Autocratic leaders exert centralized control and make decisions unilaterally, which can lead to quick decision-making but often limits employee autonomy and innovation. Holacracy leaders distribute authority across self-organizing teams, fostering collaboration and adaptability while enhancing employee engagement and accountability. Organizations adopting holacracy benefit from increased flexibility and creative problem-solving, contrasting with the more rigid and top-down approach of autocratic leadership.
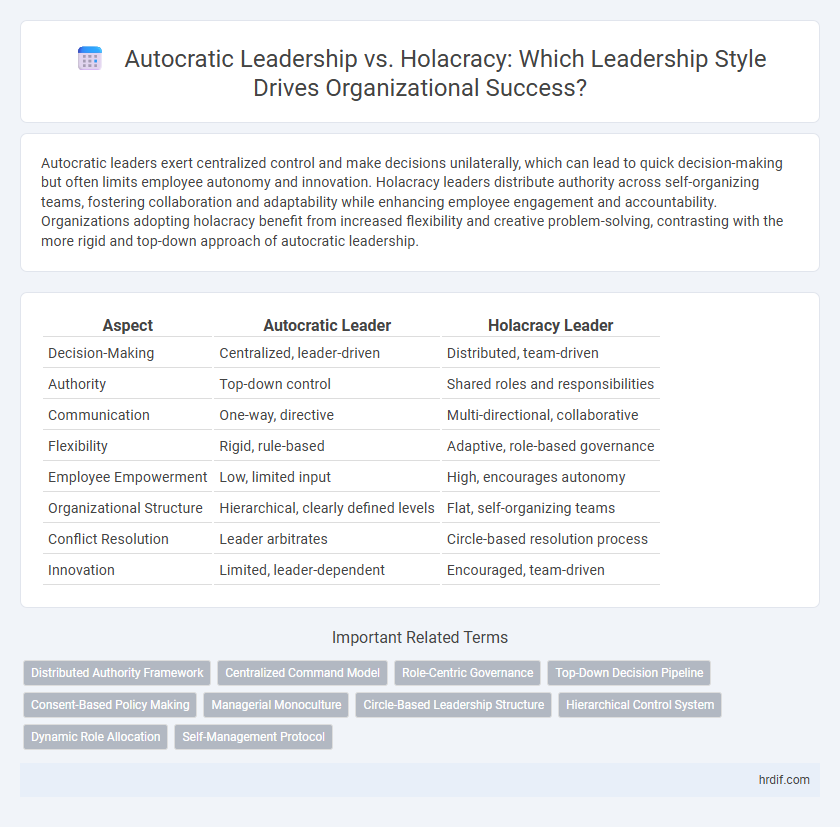
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Autocratic Leader | Holacracy Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Centralized, leader-driven | Distributed, team-driven |
| Authority | Top-down control | Shared roles and responsibilities |
| Communication | One-way, directive | Multi-directional, collaborative |
| Flexibility | Rigid, rule-based | Adaptive, role-based governance |
| Employee Empowerment | Low, limited input | High, encourages autonomy |
| Organizational Structure | Hierarchical, clearly defined levels | Flat, self-organizing teams |
| Conflict Resolution | Leader arbitrates | Circle-based resolution process |
| Innovation | Limited, leader-dependent | Encouraged, team-driven |
Understanding Autocratic Leadership: Key Characteristics
Autocratic leadership is characterized by centralized decision-making, where the leader holds absolute authority and expects strict compliance from team members, ensuring quick execution of tasks. This leadership style often involves clear directives, limited employee input, and a top-down communication approach, which can streamline processes in high-pressure environments. Organizations adopting autocratic leadership benefit from strong control and consistency but may face challenges with employee motivation and innovation.
Holacracy Leadership: A New Paradigm in Organizational Structure
Holacracy leadership revolutionizes organizational structure by distributing authority and decision-making across self-organizing teams, enhancing agility and employee empowerment. Unlike autocratic leaders who centralize control and issue directives, holacracy fosters collaboration and transparent governance through defined roles and iterative processes. This paradigm shift supports adaptability and innovation, making it ideal for dynamic and complex business environments.
Decision-Making Power: Centralized vs. Distributed Approaches
Autocratic leaders maintain centralized decision-making power, exercising direct control and swift, unilateral choices to drive organizational objectives. Holacracy leaders distribute decision-making across self-managed teams, fostering collaboration, flexibility, and shared accountability within the organizational structure. This contrast in leadership style significantly impacts innovation speed, employee engagement, and responsiveness to change.
Impact on Employee Engagement and Morale
Autocratic leaders often decrease employee engagement and morale by limiting autonomy and disregarding team input, resulting in reduced motivation and creativity. Holacracy leaders foster higher engagement through decentralized decision-making and distributed authority, empowering employees to take ownership and innovate. This inclusive leadership style significantly enhances job satisfaction and organizational commitment.
Innovation and Flexibility: Which Model Wins?
Autocratic leaders centralize decision-making, often limiting innovation and flexibility due to rigid control and top-down directives. Holacracy leaders distribute authority across self-organizing teams, fostering a dynamic environment that encourages creativity and rapid adaptation. Organizations aiming for sustained innovation and agile responses benefit more from holacratic models than autocratic leadership structures.
Accountability and Responsibility in Each Leadership Style
Autocratic leaders centralize accountability by retaining full control over decision-making, ensuring clear lines of responsibility but often limiting individual autonomy. Holacracy leaders distribute accountability across self-managing teams, fostering shared responsibility and enhancing employee empowerment within defined roles. This contrast significantly impacts organizational agility, with autocratic structures emphasizing top-down control while holacratic models promote decentralized accountability.
