.
Sociocratic Governance
Sociocratic governance in workplace structures emphasizes distributed authority and decision-making, favoring flat structure leaders who facilitate collaboration and equal participation over hierarchical leaders who concentrate power at the top. This approach enhances organizational adaptability, employee engagement, and transparency by integrating feedback loops and consent-based decision processes inherent to sociocracy.
Dynamic Role Allocation
Hierarchical leaders assign roles through clear chains of command, ensuring defined responsibilities but potentially limiting flexibility in dynamic environments. Flat structure leaders promote dynamic role allocation by enabling team members to adapt and shift responsibilities fluidly, enhancing responsiveness and collaboration in the workplace.
Lattice Leadership
Lattice Leadership fosters a dynamic workplace structure by blending the transparency of flat structures with the clear guidance of hierarchical leaders, promoting collaboration and innovation across all levels. This approach enhances decision-making agility and employee empowerment, resulting in increased organizational adaptability and engagement.
Autonomy-Enabled Leadership
Hierarchical leaders typically maintain top-down control, limiting employee autonomy to ensure clear accountability and consistent decision-making. In contrast, flat structure leaders promote autonomy-enabled leadership by decentralizing authority, fostering innovation, and empowering teams to make decisions that drive agility and engagement.
Polycratic Structure
Polycratic structures combine hierarchical leadership's clear authority lines with flat structure leaders' emphasis on collaboration, allowing for adaptive decision-making and distributed accountability. This hybrid approach improves organizational agility, enhances employee engagement, and fosters innovation by integrating centralized control with decentralized input.
Hierarchical Leader vs Flat Structure Leader for workplace structure. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com