Executives steer organizations through structured decision-making, leveraging hierarchy and established processes to achieve strategic goals. Intrapreneurs drive innovation within organizations by adopting entrepreneurial mindsets, embracing risk, and fostering creative solutions from within. Both roles are essential for balancing stability with agility in leadership.
Table of Comparison
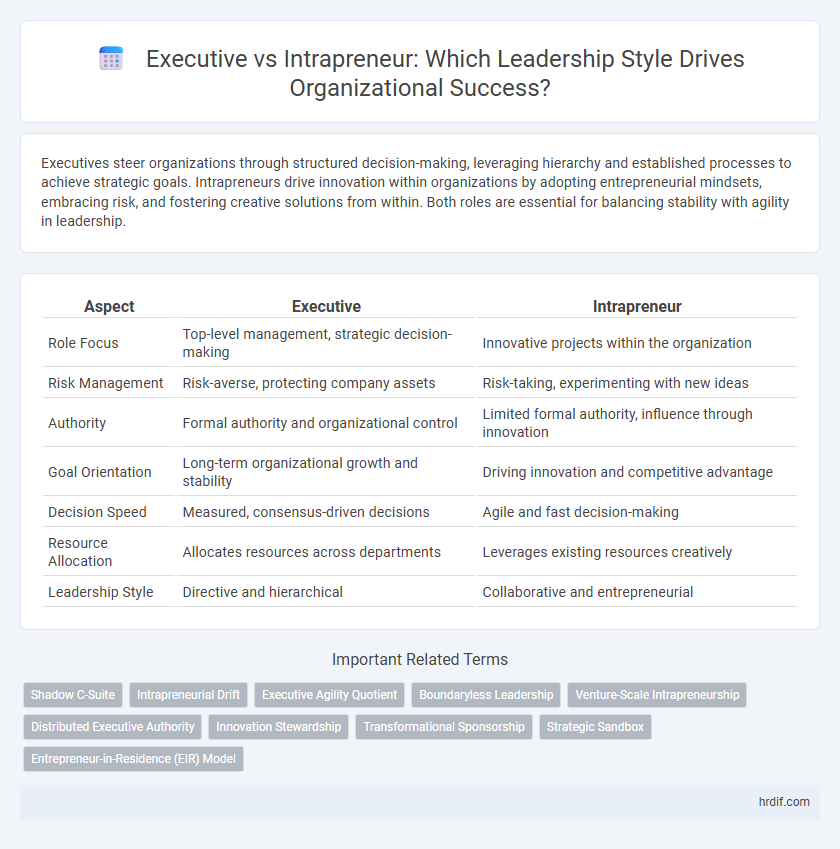
| Aspect | Executive | Intrapreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Top-level management, strategic decision-making | Innovative projects within the organization |
| Risk Management | Risk-averse, protecting company assets | Risk-taking, experimenting with new ideas |
| Authority | Formal authority and organizational control | Limited formal authority, influence through innovation |
| Goal Orientation | Long-term organizational growth and stability | Driving innovation and competitive advantage |
| Decision Speed | Measured, consensus-driven decisions | Agile and fast decision-making |
| Resource Allocation | Allocates resources across departments | Leverages existing resources creatively |
| Leadership Style | Directive and hierarchical | Collaborative and entrepreneurial |
Defining Executive and Intrapreneurial Leadership
Executive leadership centers on strategic decision-making, emphasizing organizational hierarchy, resource allocation, and long-term vision to steer companies toward set goals. Intrapreneurial leadership drives innovation within existing structures by encouraging creativity, risk-taking, and agile problem-solving to adapt and grow internally. Both forms focus on guiding organizations but differ in their approach: executives maintain control and stability while intrapreneurs foster transformative change from within.
Core Responsibilities: Executives vs. Intrapreneurs
Executives primarily focus on strategic planning, resource allocation, and maintaining organizational stability to achieve long-term goals, ensuring alignment with corporate policies and governance. Intrapreneurs emphasize innovation, driving new initiatives, and fostering a entrepreneurial culture within the organization to adapt quickly to market changes. Core responsibilities for executives revolve around leadership and oversight, while intrapreneurs prioritize creativity and internal venture development.
Organizational Impact: Decision-Making and Innovation
Executives drive organizational impact through strategic decision-making, leveraging authority to align resources and ensure stability, while intrapreneurs foster innovation by challenging existing processes and promoting creative problem-solving within teams. Decision-making by executives often emphasizes risk management and scalability, whereas intrapreneurs prioritize experimentation and agile responses to market changes. Combining executive oversight with intrapreneurial agility enhances both operational efficiency and breakthrough innovation, accelerating sustainable growth.
Leadership Styles: Top-Down vs. Grassroots Approaches
Executives typically apply a top-down leadership style, emphasizing hierarchical decision-making and centralized control to steer organizations efficiently toward established goals. In contrast, intrapreneurs embrace grassroots approaches by fostering innovation and empowering teams at various levels to drive change from within. Balancing executive authority with intrapreneurial initiative can enhance organizational adaptability and sustain competitive advantage.
Driving Change: Authority vs. Influence
Executives drive organizational change through formal authority, leveraging their hierarchical position to implement strategic decisions and enforce policies. Intrapreneurs inspire change by using influence and innovation within the company, advocating for new ideas without relying on positional power. Both roles are critical for steering organizations, balancing structured governance with agile, bottom-up transformation.