Speed of Implementation: Efficiency Compared
An autocratic leader accelerates decision-making by centralizing authority, enabling swift implementation of strategies without extensive consultation. Holacracy leaders distribute decision-making across teams, which can slow implementation due to the collaborative processes and consensus-building required. Efficiency in execution tends to favor autocratic leadership when quick, decisive action is critical, whereas holacracy supports adaptive, inclusive innovation at the cost of immediate speed.
Organizational Culture: Hierarchy vs. Self-Management
Autocratic leaders enforce a hierarchical organizational culture with top-down decision-making that emphasizes control and clear authority lines, often leading to faster but less collaborative processes. Holacracy leaders foster a self-management culture where authority is distributed across roles, encouraging autonomy, adaptability, and collective accountability. This shift from rigid hierarchy to dynamic role-based governance enhances innovation and employee engagement within organizations.
Suitability for Different Industries and Business Sizes
Autocratic leadership is well-suited for industries requiring quick decision-making and strict control, such as manufacturing, military, and crisis management, often benefiting small to medium-sized businesses with clear hierarchies. Holacracy leadership thrives in creative, tech-driven industries like software development and startups, where flexibility, innovation, and decentralized decision-making support larger, rapidly evolving organizations. Business size and industry dynamics heavily influence the effectiveness of these leadership styles, with autocratic models excelling in stable environments and holacracy adapting to complex, agile ecosystems.
Future Trends: Evolving Leadership for the Modern Workplace
Autocratic leaders maintain centralized control and decision-making authority, which can streamline processes but often stifle innovation and employee engagement in dynamic work environments. Holacracy leaders distribute authority across self-organizing teams, fostering adaptability and collaboration, essential for navigating the complexities of the modern workplace and promoting continuous innovation. Future leadership trends emphasize decentralized decision-making models, such as holacracy, to enhance organizational agility and respond effectively to rapid technological and market changes.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Authority Framework
Autocratic leaders centralize decision-making authority, maintaining strict control over organizational processes, whereas Holacracy leaders implement a Distributed Authority Framework that empowers teams through decentralized governance and role clarity. This approach enhances agility, accountability, and innovation by distributing decision rights across self-organizing circles rather than relying on hierarchical commands.
Centralized Command Model
Autocratic leaders maintain centralized command by making all decisions independently, which can streamline processes but often limits employee autonomy and innovation. In contrast, Holacracy leaders distribute authority across self-managing teams, reducing centralized control and fostering a collaborative environment that can enhance adaptability and employee engagement.
Role-Centric Governance
Autocratic leaders centralize decision-making authority, enforcing strict hierarchical control that limits employee autonomy, whereas Holacracy leaders implement a role-centric governance model distributing authority across defined roles and circles to enhance agility and collaborative accountability. In organizational leadership, Holacracy's decentralized structure fosters adaptive workflows and empowered teams, contrasting sharply with the top-down command typical of autocratic leadership.
Top-Down Decision Pipeline
Autocratic leaders centralize decision-making authority, ensuring a top-down pipeline where directives flow unilaterally from executives to employees, fostering quick but rigid executions. Holacracy leaders distribute authority through self-organizing teams, minimizing top-down controls and enabling decentralized decision pipelines that promote agility and collaborative leadership.
Consent-Based Policy Making
Autocratic leaders maintain centralized control with top-down decision-making, often limiting employee input, whereas holacracy leaders implement consent-based policy-making that distributes authority and fosters collaborative governance. This approach in holacracy enhances organizational agility and inclusivity by ensuring policies evolve through collective agreement rather than unilateral directives.
Managerial Monoculture
Autocratic leaders centralize decision-making, fostering a managerial monoculture that limits innovation and employee autonomy, which contrasts sharply with holacracy leaders who distribute authority across self-managing teams, promoting adaptability and diverse leadership dynamics within organizations. Emphasizing hierarchical control undermines organizational agility, whereas holacracy enhances responsiveness by integrating multiple leadership perspectives and evolving governance structures.
Circle-Based Leadership Structure
Autocratic leaders centralize decision-making, often limiting team autonomy and innovation, whereas holacracy leaders implement a circle-based leadership structure that distributes authority across self-organizing teams, enhancing agility and accountability. This decentralized model promotes transparency and collaborative governance, enabling organizations to adapt swiftly to complex environments while empowering individuals within defined roles and circles.
Hierarchical Control System
An autocratic leader maintains strict hierarchical control, centralizing decision-making authority and enforcing top-down directives that streamline accountability but limit employee autonomy. Holacracy leaders distribute authority through self-managed teams, dismantling traditional hierarchies to foster flexibility, rapid innovation, and shared leadership within complex organizations.
Dynamic Role Allocation
Autocratic leaders centralize decision-making power, limiting flexibility in role allocation, whereas Holacracy leaders implement dynamic role allocation by distributing authority across self-organizing teams, enhancing adaptability and responsiveness within the organization. This decentralized framework in Holacracy promotes continuous role evolution based on project needs and individual strengths, contrasting sharply with the fixed, top-down assignments typical of autocratic leadership.
Self-Management Protocol
Autocratic leaders emphasize centralized decision-making with strict control over tasks, limiting employee autonomy and relying on top-down directives to enforce organizational goals. In contrast, Holacracy leaders implement a self-management protocol that distributes authority across roles and circles, empowering team members to make decisions and continuously evolve processes within a flexible organizational structure.
Autocratic Leader vs Holacracy Leader for organizational leadership. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com