A boss directs tasks and enforces authority, often limiting collaboration and innovation within the team. In contrast, a thought partner engages in active dialogue, fostering shared problem-solving and empowering others to contribute ideas. This shift from command to collaboration enhances leadership effectiveness and drives collective success.
Table of Comparison
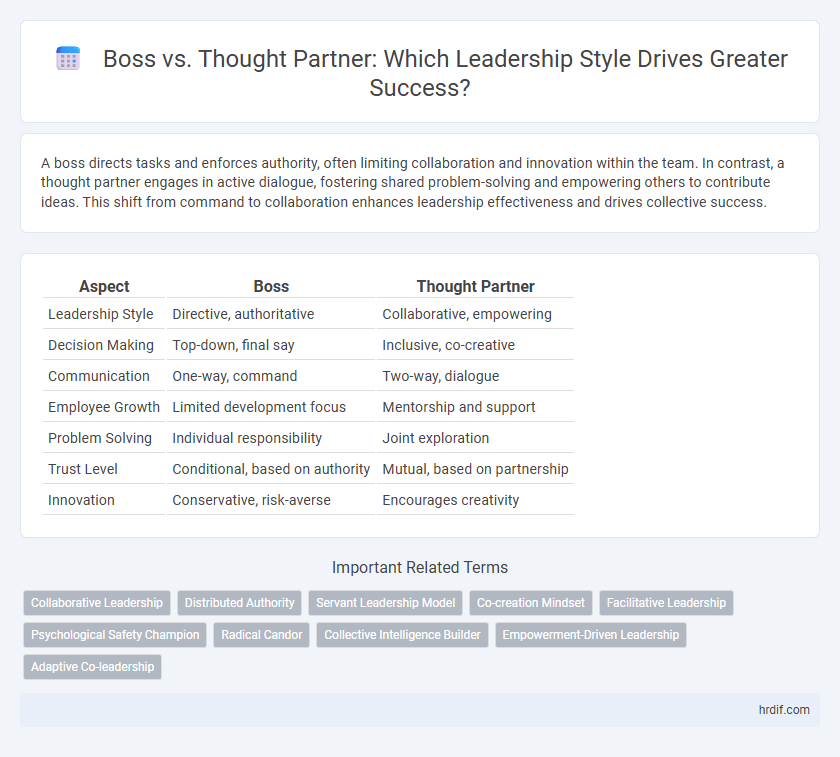
| Aspect | Boss | Thought Partner |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership Style | Directive, authoritative | Collaborative, empowering |
| Decision Making | Top-down, final say | Inclusive, co-creative |
| Communication | One-way, command | Two-way, dialogue |
| Employee Growth | Limited development focus | Mentorship and support |
| Problem Solving | Individual responsibility | Joint exploration |
| Trust Level | Conditional, based on authority | Mutual, based on partnership |
| Innovation | Conservative, risk-averse | Encourages creativity |
Defining the Boss: Command and Control Leadership
A boss embodies command and control leadership by exerting authority to direct tasks and enforce compliance, often prioritizing hierarchy and structured decision-making. This leadership style emphasizes clear instructions, rigid oversight, and measurable outcomes to maintain order and productivity. The focus remains on asserting power and ensuring followers adhere strictly to established rules and objectives.
The Thought Partner: Collaborative Leadership Explained
The Thought Partner embodies collaborative leadership by actively engaging team members in problem-solving and decision-making processes, fostering a culture of trust and innovation. Unlike a traditional boss who directs and controls, the Thought Partner encourages open dialogue, mutual respect, and shared accountability to drive collective success. This leadership style enhances organizational agility and cultivates diverse perspectives essential for sustainable growth and adaptive strategy.
Key Traits: Boss vs Thought Partner in the Workplace
A boss typically exercises authority and decision-making power, focusing on directing tasks and enforcing rules, whereas a thought partner fosters collaboration, encourages innovation, and supports mutual problem-solving in the workplace. Key traits of a boss include control, command, and unilateral communication, while a thought partner emphasizes empathy, active listening, and shared accountability. Leaders who adopt the thought partner approach promote employee engagement, trust, and collective growth, driving organizational success through partnership rather than hierarchy.
Decision-Making Styles: Top-Down vs Inclusive Approach
A boss typically employs a top-down decision-making style, where directives flow from authority to subordinates, ensuring quick execution but potentially limiting team input and innovation. In contrast, a thought partner embraces an inclusive approach, fostering collaboration and diverse perspectives that enhance problem-solving and buy-in among team members. This shift from authoritative to participative leadership strengthens organizational agility and employee engagement.
Impact on Team Motivation and Morale
A leadership style that shifts from a traditional boss to a thought partner significantly boosts team motivation and morale by fostering collaboration and open communication. Thought partners empower team members to contribute ideas, enhancing a sense of ownership and commitment to goals. This inclusive approach cultivates trust and drives higher performance, resulting in a more engaged and motivated workforce.