Risk Management in Executive and Intrapreneurial Roles
Executives prioritize risk management by implementing structured frameworks and compliance protocols to safeguard organizational stability and shareholder interests. Intrapreneurs manage risks through agile experimentation and iterative innovation, balancing potential disruptions with breakthrough opportunities. Effective leadership integrates executive control with intrapreneurial adaptability to optimize risk-benefit outcomes and drive sustainable growth.
Navigating Corporate Culture and Resistance
Executives steer organizations by leveraging formal authority to align teams with corporate goals, often encountering resistance rooted in established hierarchies and traditional processes. Intrapreneurs navigate corporate culture through innovation and agility, using influence and collaboration to drive change from within while mitigating resistance by fostering trust and demonstrating value. Understanding the distinct approaches in managing culture and resistance is crucial for effective organizational transformation and sustainable growth.
Success Metrics: Measuring Leadership Effectiveness
Leadership effectiveness in organizations is measured by distinct success metrics for executives and intrapreneurs; executives are evaluated based on financial performance, market share growth, and shareholder value, while intrapreneurs are assessed through innovation outcomes, project scalability, and internal process improvements. Key performance indicators (KPIs) for executives often emphasize strategic vision execution and organizational stability, whereas intrapreneurs focus on agility, risk-taking capabilities, and fostering a culture of creativity. Combining these metrics offers a comprehensive view of leadership impact, balancing operational excellence with transformative innovation.
Collaboration and Conflict Resolution
Executives drive organizational success through strategic decision-making and hierarchical leadership, promoting collaboration by aligning teams with corporate goals and resolving conflicts via formal protocols. Intrapreneurs foster innovation within companies by encouraging cross-functional collaboration and addressing conflicts through adaptive problem-solving and open communication channels. Both roles require strong interpersonal skills to balance diverse perspectives and maintain organizational harmony while steering towards common objectives.
Choosing the Right Path: Executive or Intrapreneur?
Effective organizational steering depends on selecting between the executive path, characterized by structured decision-making and hierarchical authority, and the intrapreneur approach, which fosters innovation and agility within established companies. Executives drive strategic alignment and operational efficiency, leveraging their positional power to implement company-wide initiatives. Intrapreneurs prioritize creative problem-solving and entrepreneurial risk-taking, accelerating growth and adaptability in dynamic markets.
Related Important Terms
Shadow C-Suite
Shadow C-Suite members often act as intrapreneurs within organizations, driving innovation and agile decision-making unlike traditional executives constrained by hierarchical roles. This dual dynamic enhances organizational agility, enabling proactive problem-solving and fostering a culture of continuous improvement essential for competitive leadership.
Intrapreneurial Drift
Intrapreneurial drift occurs when leaders within an organization prioritize innovation and entrepreneurial initiatives over traditional executive control, driving transformative growth from within. This shift challenges conventional executive roles by fostering a culture where risk-taking and creative problem-solving become central to steering organizational strategy.
Executive Agility Quotient
Executive Agility Quotient measures the ability of leaders to swiftly adapt strategies and decision-making processes in dynamic environments, distinguishing executives from intrapreneurs who primarily drive innovation within established frameworks. High Executive Agility enables top leaders to navigate complex organizational challenges, align diverse teams, and steer companies toward sustainable growth amidst volatility.
Boundaryless Leadership
Boundaryless leadership transcends traditional executive hierarchies by integrating intrapreneurs who drive innovation within organizations without rigid structural constraints. This approach fosters agile decision-making and cross-functional collaboration, enabling both executives and intrapreneurs to steer organizations toward dynamic growth and adaptability.
Venture-Scale Intrapreneurship
Executive leaders typically drive organizational strategy through hierarchical decision-making and resource allocation, while venture-scale intrapreneurs catalyze innovation by creating scalable internal startups that disrupt traditional business models. Emphasizing autonomy, risk-taking, and cross-functional collaboration, intrapreneurs accelerate growth within established companies by leveraging entrepreneurial tactics to unlock new revenue streams and competitive advantages.
Distributed Executive Authority
Distributed executive authority enhances organizational agility by empowering intrapreneurs to innovate within established structures, contrasting with traditional executives who often centralize decision-making to maintain control. Balancing executive oversight with intrapreneurial autonomy fosters adaptive leadership that drives sustainable growth and responsiveness in complex environments.
Innovation Stewardship
Executives drive organizational success by leveraging strategic oversight and resource management to ensure sustainable innovation cycles, while intrapreneurs act as catalysts within companies, fostering creative problem-solving and agile project leadership to accelerate transformative ideas. Both roles are essential for innovation stewardship, balancing structured governance with entrepreneurial agility to propel competitive advantage and long-term growth.
Transformational Sponsorship
Transformational sponsorship in organizational leadership differentiates executives as vision-driven architects who set broad strategic directions, while intrapreneurs act as dynamic change agents driving innovation and operational adaptability within teams. Both roles synergize to accelerate growth by fostering a culture of empowerment and continuous transformation across hierarchical levels.
Strategic Sandbox
Executives drive organizational growth by leveraging the Strategic Sandbox to establish clear boundaries for decision-making and resource allocation, ensuring alignment with company goals. Intrapreneurs utilize the Strategic Sandbox to innovate within those parameters, fostering creativity and agility while managing risks to deliver impactful business solutions.
Entrepreneur-in-Residence (EIR) Model
The Executive versus Intrapreneur debate intensifies in organizations adopting the Entrepreneur-in-Residence (EIR) model, where seasoned entrepreneurs drive innovation from within, blending strategic leadership with agile intrapreneurship. This hybrid approach leverages EIRs to accelerate transformative projects, foster a startup mentality, and steer corporate growth by bridging executive vision with entrepreneurial execution.
Executive vs Intrapreneur for steering organizations. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com