Autocratic leadership centralizes decision-making authority, enabling quick, decisive actions but often limiting team input and creativity. Holacratic leadership distributes decision-making across self-organizing teams, fostering collaboration and innovation while potentially slowing the process with consensus-building. Choosing between autocratic and holacratic approaches depends on the organization's need for control versus flexibility in decision-making dynamics.
Table of Comparison
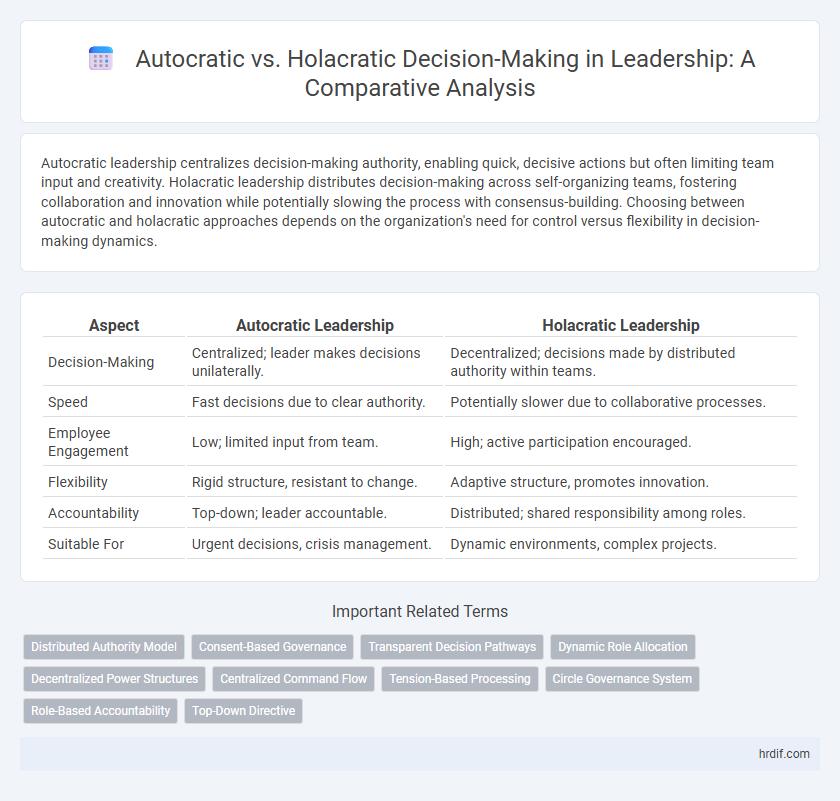
| Aspect | Autocratic Leadership | Holacratic Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Centralized; leader makes decisions unilaterally. | Decentralized; decisions made by distributed authority within teams. |
| Speed | Fast decisions due to clear authority. | Potentially slower due to collaborative processes. |
| Employee Engagement | Low; limited input from team. | High; active participation encouraged. |
| Flexibility | Rigid structure, resistant to change. | Adaptive structure, promotes innovation. |
| Accountability | Top-down; leader accountable. | Distributed; shared responsibility among roles. |
| Suitable For | Urgent decisions, crisis management. | Dynamic environments, complex projects. |
Understanding Autocratic and Holacratic Leadership Styles
Autocratic leadership centralizes decision-making authority, enabling quick, decisive actions often suitable for crisis or high-pressure environments. Holacratic leadership distributes decision-making across self-organizing teams, fostering innovation and employee empowerment by leveraging collective intelligence. Understanding these styles helps organizations align their leadership approach with operational needs and cultural values for optimized decision outcomes.
Defining Decision-Making in the Workplace
Decision-making in the workplace varies significantly between autocratic and holacratic leadership styles, with autocratic emphasizing centralized authority where leaders make quick, unilateral decisions. Holacratic decision-making distributes authority across self-managing teams, fostering collaborative input and adaptive responses. This contrast impacts organizational agility, employee empowerment, and the speed at which strategic choices are implemented.
Key Principles of Autocratic Decision-Making
Autocratic decision-making centers on centralized authority where leaders make decisions independently without input from team members, ensuring swift and clear outcomes. Key principles include absolute control, unilateral decision authority, and limited delegation, emphasizing efficiency and directive leadership. This approach is often effective in crisis situations or when tasks require quick, precise execution without the need for consensus.
Core Elements of Holacratic Decision-Making
Holacratic decision-making centers on distributed authority, empowering teams through clearly defined roles and circle structures that enable faster, transparent governance. Core elements include integrative decision processes, where objections refine proposals for alignment, and governance meetings that continuously adapt organizational policies to emergent needs. This contrasts with autocratic styles by fostering collective responsibility and iterative improvement over centralized command.
Comparing Speed and Efficiency in Both Systems
Autocratic leadership enables faster decision-making by centralizing authority, which reduces delays caused by consultations. Holacratic systems promote efficiency through distributed decision-making but may slow the process due to collective input and consensus-building. Organizations prioritizing speed often favor autocratic methods, while those emphasizing collaborative efficiency adopt holacracy.