Innovation and Creativity: Which Style Drives Progress?
A thought partner fosters innovation and creativity by encouraging collaboration, open dialogue, and diverse perspectives, which drives progress more effectively than the traditional boss who often imposes decisions top-down, limiting creative input. Research shows organizations led by inclusive leaders who act as thought partners report higher rates of breakthrough innovation and adaptive problem-solving. By valuing ideas equally and challenging assumptions together, thought partners create an environment where creative solutions thrive and continuous improvement is the norm.
Communication Dynamics: Directive vs Facilitative Leadership
Directive leadership relies on clear, top-down communication where the boss issues specific instructions and expects compliance, often limiting open dialogue. Thought partners embrace facilitative leadership by encouraging collaborative conversations that foster mutual problem-solving and innovative ideas. This dynamic shifts communication from command-driven to reciprocal engagement, enhancing team autonomy and trust.
Employee Growth: Mentorship vs Management
Thought partners prioritize mentorship by fostering employee growth through guidance, open dialogue, and collaborative problem-solving, which encourages innovation and skill development. Bosses, focused on management, often emphasize task completion and adherence to directives, potentially limiting creativity and personal growth. Emphasizing mentorship over traditional management supports a culture of continuous learning and empowerment within leadership frameworks.
Workplace Culture: Fear or Trust?
A boss often fosters a workplace culture rooted in fear, where employees hesitate to share ideas or take risks due to potential repercussions. In contrast, a thought partner cultivates trust by encouraging open dialogue, collaboration, and mutual respect, leading to increased innovation and employee engagement. Trust-based leadership enhances organizational resilience and drives sustained performance by empowering teams to contribute their best.
Choosing the Right Approach: Situational Leadership Strategies
Selecting between a boss and a thought partner approach hinges on situational leadership strategies that prioritize adaptability and collaboration. A boss-centric style may drive decisive authority during crises, while a thought partner fosters innovation and employee engagement in complex, evolving scenarios. Effective leaders assess context-specific needs to balance command and collaboration for optimal team performance and growth.
Related Important Terms
Collaborative Leadership
A boss directs tasks and expects compliance, whereas a thought partner actively engages in dialogue, fostering collaborative leadership through mutual trust and shared decision-making. Collaborative leadership enhances team innovation and resilience by encouraging diverse perspectives and collective problem-solving.
Distributed Authority
Distributed authority in leadership shifts power from a traditional boss-centered model to a collaborative thought partner dynamic, empowering team members to contribute ideas and make decisions. This approach fosters innovation and accountability by leveraging diverse perspectives and shared responsibility across the organization.
Servant Leadership Model
A servant leadership model transforms traditional boss roles by emphasizing collaboration, empathy, and the growth of team members, positioning leaders as thought partners rather than authoritative figures. This approach fosters trust and innovation, driving organizational success through shared vision and mutual support.
Co-creation Mindset
A boss typically directs tasks with a top-down approach, while a thought partner fosters a co-creation mindset by encouraging collaboration, mutual trust, and shared problem-solving. Embracing a thought partner role in leadership enhances innovation, employee engagement, and collective accountability, driving stronger organizational outcomes.
Facilitative Leadership
A thought partner in leadership fosters collaboration and innovation by encouraging open dialogue and shared problem-solving, contrasting with a traditional boss who often directs and controls decisions. Facilitative leadership thrives on empowering teams, promoting active listening, and enabling collective intelligence to drive organizational success.
Psychological Safety Champion
A leadership style that shifts from a traditional boss to a thought partner fosters psychological safety by encouraging open dialogue, risk-taking, and innovation among team members. This approach cultivates trust and collaboration, enabling individuals to share ideas without fear of judgment or repercussions.
Radical Candor
Radical Candor elevates leadership by transforming the traditional boss role into a thought partner who challenges and supports team members through honest, empathetic feedback. This approach fosters trust and accelerates growth by balancing directness with genuine care, creating a collaborative environment that drives performance and innovation.
Collective Intelligence Builder
A Thought Partner in leadership fosters collective intelligence by encouraging collaboration, open dialogue, and diverse perspectives, unlike a traditional Boss who imposes directives and limits team input. Emphasizing shared problem-solving and mutual trust, Thought Partners drive innovation and stronger team performance through active engagement and co-creation.
Empowerment-Driven Leadership
Empowerment-driven leadership transforms the traditional boss role by fostering collaboration, encouraging autonomy, and facilitating growth through active listening and shared decision-making. Thought partners prioritize influence over authority, enabling teams to innovate and take ownership of outcomes, resulting in heightened engagement and sustainable success.
Adaptive Co-leadership
Adaptive co-leadership thrives when leaders shift from traditional boss roles to thought partners, fostering collaboration and shared decision-making. This approach enhances organizational agility by leveraging diverse perspectives and promoting mutual accountability.
Boss vs Thought Partner for Leadership. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com