Employee Engagement: Autocracy vs. Holacracy
Autocratic leadership often results in low employee engagement due to limited participation in decision-making, causing reduced motivation and innovation. Holacracy encourages decentralized authority and distributed decision-making, significantly increasing employee involvement and ownership in organizational outcomes. Organizations adopting holacracy report higher job satisfaction and collaborative problem-solving, driving sustained engagement.
Impact on Organizational Culture
Autocratic decision-making typically creates a hierarchical organizational culture characterized by centralized authority and limited employee autonomy, which can stifle creativity and reduce engagement. In contrast, holacratic structures promote a decentralized culture emphasizing distributed authority, transparency, and collaborative decision-making, fostering innovation and employee empowerment. Organizations adopting holacracy often experience higher adaptability and stronger alignment with evolving strategic goals due to inclusive participation in the decision process.
Suitability By Industry and Business Size
Autocratic decision-making suits industries requiring rapid, centralized control like manufacturing and military, and thrives in small to medium-sized businesses with clear hierarchies. Holacratic governance excels in creative sectors such as technology and design, promoting distributed decision-making ideal for startups and agile, innovative enterprises. Choosing between these models depends on the organization's need for control versus flexibility, aligning leadership style with industry demands and business scale.
Challenges and Pitfalls of Each Approach
Autocratic leadership often faces challenges such as limited employee engagement and innovation due to centralized decision-making, leading to potential burnout and reduced morale. Holacratic decision-making can suffer from ambiguity and slower processes as power is distributed across roles, causing confusion and inefficiency in urgent situations. Both approaches risk undermining organizational agility if not carefully balanced with clear communication and adaptive structures.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Team
Choosing the right decision-making model hinges on your team's size, complexity, and need for agility; autocratic leadership offers clear, swift decisions ideal for high-pressure environments, while holacratic models empower distributed authority, fostering innovation and adaptability in dynamic settings. Teams with experienced, self-motivated members thrive under holacracy, leveraging decentralized governance to enhance collaboration and accountability. Evaluating organizational culture and project scope ensures alignment of leadership style with strategic goals, optimizing performance and employee engagement.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Authority Model
The Distributed Authority Model in Holacratic leadership decentralizes decision-making, empowering teams with autonomy and fostering innovation through collaborative input. In contrast, Autocratic leadership centralizes authority, enabling rapid decisions but potentially limiting adaptability and employee engagement.
Consent-Based Governance
Autocratic decision-making centralizes authority in a single leader, enabling swift choices but often limiting team input and innovation. In contrast, holacratic frameworks emphasize consent-based governance, distributing decision-making power across roles to enhance collaboration, transparency, and adaptive problem-solving.
Transparent Decision Pathways
Autocratic leadership centralizes decision-making authority, often limiting transparency as decisions flow top-down without broad input, potentially obscuring the rationale behind choices. Holacratic governance promotes transparent decision pathways by distributing authority across roles, ensuring collective clarity and accountability in how decisions are made and implemented.
Dynamic Role Allocation
Autocratic leadership centralizes decision-making authority in a single leader, resulting in faster, top-down directives but limited team input and adaptability. Holacratic leadership employs dynamic role allocation where decision-making is distributed across defined roles, enhancing organizational agility and fostering collaborative problem-solving.
Decentralized Power Structures
Holacratic decision-making promotes decentralized power structures by distributing authority across self-organizing teams, enhancing agility and employee empowerment. In contrast, autocratic leadership centralizes decision-making power in a single leader, often resulting in faster but less flexible responses and reduced team autonomy.
Centralized Command Flow
Autocratic decision-making features a centralized command flow where authority is concentrated in a single leader, enabling swift and clear directives but limiting team input and flexibility. In contrast, holacratic structures distribute decision-making across self-organizing teams, promoting autonomy and adaptability but potentially slowing response time due to consensus-driven processes.
Tension-Based Processing
Autocratic leadership centralizes decision-making authority, creating tension by limiting input and enforcing unilateral control, which can accelerate resolution but stifle innovation. Holacratic structures distribute decision rights through tension-based processing, where tensions signal organizational needs and are addressed collaboratively to enhance adaptability and collective problem-solving.
Circle Governance System
Circle Governance System in holacratic leadership decentralizes decision-making by distributing authority across self-organizing circles, enhancing transparency and accountability. This contrasts with autocratic leadership, where decision-making power is centralized in a single leader, potentially limiting agility and team engagement.
Role-Based Accountability
Autocratic leadership centralizes decision-making power, assigning clear, top-down accountability, which can expedite resolutions but limits team autonomy. Holacratic structures distribute decision-making through role-based accountability, empowering individuals within defined roles to make choices, enhancing agility and collaborative responsibility.
Top-Down Directive
Autocratic leadership centralizes decision-making authority at the top, enabling swift, top-down directive execution ideal for crisis situations or organizations requiring clear control. Holacratic systems distribute decision power through self-managing teams, reducing reliance on hierarchical directives and fostering collaborative, adaptive decision-making environments.
Autocratic vs Holacratic for decision-making. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com